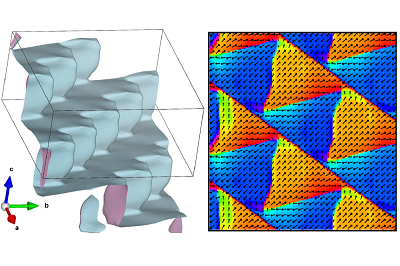
Pyramidal charged domain walls in ferroelectric BiFeO3
We uncover the physical origins of the enigmatic zigzag domain structure in the prototypical multiferroic material BiFeO3. Using phase-field simulations, we demonstrate that spatially-homogeneous defect charges result in domain structures that closely resemble those observed experimentally. The acquired understanding of the underlying physics of pyramidal-domain formation may enable the engineering of new materials with self-assembled domain structures. [Commun. Mater. 6, 161 (2025)].
We addressed a long-standing puzzle in ferroelectric research: the origin of unusual zigzag and pyramidal domain structures in the multiferroic material BiFeO3. These complex patterns had been observed experimentally for years, but their physical cause remained unclear. Using phase-field simulations within the Landau–Ginzburg–Devonshire framework, we demonstrated that they can naturally form when defect charges are distributed homogeneously in the crystal. The system compensates these charges by creating pyramid-like domains in which the polarization rotates to lower the overall energy. Our simulated patterns agree closely with transmission electron microscopy observations of BiFeO3 crystals from our colleagues at the University of Warwick, giving strong support to our model. Beyond solving a fundamental question, this insight has practical value. The pyramidal domains are highly regular and self-assembled with nanometer-scale periodicity, making them attractive for applications requiring precise ordering, such as optics or topological defect-based devices.
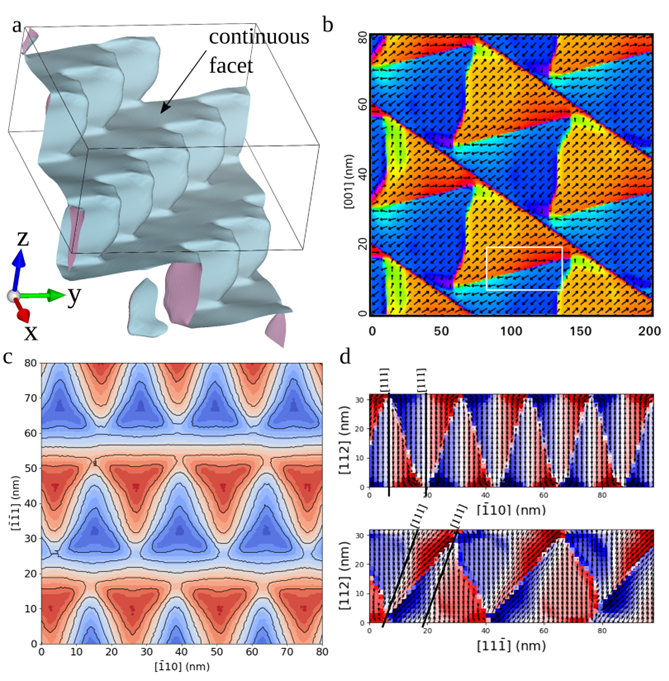
Phase-field simulations for a rhombohedral ferroelectric material:
a) 3D visualization of the wall surface.
b) Ferroelectric polarization visualized in the plane (-110).
c) Distance of the domain wall from the center of the charged layer measured along [111].
d) Deviation of the polarization from the pyramid’s axis.
Polarization is projected to two selected planes, color indicates polarization component perpendicular to [111] direction.
Red: positive, blue: negative, white: no deviation.
[1] P. Marton, M. Paściak, M. A. P. Gonçalves, O. Novák, J. Hlinka, R. Beanland, and M. Alexe, Pyramidal charged domain walls in ferroelectric BiFeO3, Commun. Mater. 6, 161 (2025).
(show less)
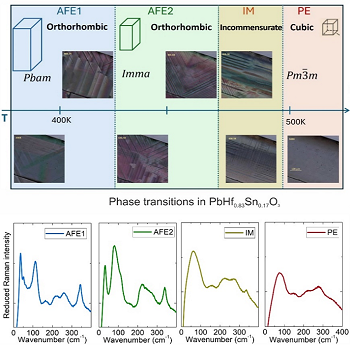
Phonon studies of the phase transition sequence in an antiferroelectric single crystal
The sequence of phase transitions in PbHf0.83Sn0.17O3 was studied using THz, far-infrared, and Raman spectroscopies.
These investigations revealed the complementary roles of polar and non-polar phonons in lattice dynamics,
establishing the sequence of transitions on cooling as PE → IM → AFE2 → AFE1
[J. Appl. Phys. 138, 104101 (2025)].
The investigation of Pb(Hf,Sn)O3 and the fundamental mechanism of its antiferroelectric properties help to advance in the field of materials for energy storage. This paper aims to better understand the lattice dynamics and the different phonons that drive the exotic phase transitions of this system, including an unknown intermediate phase at high temperatures.
The sequence of phase transitions in PbHf0.83Sn0.17O3 (PHS-17) has been studied by THz, far infrared, and Raman spectroscopies. Spectroscopic investigations revealed the complementary behaviour of both polar and non-polar phonons and their impact on the lattice dynamics, concluding that the sequence of phase transitions for PHS-17 on cooling is PE → IM → AFE2 → AFE1.
Symmetry analysis and optical observations revealed that the intermediate IM phase has plausible tetragonal symmetry and it is, driven by an polar instability from the center of the Brillouin zone. Domain dynamics suggests that the presence of Sn triggers the development of the IM phase with its distinctive tweed pattern. The overall transformation from the cubic paraelectric phase (PE) to the final antiferroelectric orthorhombic Pbam phase (AFE1) thus involves two middle phases that sequentially accommodate the shifts of Pb atoms and tilts of the oxygen octahedra. The Pb atom is more sensitive to the high temperature phase transitions through strong dielectric anomalies, while oxygen atoms are more significant in the AFE2 and AFE1 phases, where their antiferrodistortive modes become the main driving force.
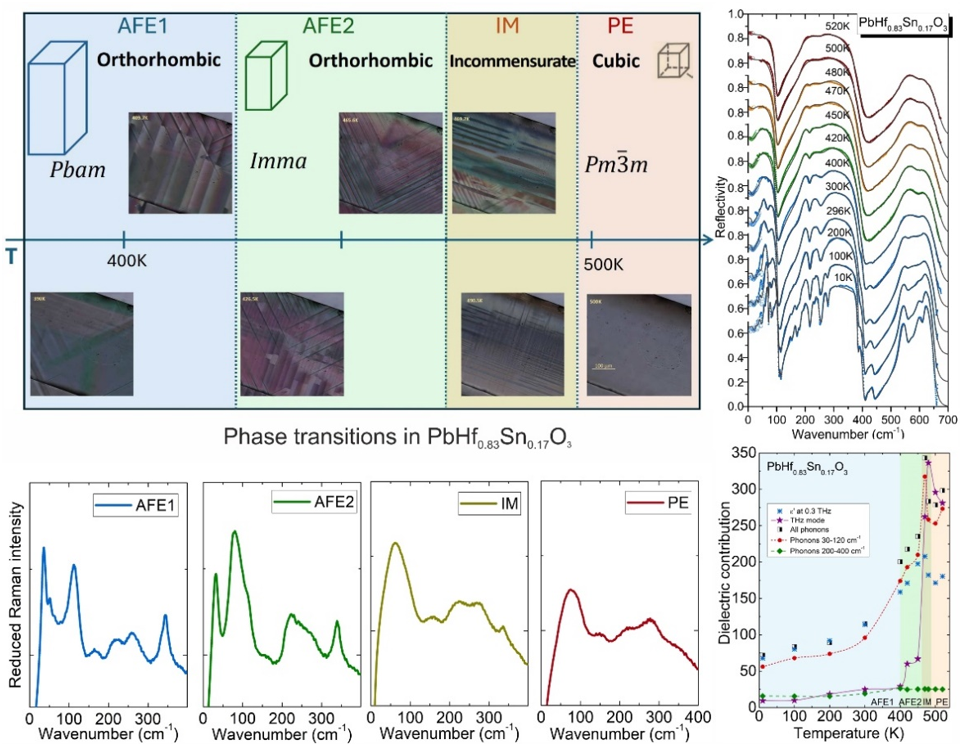
Schematics of the phase transition sequence in antiferroelectric Pb(Hf0.83Sn0.17)O3.
[1] Anirudh K R, C. Milesi-Brault, C. Kadlec, D. Nuzhnyy, A. Majchrowski, M. Krupska-Klimczak, I. Jankowska-Sumara, and E. Buixaderas,
Phonon studies of the phase transition sequence in antiferroelectric single crystal of Pb(Hf0.83Sn0.17)O3,
J. Appl. Phys. 138, 104101 (2025).
(show less)
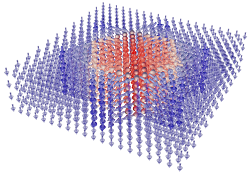
Antiskyrmions in ferroelectric barium titanate
Our recent molecular dynamics computational study reveals that the bulk crystal of the archetypal ferroelectric perovskite BaTiO3 can host ferroelectric antiskyrmions at zero field. We show that the antiskyrmion has just 2-3 nm in diameter and that it carries a very exotic topological charge of minus two [Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 066802 (2024)].
The prediction and experimental confirmation of magnetic skyrmions revolutionized the physics of nanoscale magnetism and opened new horizons for spintronics. In spite the inherently shorter and faster correlations of the electric polarization and challengingly smaller correlation lengths, the recent developments in electric skyrmionics follow these innovations. It is only 5 years since the first observation of a ferroelectric skyrmion in thin lead-strontium titanate superlattices [1].
The present molecular dynamics computational study [2)] reveals that the bulk crystal of the archetypal ferroelectric perovskite (barium titanate) can host peculiar 2-3 nm wide standalone polar columns stable till temperatures of several tens of Kelvins. They are spontaneously surrounded by a unique noncollinear polarization pattern (see figure) that has never been described before. We explained how and why this pattern is formed and stabilized. Since its invariant skyrmion topological charge is an integer with a sign opposite to that of the usual skyrmions, they named this soliton as ferroelectric antiskyrmion. They clarify that formation of antiskyrmions consists in breakdown of high-curvature 180-degree ferroelectric walls into triplets of lower-energy 71-degree walls. It is explained that this process is favored by a fortunate combination of the moderate anisotropy of the anharmonic electric susceptibility and the pronounced anisotropy of the polarization correlations in barium titanate crystals. These findings represent a clear milestone in the studies of topological defects in ferroelectrics.
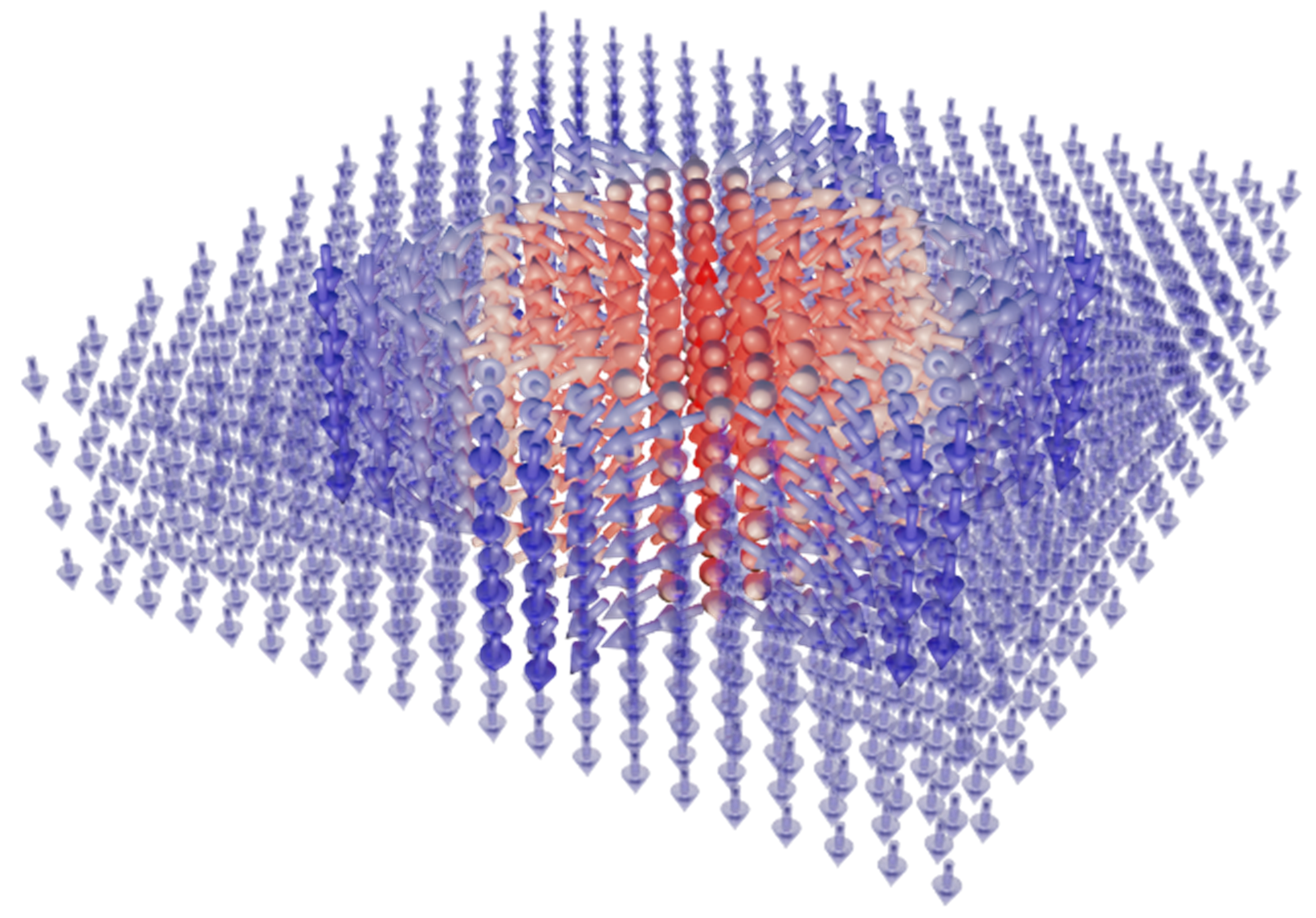
Figure: Polarization pattern of the ferroelectric antiskyrmion in rhombohedral BaTiO3 obtained from atomistic shell-model based computational experiment.
[1] S. Das, Y. L. Tang, Z. Hong, et al., Observation of room-temperature polar skyrmions, Nature 568, 368 (2019).
[2] M.A.P. Gonçalves, M. Paściak, and J. Hlinka, Antiskyrmions in ferroelectric barium titanate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 066802 (2024).
(show less)
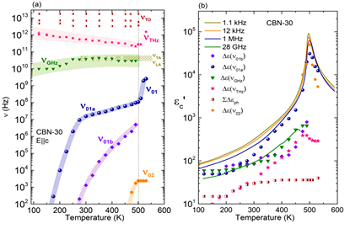
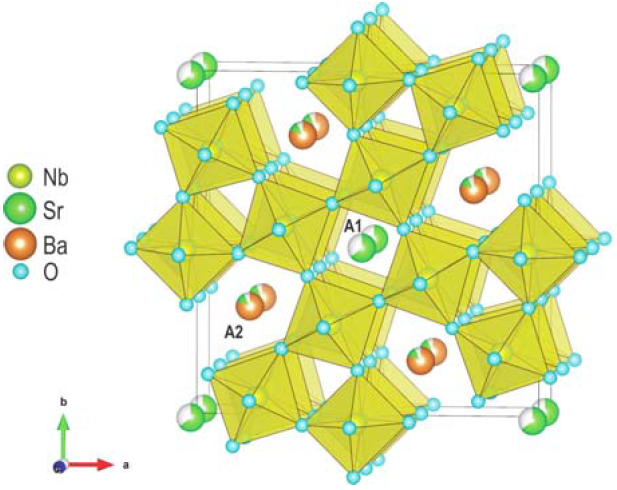
Coexisting polarization mechanisms in tetragonal tungsten bronze Ca0.3Ba0.7Nb2O6
We have proven that Ca0.3Ba0.7Nb2O6 displays a ferroelectric phase transition of mixed displacive and order-disorder character, and that its paraelectric phase does not show traces of relaxor behaviour but precursor effects as polar fluctuations below about 550 K [Phys. Rev. B 110, 104302 (2024)].
Tetragonal tungsten bronzes are the second most important ferroelectric family after the perovskite one, and they give more versatility to play with multiferroic properties, as it has 5 different crystallographic sites to fill with different elements (see Figure 1). In this work we have used a broad band dielectric spectroscopy approach to study the dielectric response of one of these interesting compounds Ca0.3Ba0.7Nb2O6 (CBN3-30) within an impressive frequency range of 14 decades: from 1 Hz to 1014 Hz. We have proven that CBN-30 displays a ferroelectric phase transition of mixed displacive and order-disorder character, and that its paraelectric phase does not show traces of relaxor behaviour but precursor effects as polar fluctuations below about 550 K. This is partially attributed to the presence of Ca in the lattice, and its effect on maintaining the long-range polarization due to the Nb displacements along the main axis and suppressing the perpendicular displacements.
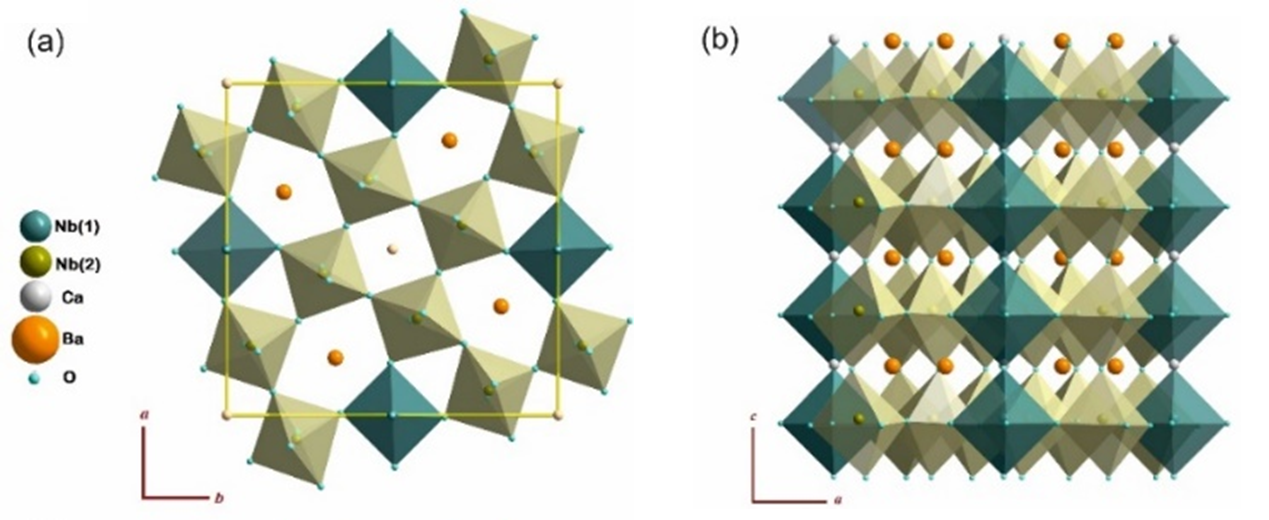
Figure 1: Structure of CBN-30 in two orientations. Nb(1) are inside the linking octahedra in dark colour, and Nb(2) inside the perovskite-like octahedra in light colour.
The analysis of the sub-MHz dielectric response together with infrared and Raman spectroscopy reveals that simultaneous polarization mechanisms are responsible for the phase transition. The main excitations have been phenomenologically assigned to phonons, to a soft anharmonic vibration of cationic origin, and to a relaxation in the GHz range related to polarization fluctuations of nanometric size. This GHz relaxation carries the main part of the permittivity at high temperatures in the paraelectric phase and on cooling it splits below TC into several weaker excitations with different polarization correlation lengths. The comparison of the excitations found in CBN-30 with those of the famous (Sr,Ba)Nb2O6 reveals that these mechanisms are congruous, although in CBN-30 the main relaxation process behaves differently due to the different domain structure and the presence of more distorted oxygen octahedra network. The overall dielectric response was therefore explained by coexistence of several excitations with different thermal behaviors, corroborating the complexity of the tetragonal tungsten bronze structures.
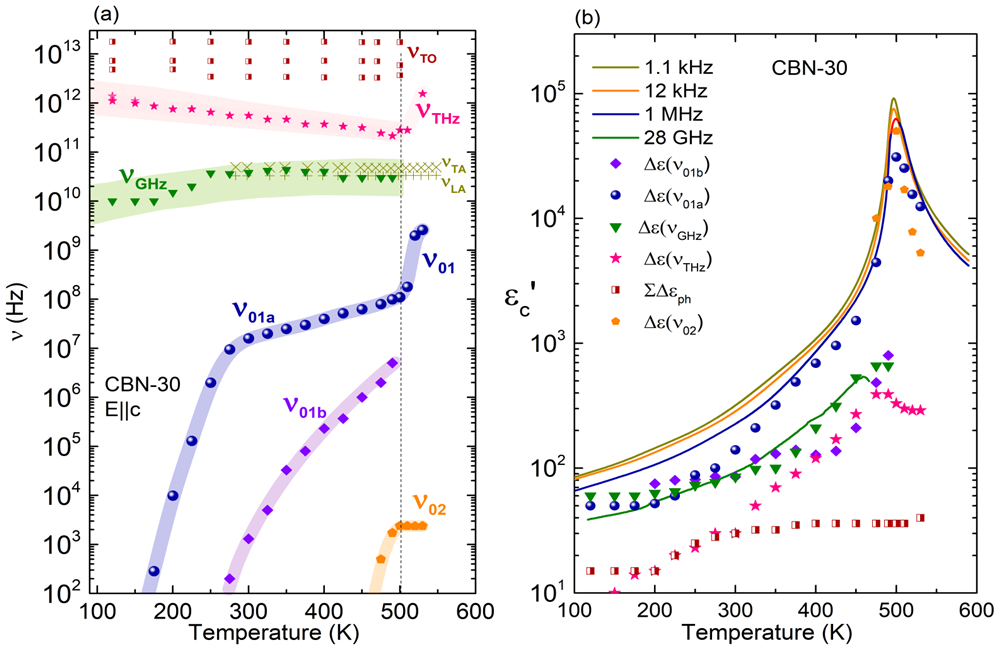
Figure 2: Temperature dependence of the frequencies of the main excitations in CBN-30 (a), and their dielectric contribution to the permittivity (b), together with selected experimental data.
This work was partially supported by the Czech Academy of Sciences and the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences through the bilateral Project No. LAS-21–02. E.B. acknowledges support from the Ministry of Education, Youth, and Sports of the Czech Republic by the EU cofunded grant “Ferroic Multifunctionalities”, Project No. CZ.02.01.01/00/22_008/0004591.
Reference
[1] E. Buixaderas, Š. Svirskas, C. Kadlec, M. Savinov, P. Lapienytė, Anirudh K.R., C. Milesi-Brault, D. Nuzhnyy, and J. Dec Coexisting polarization mechanisms in ferroelectric uniaxial tetragonal tungsten bronze Ca0.3Ba0.7Nb2O6 (CBN-30) Phys. Rev. B 110, 104302 (2024).
(show less)
Discrepancy between microscopic quantum dynamics and macroscopic order in strongly correlated electron systems
We disclose a serious deficiency of the Baym-Kadanoff construction of thermodynamically consistent conserving approximations [Phys. Rev. B 109, 075171 (2024)].
We disclosed in this paper a long-neglected problem of matching microscopic quantum many-body dynamics with the macroscopic long-range order. The latter is presently derived from the former within the canonical Baym-Kadanoff construction of thermodynamically consistent conserving approximations. Two two-particle vertices, responsible for the system’s response to the external perturbations, must be introduced: microscopic dynamic and macroscopic conserving vertices. The former is determined from the diagrammatic perturbation theory, while the latter is obtained from the respective Ward identity, guaranteeing macroscopic conservation laws. The divergence of each vertex indicates an instability.
We revealed an ambiguity of the Baym-Kadanoff construction in determining the critical behavior with a transition to a thermodynamic long-range order. We demonstrated that each vertex leads to incomplete and distinct critical behavior with distinct instability points. The diagrammatically controlled dynamic vertex from the Schwinger-Dyson equation cannot directly be linked with a macroscopic long-range order, since it does not obey the Ward identity. Consequently, it cannot be continued beyond its instability. On the other hand, the divergence in the macroscopic vertex, obeying the conservation laws, has no direct microscopic consequences and does not invoke critical behavior of the spectral function and the specific heat as derived from the dynamic vertex. Consequently, the description of the critical behavior of correlated electrons becomes consistent and reliable only if the fluctuations of the order parameter in the conserving vertex lead to a divergence coinciding with that of the dynamical one. None of the existing approximate schemes fulfills this condition.
The ambiguity in the definition of phase instabilities of the Baym-Kadanoff scheme disclosed by us has a firm conclusion that an entirely consistent theory beyond the weak-coupling static Hartree-Fock approximation of the critical behavior of strongly correlated electrons is to be devised.
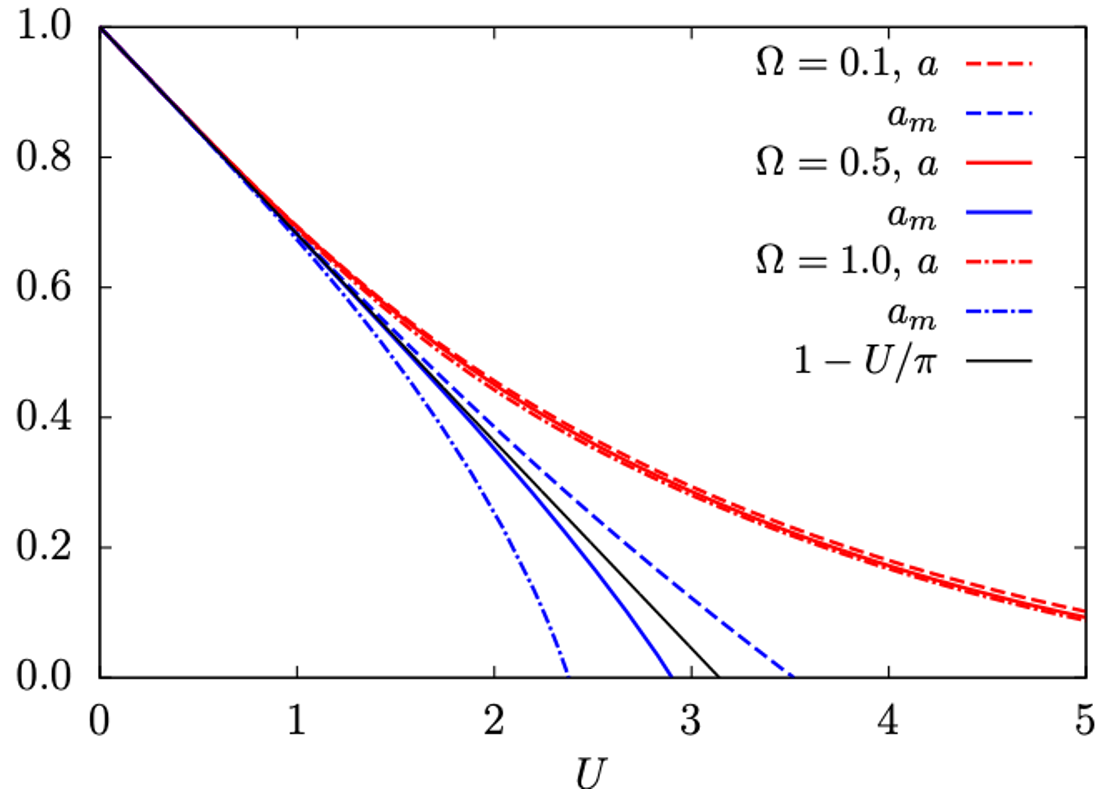
Demonstration of the ambiguity of the definition of phase instability. The dependence on the interaction strength U of the dimensionless Kondo scale a, measuring the distance to the magnetic instability from the dynamic vertex of the microscopic dynamic theory, red curves, and the Kondo scale from the macroscopic susceptibility am=χ0/χ, blue curves, plotted for different values of the ultraviolet cutoff in the polar approximation, accurate in determining the critical point, Ω; χ0,χ are zero-temperature bare and full susceptibilities. The black solid line is the Hartree static solution (1-U/π). Notice that the exact solution suppresses the magnetic instability, as obtained for the dynamic solution, red lines. The thermodynamic macroscopic criterion, blue lines, leads to a spurious instability, disqualifying the credibility of the dynamic approximations in determining consistently macroscopic instabilities of strongly correlated electrons.
[1] V. Janiš, V. Pokorný, and Š. Kos, Failure of the Baym-Kadanoff construction to consistently match quantum dynamics with thermodynamic critical behavior, Phys. Rev. B 109, 075171 (2024).
(show less)
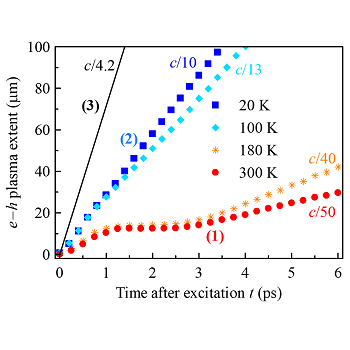
Ultrafast long-distance expansion of electron-hole plasma in direct bandgap semiconductors
Transport of charge carriers inside crystals is determined by their energy band structure which only permits velocities smaller than ~c/100 in known materials. We demonstrated that ultrafast and long-distance propagation of electron-hole plasma (velocities up to c/10, reaching more than 100 μm) is possible as a quite general result of fundamental electron-photon interaction in direct bandgap semiconductors upon strong pulse photoexcitation with low photon excess energy above the bandgap [PRL 130, 226301 (2023) & Nanophotonics 13, 1859 (2024)].
Electron-hole plasma expansion with velocities exceeding c/50 and lasting over 10 ps at 300 K was evidenced by time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy [1]. This regime, in which the carriers are driven over >30 μm is governed by stimulated emission due to low-energy electron-hole pair recombination and reabsorption of the emitted photons outside the plasma volume. At low temperatures a speed of c/10 was observed in the regime where the excitation pulse spectrally overlaps with emitted photons, leading to strong coherent light-matter interaction and optical soliton propagation effects.
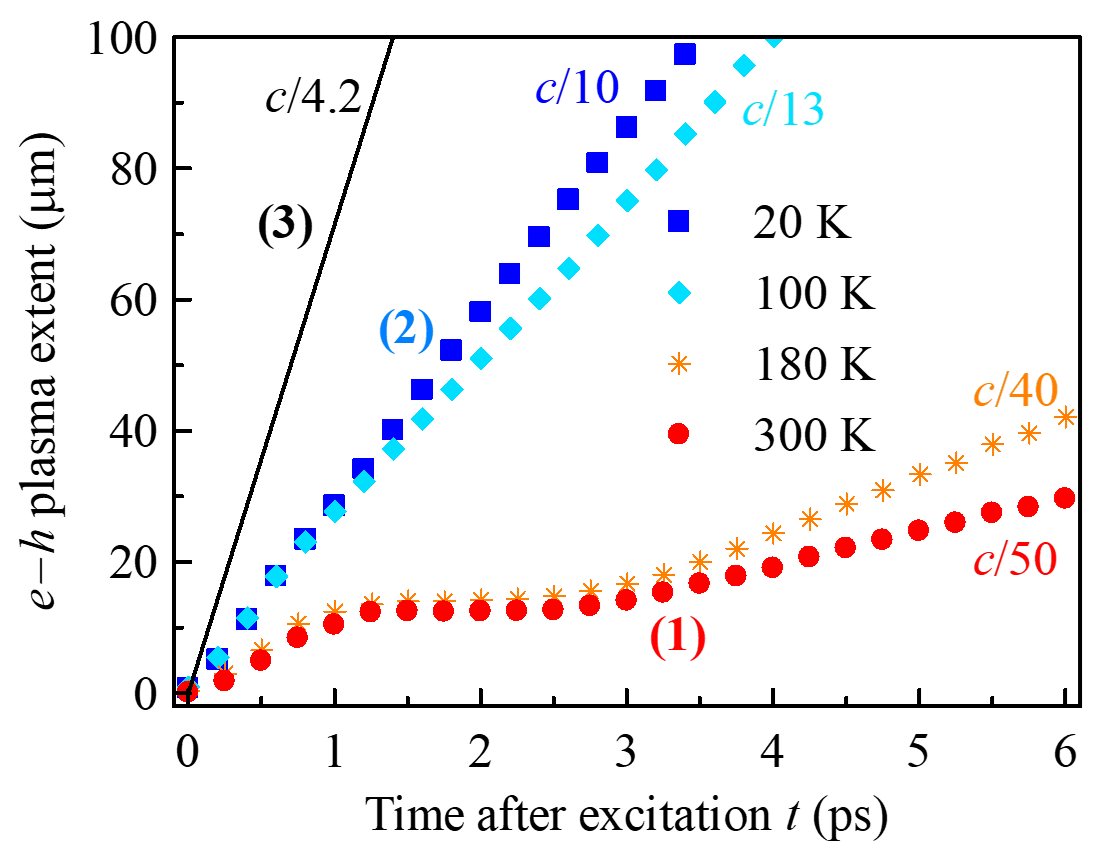
Figure:
Propagation of plasma as measured by THz pulse probing of photocarriers in GaAs shows that assistance of light can dramatically enhance
the charge propagation rates.
(1) In incoherent regime the plasma propagation is due to stimulated emission and reabsorption of photons;
(2) In coherent regime at low temperature the electron – photon interaction leads to Rabi dynamics and soliton formation and propagation;
(3) for comparison: group velocity of light in GaAs.
[1] T. Troha, F. Klimovič, T. Ostatnický, F. Kadlec, P. Kužel, and H. Němec, Ultrafast long-distance electron-hole plasma expansion in GaAs mediated by stimulated emission and reabsorption of photons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 226301 (2023).
[2] T. Troha, F. Klimovič, T. Ostatnický, H. Němec and P Kužel, Photon-assisted ultrafast electron–hole plasma expansion in direct band semiconductors, Nanophotonics 13, 1859 (2024).
(show less)
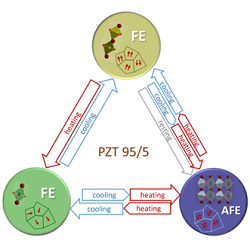
Paving the way to a 3-state thermal switch using antiferroelectric Pb(Zr1-xTix)O3
We propose a novel approach of phase-control in Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 (PZT95/5) based on the thermal behavior of its phases. Our results show the possibility to thermally switch among three states near room temperature using small temperature gradients by heating-cooling cycles at slow rates. Thus, PZT95/5 ceramics are potential materials for room temperature device applications [Acta Materialia, 119208 (2023), online].
Pb(Zr1-xTix)O3 with very high content of Zr shows an antiferroelectric ground state and possesses an exceptional property: the coexistence of several built-in structural instabilities at high temperatures. This leads to the possibility of their successive condensation on cooling to trigger a sequence of phase transitions, instead of reaching directly the antiferroelectric state, as in pure PbZrO3. This peculiar behaviour is more pronounced in compositions near the antiferroelectric morphotropic phase boundary and the tricritical point around room temperature, as Pb(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 (PZT 95/5), where three phases are energetically available.
Raman scattering experiments performed out of the thermodynamical equilibrium revealed a complex and hysteretic thermal behaviour of the phase transition dynamics, due to the inhomogeneous microstructure and the coexistence of regions with different phases within the samples. A way to control the thermal development of these different phases is to selectively condense the different instabilities by an external parameter such as temperature, hence creating a sequence of phase transitions instead of a direct phase transition.
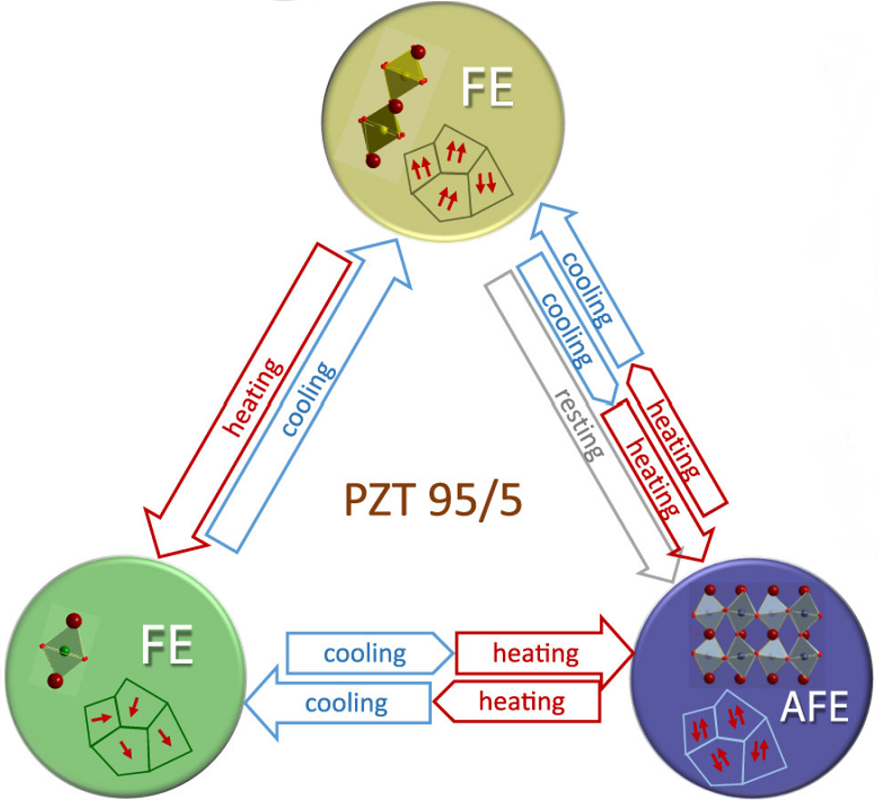
Figure: Scheme of thermal switching using the three near-room-temperature phases of PZT 95/5.
Our results, obtained under many different experimental conditions and specific pre-history, suggest that ceramics with composition near PZT 95/5 are potential materials for novel 3-state thermal switches. An innovative approach of phase-control is proposed, based on the thermal behaviour of the intermediate polar states observed and using small temperature gradients by appropriate heating-cooling cycles around room temperature.
Reference:
[1] E. Buixaderas, C. Milesi-Brault, P. Vaněk, J. Kroupa, F. Craciun, F. Cordero, C. Galassi,
Peculiar Dynamics of Polar States at the Morphotropic Phase Boundary of Antiferroelectric Pb(Zr1-xTix)O3,
Acta Materialia, 119208 (2023), online.
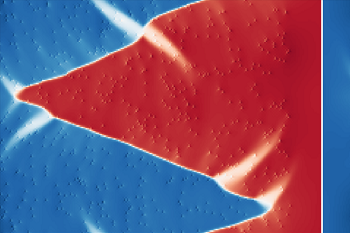
Zigzag charged domain walls in ferroelectric PbTiO3
We report a theoretical investigation of a charged 180-degree domain wall in ferroelectric PbTiO3, compensated by randomly distributed immobile charge defects. We predict that domain walls form a zigzag pattern and we discuss their properties in a broad interval of compensation-region widths. The zigzag is accompanied by a local polarization rotation which we explain to provide an efficient mechanism for charge compensation [Phys. Rev. B 107, 094102 (2023)].
Our study delved into a theoretical exploration of charged domain walls in ferroelectric PbTiO3, which were compensated by randomly distributed immobile charge defects located within a relatively broad slab. To achieve this, we employed a combination of atomistic shell-model simulations and continuous phase-field simulations based on the Ginzburg-Landau-Devonshire model. Our findings showed that domain walls form a zigzag pattern, and we examined their properties across a broad range of compensation-region widths, ranging from a few nanometers to over 100 nm, focusing in particular on understanding the zigzag modulation lengths in terms of material properties of PbTiO3. The zigzag formation is accompanied by a local ferroelectric-polarization rotation, which we proposed as an efficient mechanism for local charge compensation. Our study provides a new understanding of the behavior of charged domain walls in ferroelectric materials and highlights the significance of the considered compensation charges in their formation. The insights gained from our study may contribute to the development of advanced ferroelectric materials with applications in the field of smart-materials for electronics.
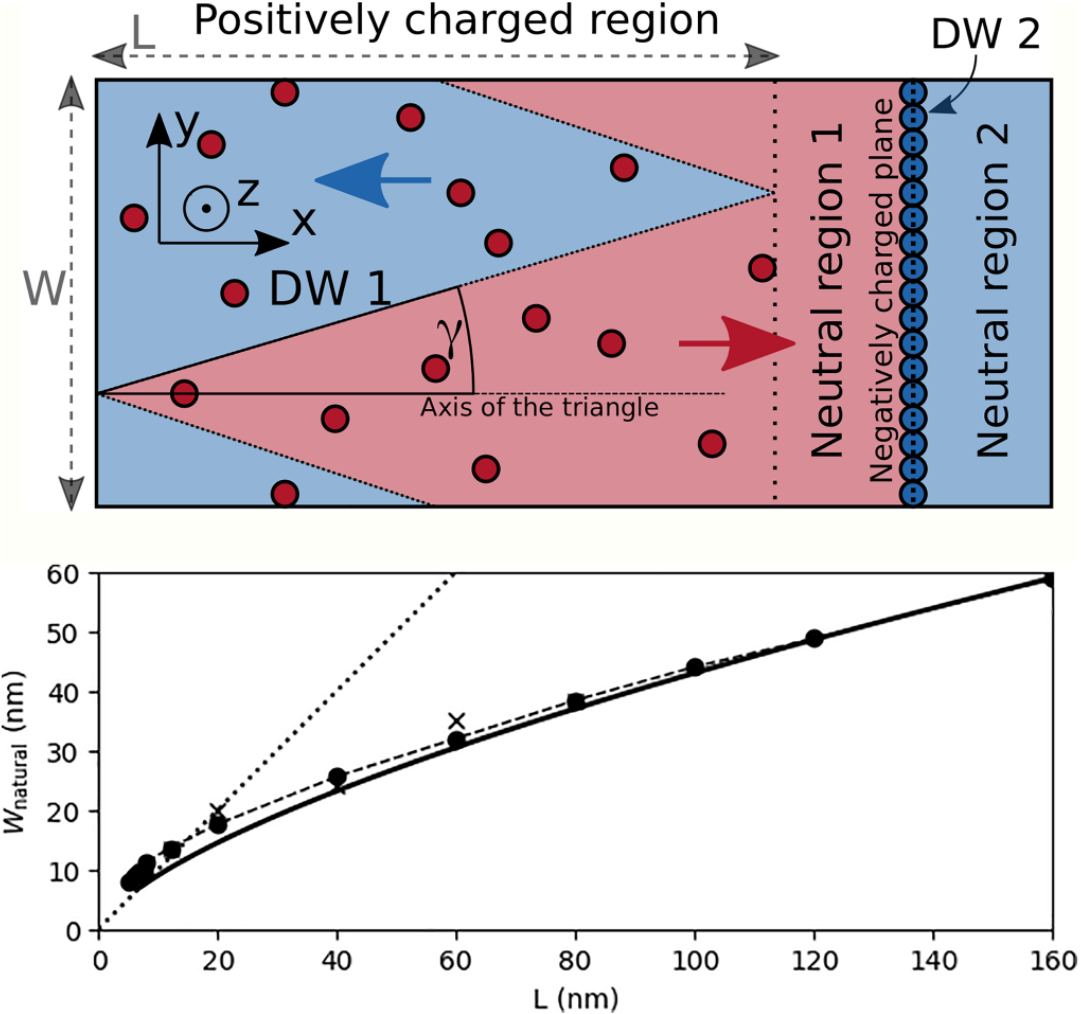
Figure:
Top panel: Schematic picture of the zigzag pattern, which is used in the derivation of natural width of triangles.
Red and blue colors and arrows correspond here to positively and negatively oriented ferroelectric domains
(with respect to the x axis). The color of the defects is red for positive and blue for negative point defects.
Bottom panel: Dependence of natural width of the zigzag triangles. Bullets: Phase-field simulations
with homogeneous compensation charge; the dashed line is just a connection of these.
Crosses: Phase-field simulations with randomly distributed defect charges.
Solid line: Simplified analytical model. Numerical and analytical approaches show
an excellent corespondence for large thicknesses of the compensation-region L.
[1] P. Marton, M. A. P. Gonçalves, M. Paściak, S. Körbel, V. Chumchal, M. Plešinger, A. Klíč, and J. Hlinka, Zigzag charged domain walls in ferroelectric PbTiO3, Phys. Rev. B 107, 094102 (2023).
(show less)
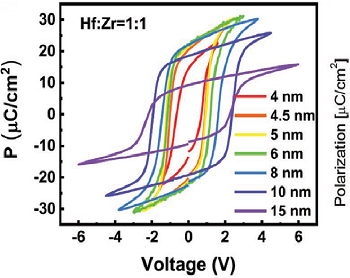
Application of HfO2 thin films in non-volatile memories – a review
We review main factors in preparation of HfO2 thin films and their physical properties which are important for applications in high-density resistive random access memories and ferroelectric memories [Small 18, 2107575 (2022)].
Ultrathin films of HfO2 become ferroelectric although bulk crystals are paraelectric. In this review we describe how grain size, thermal stress, dopants, oxygen vacancies, film thickness, annealing process and electrodes influence dielectric properties of HfO2, which are important for applications in high-density resistive random access memories and ferroelectric memories. We also discuss how to achieve superlative performance with high-speed reliable switching, excellent endurance and retention.
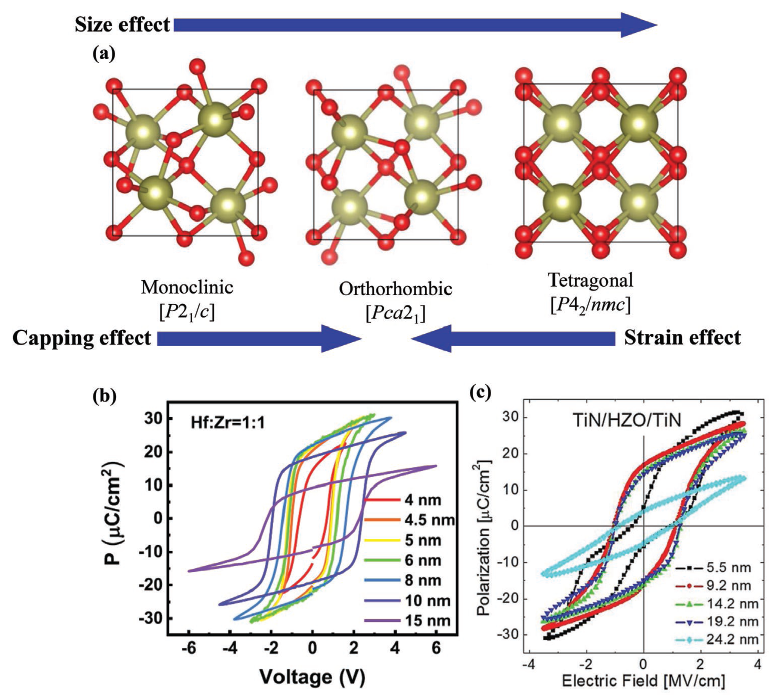
Figure: Dependence of crystal structure of HfO2 on the thin film thickness, strain and electrodes.
[1] W. Banerjee, A. Kashir, and S. Kamba, Hafnium Oxide (HfO2) – A Multifunctional Oxide: A Review on the Prospect and Challenges of Hafnium Oxide in Resistive Switching and Ferroelectric Memories, Small 18, 2107575 (2022).
(show less)
Out-of-equilibrium impurities with correlated electrons: Spectral and transport properties
We apply a two-particle semianalytic approach to a single Anderson impurity attached to two biased metallic leads. Furthermore, we qualitatively reproduce the three transport regimes with the increasing temperature: from the Kondo resonant tunneling through the Coulomb-blockade regime up to a sequential tunneling regime [Phys. Rev. B 105, 085122 (2022)].
Simple approximations to impurities with correlated electrons fail out of equilibrium, leading to an unphysical hysteresis loop in the current-voltage characteristics. Electron correlations are known to suppress this hysteresis. We applied a two-particle semianalytic approach to an out-of-equilibrium Anderson impurity attached to two biased metallic leads. The theory qualitatively correctly interpolates between weak and strong coupling. It is based on reduced parquet equations adapted to capture the critical regions of singularities in the Bethe-Salpeter equations. This advanced approach covers one-particle and two-particle thermodynamic and spectral quantities relatively well in both weak and strong coupling. Our approximation successfully suppressed the unphysical hysteresis loop. Furthermore, we qualitatively reproduced within the linear response the three transport regimes with the increasing temperature: from the Kondo resonant tunneling through the Coulomb-blockade regime up to a sequential tunneling regime. Far from equilibrium, we find that the bias plays a similar role as the temperature in destroying the Kondo resonant peak when the corresponding energy scale is comparable with the Kondo temperature. Aside from that, the applied voltage in low bias was shown to develop spectral peaks around the lead chemical potentials as observed in previous theoretical and experimental studies.
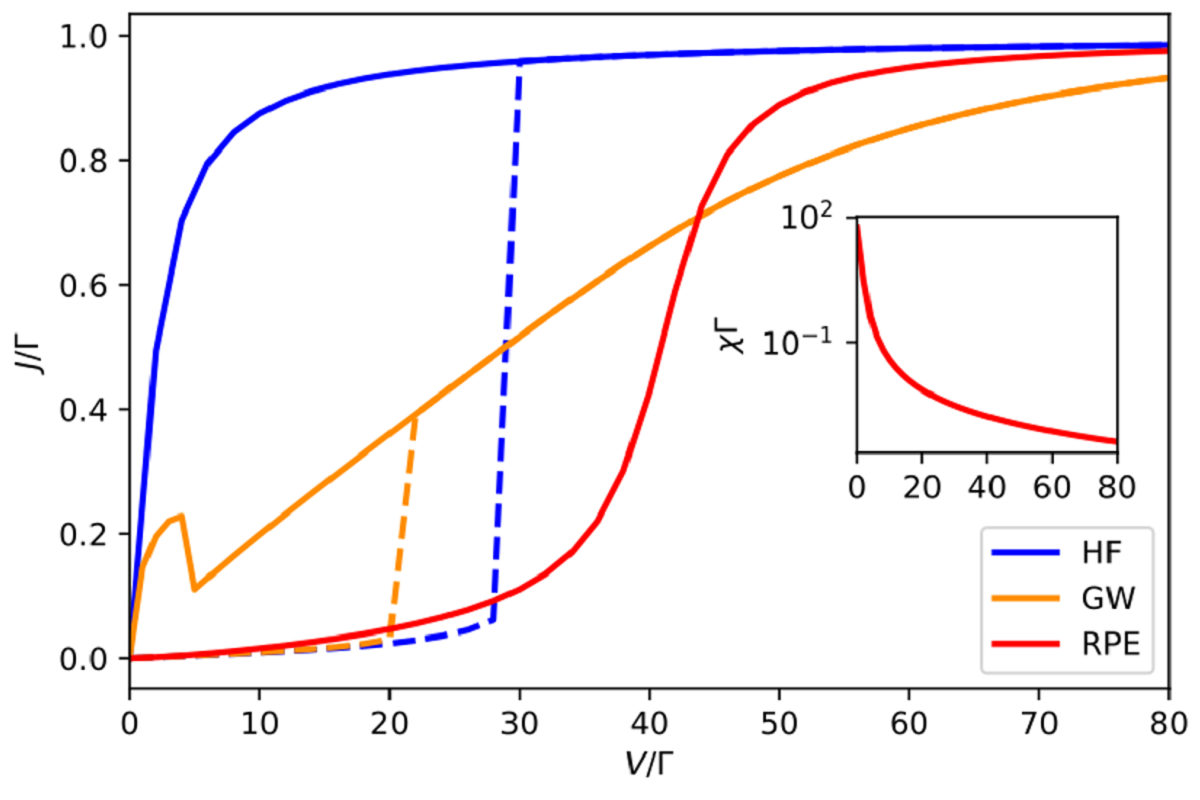
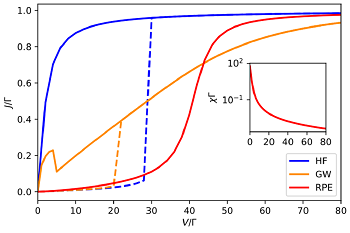
Figure: I-V characteristic curve of the Anderson impurity model at half-filling for interaction U = 40Γ and temperature T = 0.1Γ in the Coulomb-blockade regime calculated by the Hartree-Fock (HF) mean-field, GW approximation, and the reduced parquet equations (RPE). An unphysical hysteresis loop appears in the HF and GW approximations, with the solid line corresponding to the nonmagnetic solution and the dashed line to the magnetic one. The RPE suppresses the spurious magnetic order, hence it is free of hysteresis. Here, Γ is the energy unit, impurity bandwidth. The inset shows the magnetic susceptibility as a function of the bias voltage V.
[1] J. Yan and V. Janiš, Single-impurity Anderson model out of equilibrium: A two-particle semianalytic approach, Phys. Rev. B 105, 085122 (2022).
(show less)
Multidomain ordered metal–ferroelectric superlattices
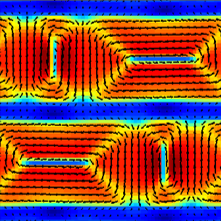
By combination of advanced experimental techniques and phase-field simulations, we found that electric dipoles in superlattices, composed of layers of a ferroelectric material separated by thin metallic spacers, form an unusual pattern of nanoscale domains that order in three dimensions. These ferroelectric multidomain ordered superlattices exhibit an outstanding dielectric response and their engineered modulated structural and electronic properties can be controlled using electric field [Nat. Mater. 20, 495 (2021)].
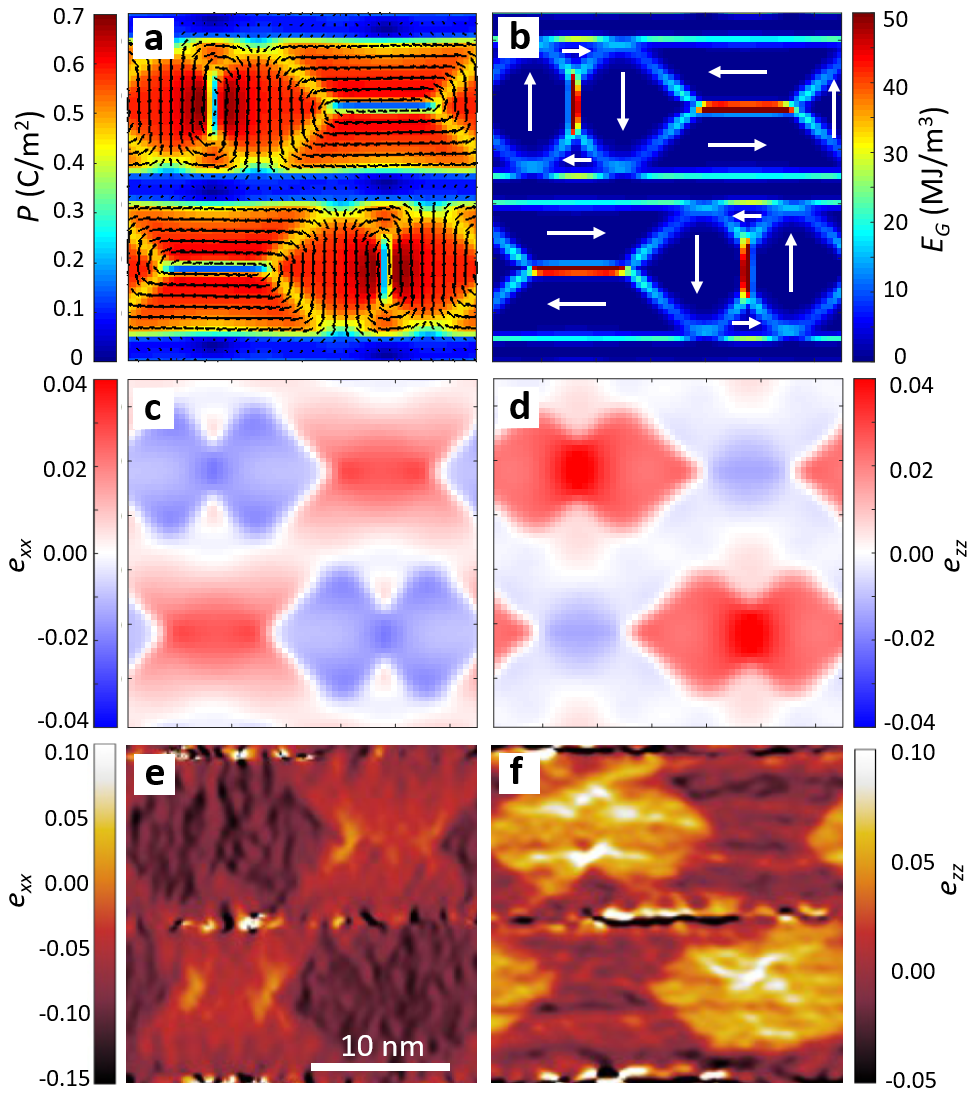
Figure:
Two-dimensional base motif of the ferroelectrically ordered PbTiO3–SrRuO3 superlattices as seen by
(a-d) phase-field simulations and (e,f) transmission electron microscopy:
(a) electric polarization showing ferroelectric domain structure in two PbTiO3 layers separated by SrRuO3 spacers
(b) gradient energy density coming from domain walls and boundaries between layers,
(c-f) in-plane (exx) and out-of-plane (ezz) strain components demonstrating correlations between ferroelectric PbTiO3 layers.
The arrows in (a,b) panels show direction of electric polarization forming characteristic flux-closure patterns.
[1] M. Hadjimichael, Y. Li, E. Zatterin, G. A. Chahine, M. Conroy, K. Moore, E. N. O’ Connell, P. Ondrejkovic, P. Marton, J. Hlinka, U. Bangert, S. Leake, and P. Zubko, Metal–ferroelectric supercrystals with periodically curved metallic layers, Nat. Mater. 20, 495 (2021).
(show less)
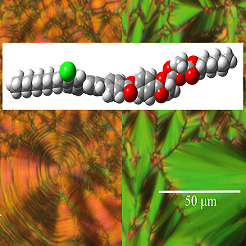
Ferroelectric and antiferroelectric phases in liquid crystalline compounds with terphenyl in the molecular coere
We designed a new type of antiferroelectric liquid crystalline structure with terphenyl in the molecular core and two lactate units attached to the chiral chain [J. Mol. Liq. 336, 116267 (2021)].
For the series of compounds, we studied the mesomorphic properties by various experimental techniques and confirmed the phase identification by x-ray measurements. For selected homologues we proved the antiferroelectric phase with orthoconic properties existing in a wide temperature interval including the room temperatures. Valuable optical properties with the tilt angle about 45 degrees promised a big potential for applications.
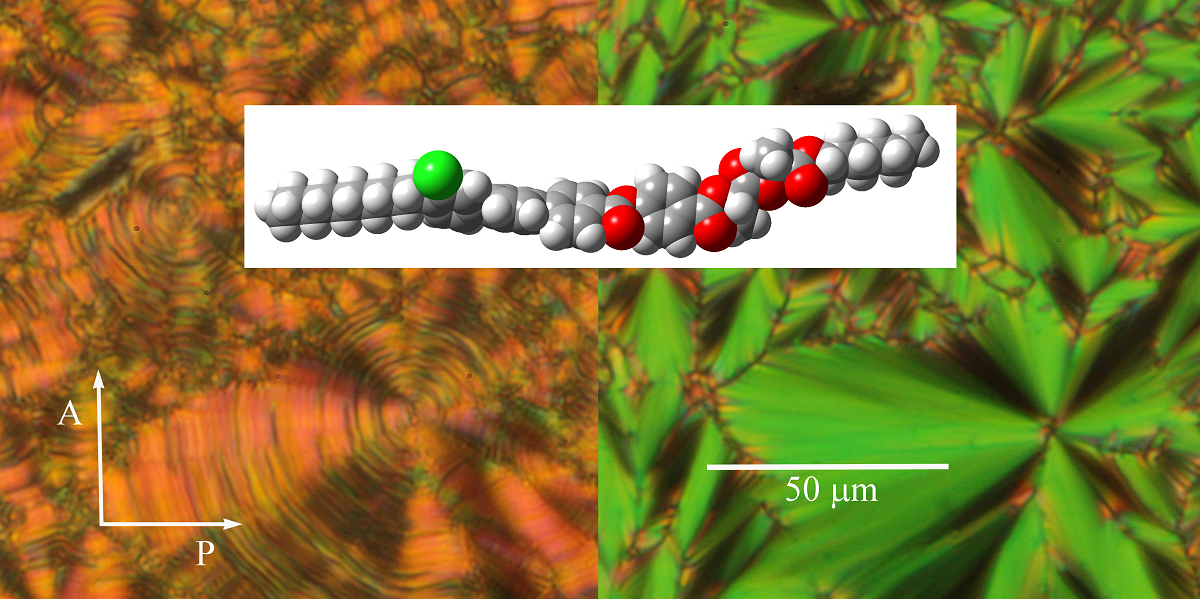
Figure: Texture of the liquid crystalline compound with a terphenyl in the molecular core in antiferroelectric phase without field (left picture) and under applied electric field (right picture). The scale, orientation of polariser (P) and analyser (A) are presented. In the centre, there is a model of the studied molecule in the optimised conformation.
[1] N. Podoliak, M. Cigl, V. Hamplová, D. Pociecha, and V. Novotná, Multichiral liquid crystals based on terphenyl core laterally substituted by chlorine atom, J. Mol. Liq. 336, 116267 (2021).
(show less)
New material for 5G mobile networks
Epitaxial strained thin films of (SrTiO3)n-1(BaTiO3)1SrO were found to be a promising new material for mobile network of the 5th generation [Nature Mater. 19, 176 (2020)].
Epitaxial strained thin films of (SrTiO3)n-1(BaTiO3)1SrO were grown on DyScO3 substrates using molecular beam epitaxy [1]. The best microwave dielectric properties were discovered in samples with n= 6. Permittivity exhibits huge tuning using electric field and microwave dielectric loss is anomalously low. Unique properties were confirmed using first-principles calculations and by experimental observation of the soft mode behavior in THz region. These films are ideal for components in 5G networks.
Collaborating institutions: Prof. D.G. Schlom from the Cornell University and other American and German institutions.
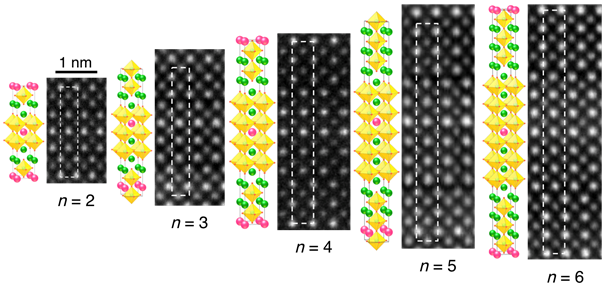
Figure: Schema of crystal structures of investigated (SrTiO3)n-1(BaTiO3)1SrO films and their view in scanning transmission electron microscope. Yellow octahedra depict TiO6 layers, green and red points mark atoms of Sr and Ba.
[1] N.M. Dawley, E.J.Marksz, A.M. Hagerstrom, G.H. Olsen, M.E. Holtz, V. Goian, C. Kadlec, J. Zhang, X. Lu, J.A. Drisko, R. Uecker, S. Ganschow, C.J. Long, J.C. Booth, S. Kamba, C.J. Fennie, D.A. Muller, N.D. Orloff, D.G. Schlomk, Targeted chemical pressure yields tuneable millimetre-wave dielectric, Nature Mater. 19, 176 (2020).
(show less)
Ferroelectric phase transition in water molecules localized in mineral cordierite
We discovered that hydrogen bonds are eliminated and the Coulombic interactions dominate in water molecules localized in nano-channels of mineral cordierite. Their dipole moment is perpendicular to the channel axis c and our dielectric spectroscopy study have revealed their ordering at ~3 K. The critical relaxation tending to this ordering is polarized along the a-axis direction and lies in the radiofrequency range. Spontaneous polarization measurements yield the saturated value of ~3 nC/cm2 at 0.3 K [Nat. Commun. 11, 3927 (2020)].
Water molecules localized in structural crystal nano-channels give a possibility to eliminate hydrogen bonds, dominating among water molecules at short distances up to ~2 Å which prevent ordering of their dipole moments. On larger distances 1-10 nm the Coulombic interactions dominate, which can lead to their ordering. We continued in our previous studies on beryl, where we, on cooling, have detected tendency to ferroelectric ordering, so called incipient ferroelectric behaviour. Mineral cordierite (Mg,Fe)2Al4Si5O18 also comprise structural channels similar to those in beryl, in which the chains of water molecules are ideally suited for the ordering study (Fig. 1).
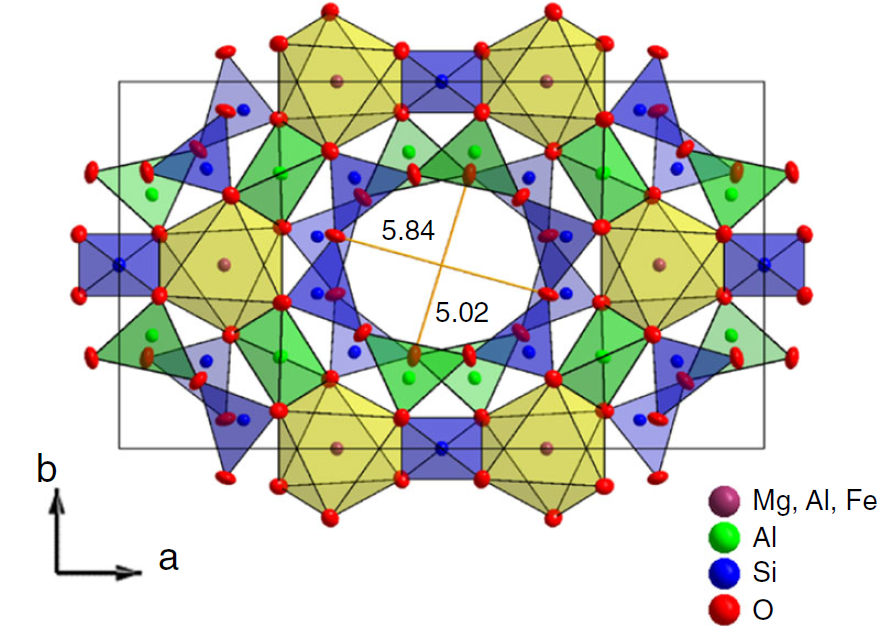
Figure 1: Cordierite crystal structure. Investigated water was localized in the free channels along the c-axis.
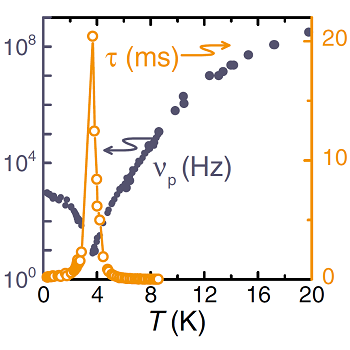
Crystal structure is orthorhombic, the channels in the c-axis direction are in the distance of 9.9 Å and the water molecules in the channels are by 4.7 Å from each other. Their dipole moment is perpendicular to the channel axis and our dielectric spectroscopy study have revealed their ordering at ~3 K. The critical relaxation tending to this ordering is polarized along the a-axis direction and lies in the radiofrequency range (Fig. 2). Spontaneous polarization measurements yield the saturated value of ~3 nC/cm2 at 0.3 K. Molecular dynamics calculations show the ferroelectric ordering in the plane perpendicular to the channels and antiferroelectric ordering along them.
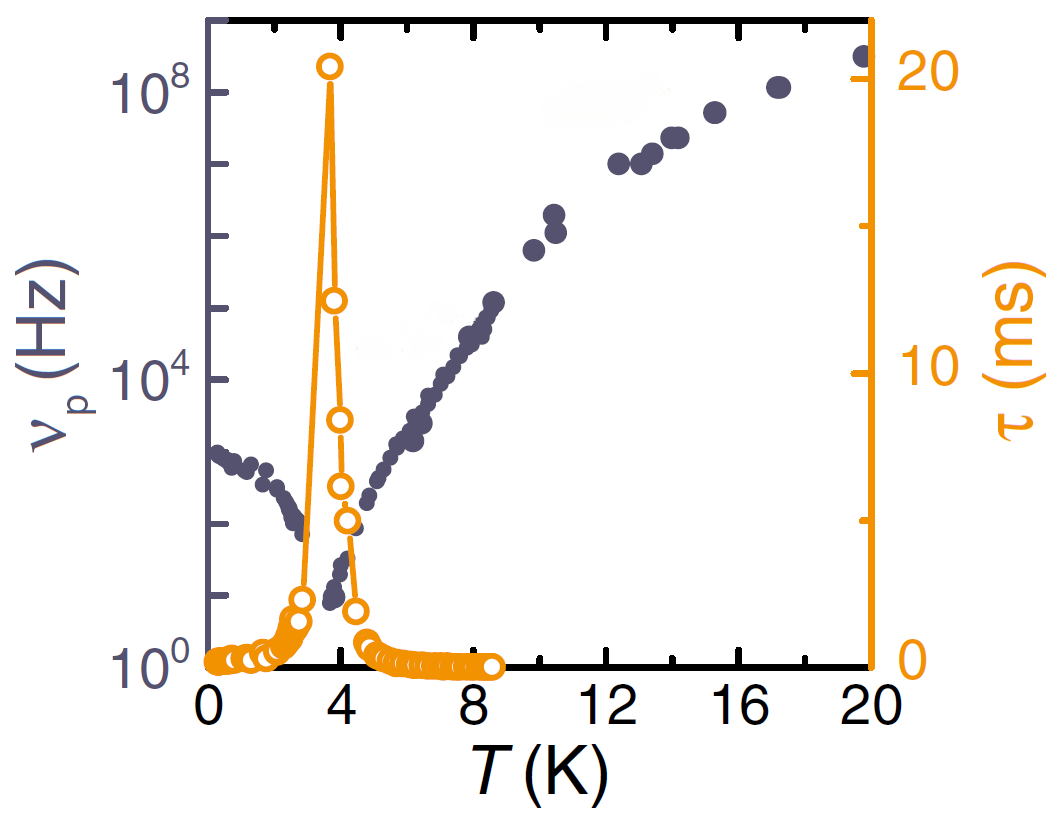
Figure 2: Ferroelectric phase transition of water in cordierite is induced by a critical slowing down of dielectric relaxation. νp denotes frequency of the maxima in the dielectric loss spectra and τ denotes the relaxation time of the relaxation.
[1] M. A. Belyanchikov, M. Savinov Z. V. Bedran, P. Bednyakov, P. Proschek, J. Prokleska, V. A. Abalmasov, J. Petzelt, E. S. Zhukova, V. G. Thomas, A. Dudka, A. Zhugayevych, A. S. Prokhorov, V. B. Anzin, R. K. Kremer, J. K. H. Fishcer, P. Lunkenheimer, A. Loidl, E. Uykur, M. Dressel, and B. Gorshunov Targeted chemical pressure yields tuneable millimetre-wave dielectric,
Nat. Commun. 11, 3927 (2020)
(show less)
Making EuO multiferroic by epitaxial strain engineering
Optical soft mode driven ferroelectric phase transition was discovered in IR spectra of tensile strained ferromagnetic EuO thin films [Commun. Mater. 1, 74 (2020)].
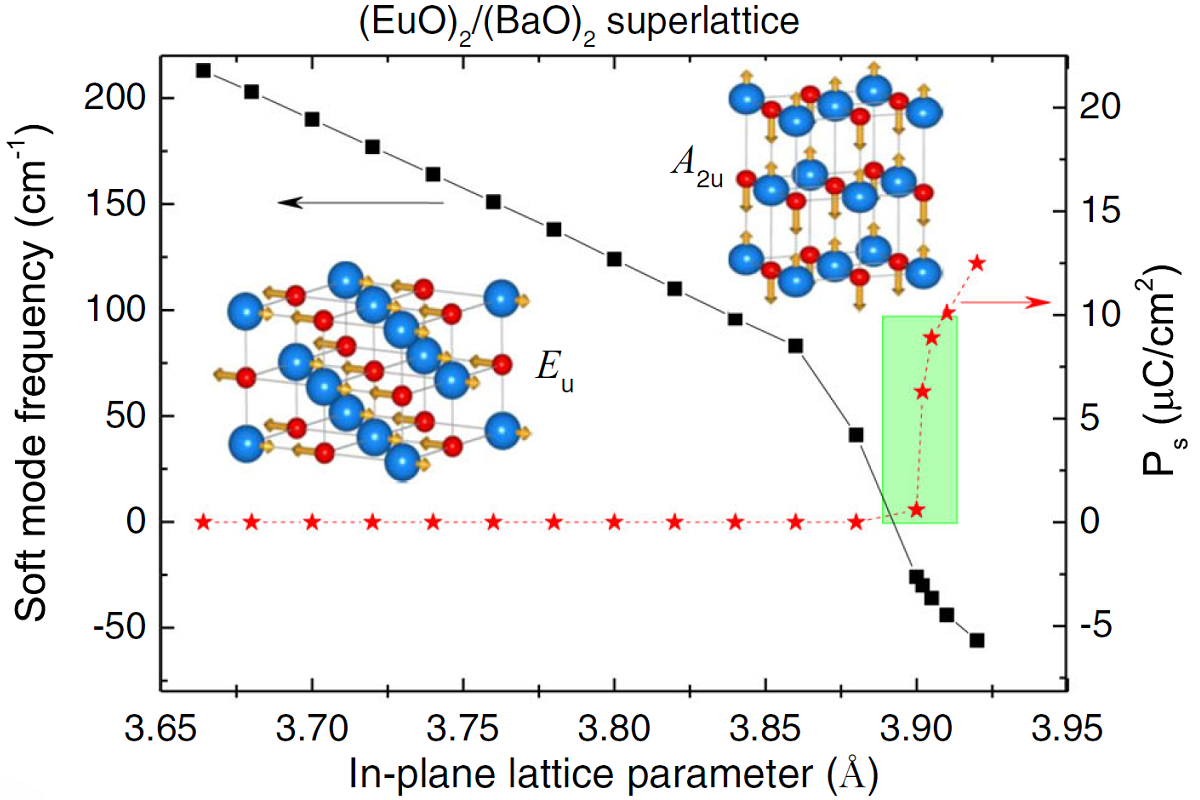
The phase transition was predicted already ten years ago in films with 4% strain, but we have observed it only now in films with 6.4% strain. As such strain tends to relax after the epitaxial growth of only a few monolayers, we have achieved it in (EuO)2/(BaO)2 superlattices grown epitaxially on LSAT substrates. The observation is supported by a new DFT calculation.
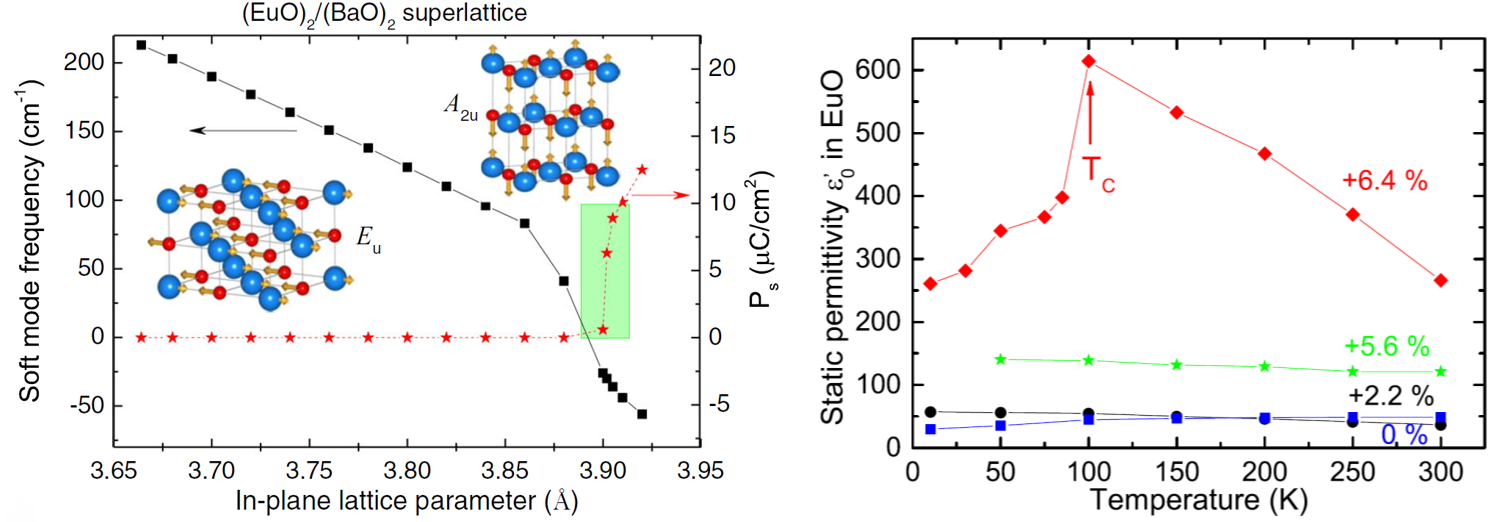
Figure:
Left: Theoretical strain dependence of the Eu ferroelectric soft mode frequency and
of the spontaneous polarization Ps in (EuO)2/(BaO)2
superlattice obtained from the DFT calculations. Insets show schematic eigenvectors of
the Eu and A2u symmetry polar phonons.
Rigth: Temperature dependence of the static permittivity of the EuO films and EuO layers
in the (EuO)x/(BaO)y superlattices with various tensile strain.
[1] V. Goian, R. Held, E. Bousquet, Y. Yuan, A. Melville, H. Zhou, V. Gopalan, P. Ghosez, N. A. Spaldin, D. G. Schlom, and S. Kamba, Making EuO multiferroic by epitaxial strain engineering, Commun. Mater. 1, 74 (2020).
(show less)
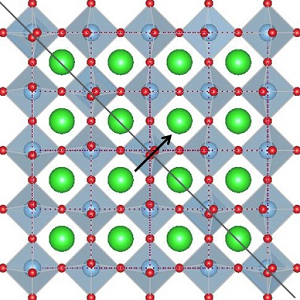
Polarization of domain boundaries in SrTiO3 studied by layer group and order-parameter symmetry
Based on a recently developed combination of layer group analysis with order-parameter symmetry, we study the polarity of antiphase domain boundaries (APBs) and ferroelastic twin boundaries (TBs) in SrTiO3 [Phys. Rev. B 102, 184101 (2020)].
In addition to the celebrated layer group analysis of domain twins, the present method allows us to investigate tensor properties of domain walls also for the case where order-parameter variables other than the spontaneous ones are active [1].
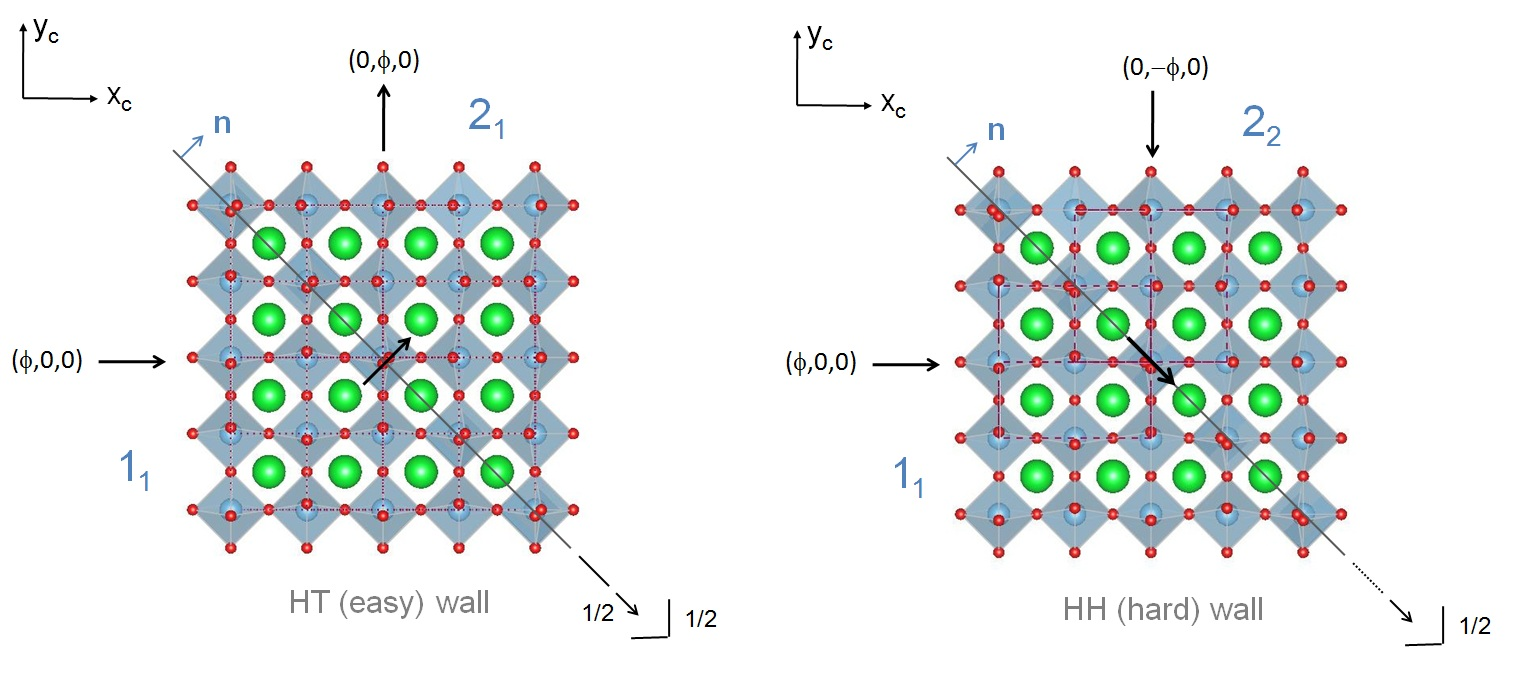
Figure: Representation of two different ferroelastic twins with normal n=[110] at position p=(0,0,0) in tetragonal SrTiO3, together with the symmetry elements of the corresponding layer groups. (a) Pure orientational twin (11|21). The corresponding twin wall is an easy (HT) wall. The twin in (b) is of mixed type, i.e., (11|22), where the corresponding twin wall is a hard (HH) one. The arrows at the centers show polarization predicted by the theory.
[1] W. Schranz, C. Schuster, A. Tröster, and I. Rychetský, Polarization of domain boundaries in SrTiO3 studied by layer group and order-parameter symmetry, Phys. Rev. B 102, 184101 (2020). (show less)
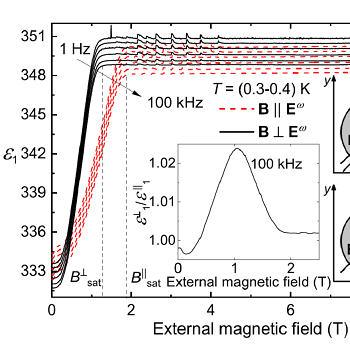
Seemingly anisotropic magnetodielectric effect in isotropic EuTiO3 ceramics
Anisotropic magnetodielectric effect was observed at 0.3 K in the low-frequency dielectric spectra of antiferromagnetic EuTiO3 ceramics [Phys. Rev. B 102, 144402 (2020)].
The effect was theoretically explained by a demagnetizing field and confirmed by magnetization measurements. THz refractive index revealed also a large anisotropy in external magnetic field. This anisotropy is due to activation of the ferromagnetic resonance only if the magnetic field is applied perpendicularly to the magnetic component of the THz radiation.
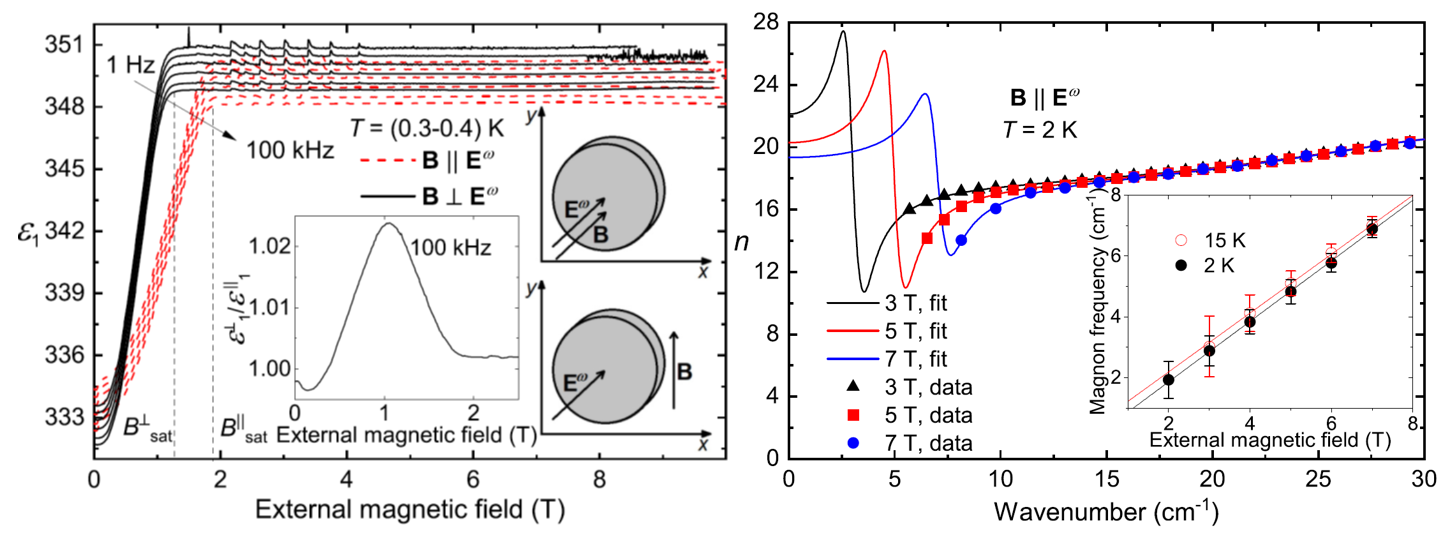
Figure:
Left: Magnetic field dependence of EuTiO3 permittivity measured for electric field applied perpendicularly to the sample plane, and with the static external magnetic field B in either of two orientations marked in the figure. Inset: Dependence of the permittivity ratio for two orientations of the magnetic field.
Rigth: THz refractive index measured at three magnetic fields applied perpendicularly to the electric vector of THz radiation. Inset: Magnetic field dependence of the magnon frequency measured at 2 and 15 K.
[1] D. Repček, C. Kadlec, F. Kadlec, M. Savinov, M. Kachlík, J. Drahokoupil, P. Proschek, J. Prokleška, K. Maca, and S. Kamba, Seemingly anisotropic magnetodielectric effect in isotropic EuTiO3 ceramics, Phys. Rev. B 102, 144402 (2020).
(show less)
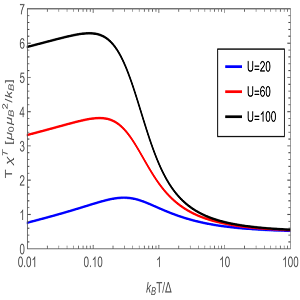
Curie-Weiss susceptibility in strongly correlated electron systems
We succeeded in identifying a microscopic mechanism combining adequately quantum and thermal fluctuations in metals with strong electron correlations that lead to the genesis of local magnetic moments and the Curie-Weiss susceptibility [Phys. Rev. B 102, 205120 (2020)].
The magnetism of solids is macroscopic evidence of microscopic quantum dynamics of spins of valence electrons. Magnetic susceptibility of metals with delocalized conduction electrons should theoretically be of Pauli character. However, the transition metals react on the magnetic field via the Curie-Weiss law due to local magnetic moments. We identified the microscopic mechanism combining adequately quantum and thermal fluctuations in metals with strong electron correlations that lead to the genesis of local magnetic moments and the Curie-Weiss susceptibility [1].
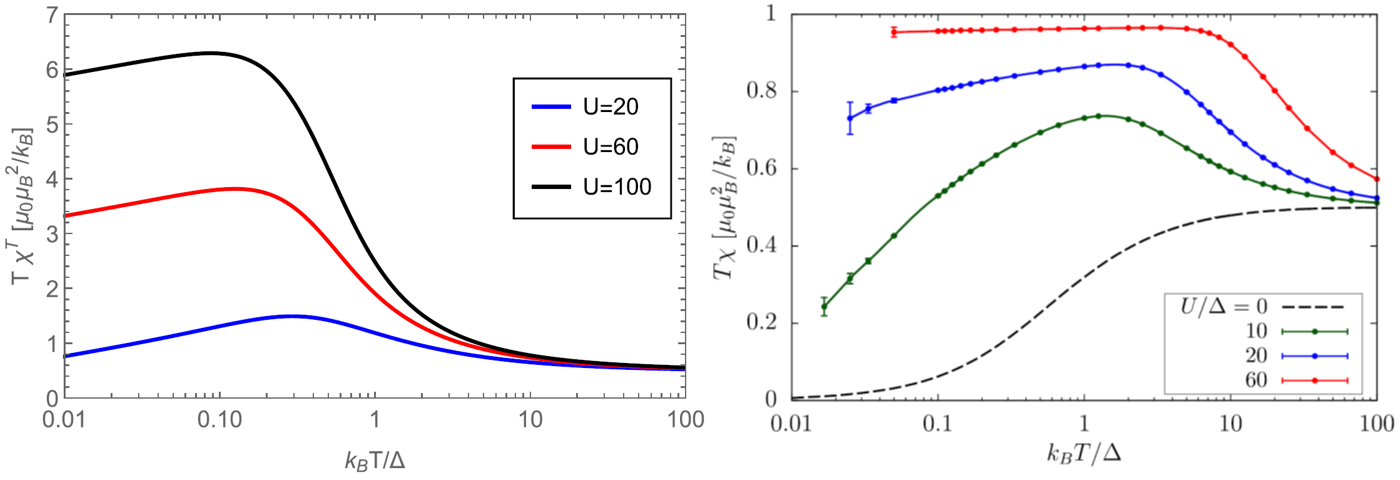
Figure: Temperature dependence of the product of temperature T and magnetic susceptibility χ, the constant value of which reflects the Curie-Weiss law, determined from our analytic theory, left panel, and from Monte-Carlo simulations, right panel, for the single-impurity Anderson model. Here Δ is the width of the band of the conduction electrons, and U is the strength of electron correlations. Both results prove the existence of the Curie-Weiss susceptibility for sufficiently strong electron correlations in a temperature interval above the Kondo temperature below which the susceptibility goes over to the Pauli one, and the plotted curves must fall to zero. The analytic theory predicts qualitatively correctly the universal character of the Curie-Weiss susceptibility but misses the nonuniversal numerical value of the Curie constant.
[1] V. Janiš, A. Klíč, J. Yan, and V. Pokorný, Curie-Weiss susceptibility in strongly correlated electron systems, Phys. Rev. B 102, 205120 (2020). (show less)
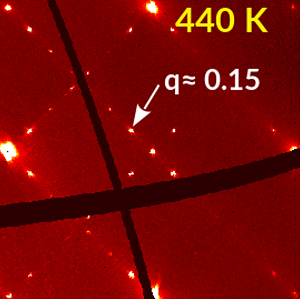
Local properties and phase transitions in Sn doped antiferroelectric PbHfO3 single crystal
Pb(Hf0.77Sn0.23)03 crystals were characterized using x-ray diffraction and 119Sn Mossbauer spectroscopy in a wide temperature range. The nature of two intermediate phases, situated between antiferroelectric ground-state and high temperature paraelectric phase, has been unveiled [J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 32, 435402 (2020)].
The lower-temperature one is characterized by incommensurate modulations while the higher-T intermediate phase is defined by anti-phase rotations of oxygen octahedra. Two kinds of quadrupole splitting indicate that the environment of Sn is locally non-centrosymmetric even in the cubic phase [1].
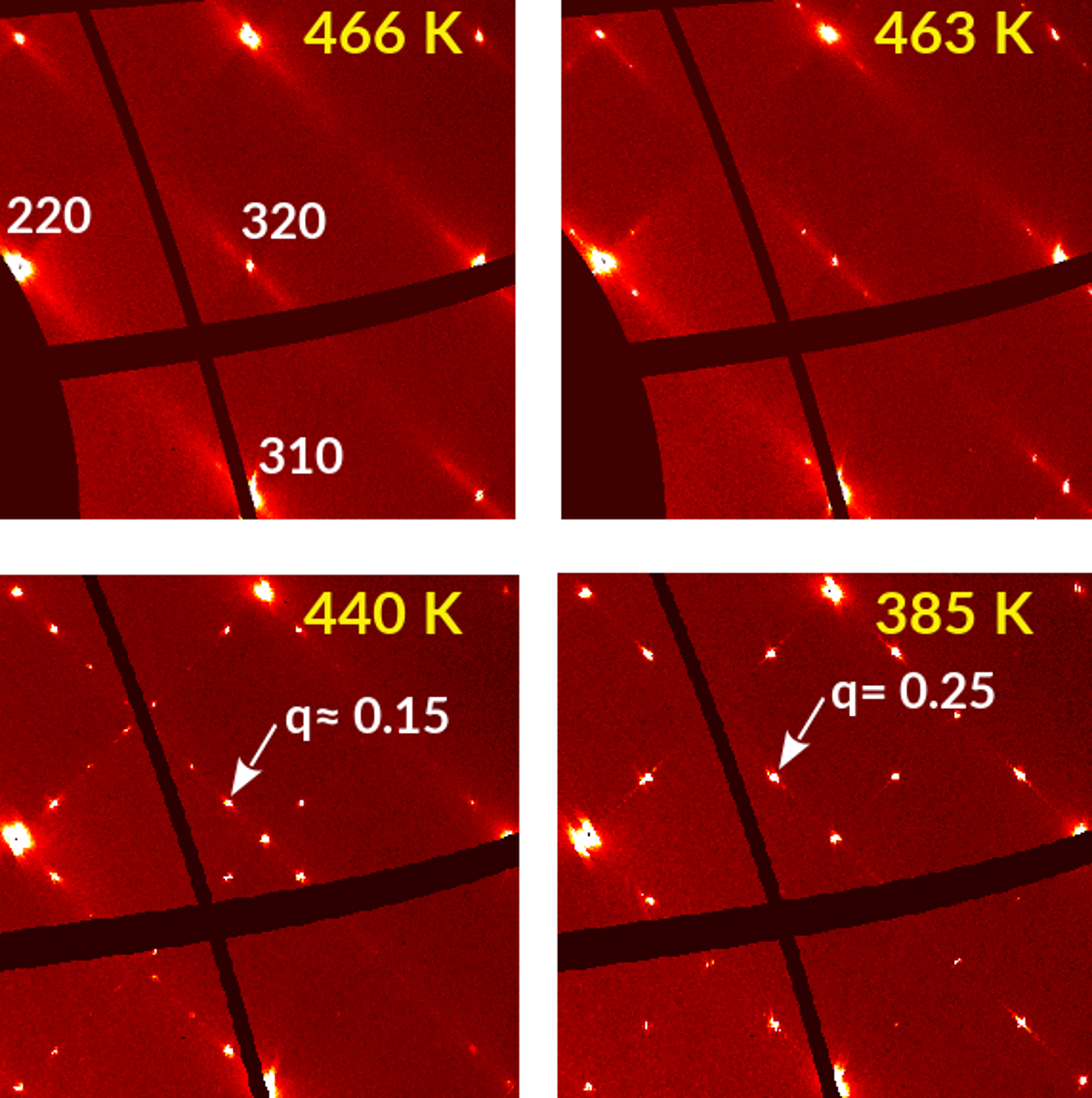
Figure: Diffraction signatures of four phases observed for Pb(Hf0.77Sn0.23)03. Diffuse streaks emerging from Bragg reflections at high temperatures are a signature of disorder (locally correlated displacements of Pb ions). They transform into broad maxima at 463 K, incommensurate peaks at 440 K and finally commensurate Bragg reflections at 385 K in the ground-state phase of this material.
[1] I. Jankowska-Sumara, M. Paściak, M. Kądziołka-Gaweł, M. Podgórna, A. Majchrowski, and K. Roleder, Local properties and phase transitions in Sn doped antiferroelectric PbHfO3 single crystal, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 32, 435402 (2020). (show less)
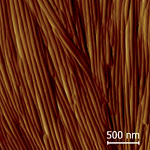
Organic nanotubes created from mesogenic lactic acid derivatives
We found a facile route how to prepare nanotubes from rod-like mesogens dissolved in typical organic solvents. For selected types of chiral rod-like molecules, both enantiomers as well as the racemic mixtures, the nanotubes are formed by slow evaporation from a solution, regardless the solvent, concentration or deposition type. Obtained supramolecular assemblies were studied using various experimental techniques and nanotubes of 50-60 nm diameter described. We proposed rolling-up mechanism related to the surface tension difference at the opposite layer surfaces.
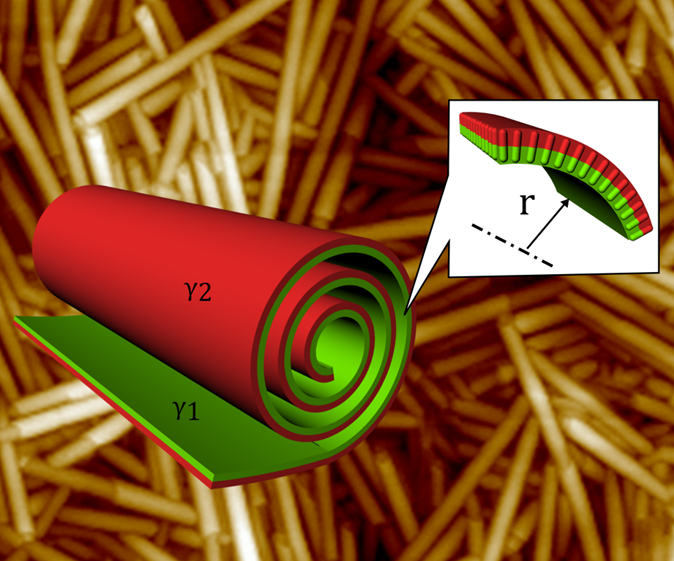
Figure: In the background AFM picture shows nanotubes, the diameter of observed nanotubes is 50-60 nm. A scrolling-up mechanism of crystalline molecular layers was proposed based on difference between the surface tension at the opposite surfaces.
[1] V. Novotná, V. Hamplová, L. Lejček, D. Pociecha, M. Cigl, L. Fekete, M. Glogarová, L. Bednárová, P. Majewski, E. Gorecka. Organic nanotubes created from mesogenic derivatives Nanoscale Adv. 1, 2835(2019).
(show less)
Mesoscopic polarization dynamics and two ferroelectric sublattices
in the uniaxial tetragonal tungsten bronze (Srx Ba1−x)Nb2O6
The high-frequency dielectric behavior of uniaxial tungsten-bronze strontium barium niobate crystals with various Sr/Ba ratios have been studied in order to thoroughly understand the evolution of the relaxation dynamics across the ferroelectric phase transition. We showed that the dielectric response along the polar axis consists of three relaxations corresponding to polarization mechanisms related to several correlation lengths of mesoscopic order and that they are closly associated with two different ferroelectric subsystems.in the structure [1].
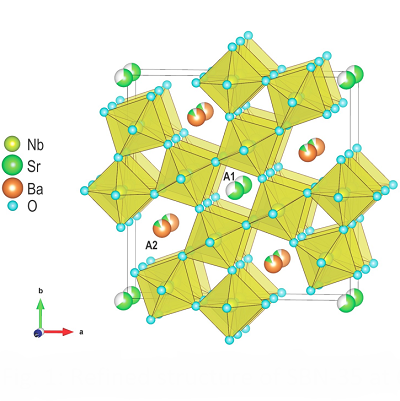
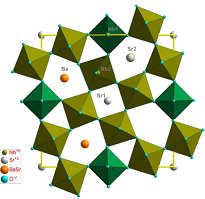
The archetypical uniaxial tungsten-bronze (Sr
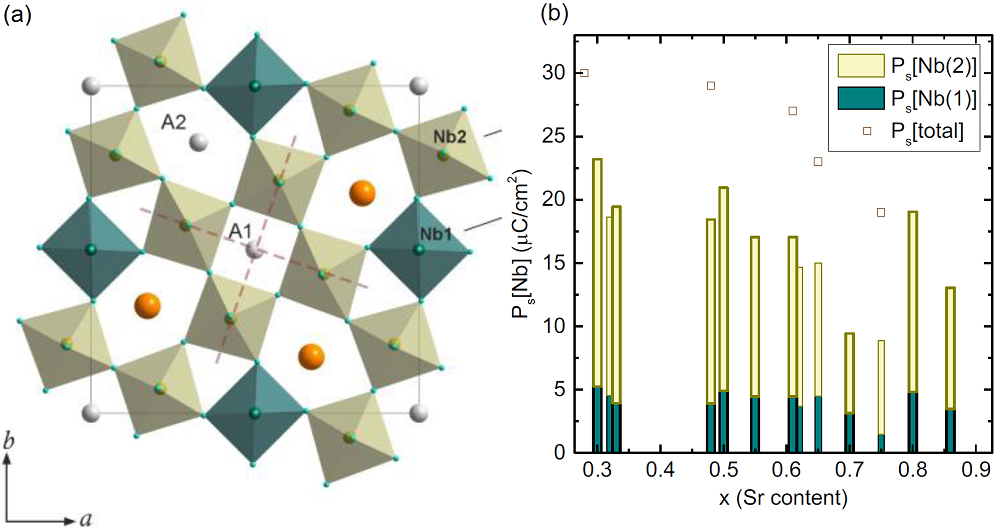
Fig. 1: (a) Structure of SBN in the ab plane [dashed red lines mark the perovskite subunit in lighter-coloured octahedra Nb(2)O6, linking oxygen octahedra Nb(1)O6 are shown in blue colour]. (b) Contribution to the spontaneous polarization of Nb(1) and Nb(2).
The high-frequency dielectric behaviour of SBN (from 104 to 1013 Hz), investigated in a broad temperature interval for compositions from pure ferroelectric (SBN-35) to relaxor (SBN-81) ones, revealed that the dielectric response along the polar axis consists of three relaxations related to polarization mechanisms with various correlation lengths of mesoscopic order [1].. All of them show dissimilar behaviours with temperature, pointing out to their distinct nature [Fig. 2]. A temperature-dependent central mode at THz frequencies and a relaxation above 10 GHz are accompanied by the slowing down of a relaxation in the MHz range. This complex response reveals coexistence of displacive and order-disorder scenarios in this family.
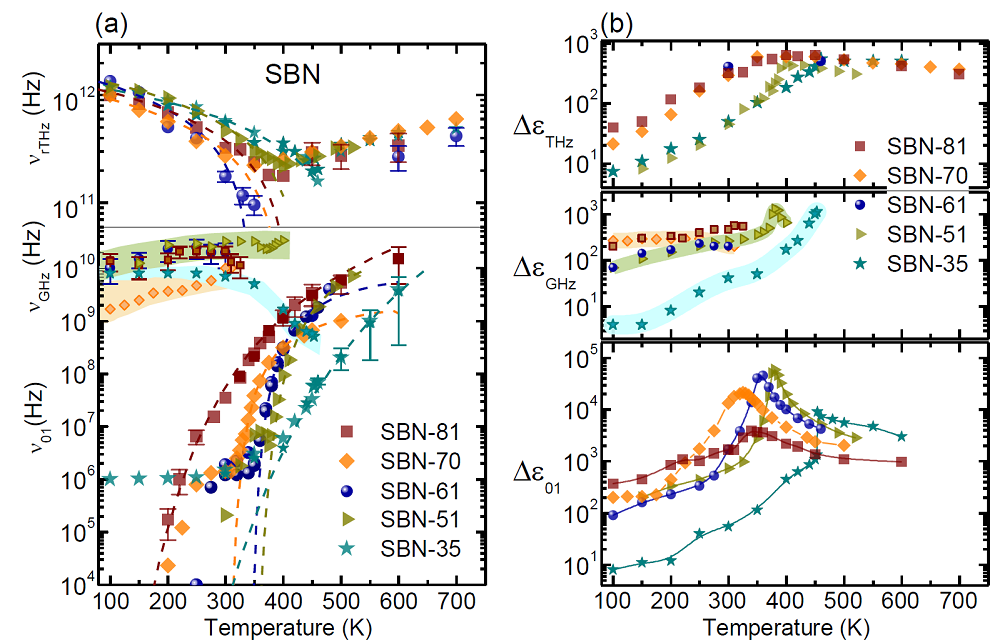
Fig. 2: (a) Temperature dependences of the frequencies of the main excitations found in SBN crystals. (b) Contribution to the permittivity of the main excitations in SBN crystals. The shaded regions refer to extended error regions found for νGHz and ΔεGHz.
[1] E. Buixaderas, M. Kempa, Š. Svirskas, C. Kadlec, V. Bovtun, M. Savinov, M. Paściak, and J. Dec, Dynamics of mesoscopic polarization in the uniaxial tetragonal tungsten bronze (Sr
(show less)
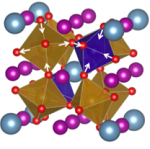
Changes in spin and lattice dynamics induced by magnetic and structural phase transitions in multiferroic SrMn7O12
Upon cooling, SrMn7O12 undergoes a series of structural and magnetic phase transitions from cubic to rhombohedral symmetry, and to an incommensurately modulated crystal structure, which is connected with charge and orbital ordering of the Mn cations. We report IR, THz, and Raman spectra of SrMn7O12 ceramics reflecting corresponding changes in the phonon selection rules, including new phonons appearing in spin-order-induced ferroelectric phases [1].
The observed phonon activities are compared with the predictions from the factor-group analysis. In the high-temperature phase, more phonons are observed than the number predicted for the cubic symmetry. This is explained by the presence of rhombohedral clusters in the cubic phase. The strongest variations occur in the THz spectra near the two magnetic phase transitions, at TN1 = 87 K and TN2 = 63 K. These activate new modes in the spectra, with resonance frequencies and intensities changing with temperature and magnetic field. Below TN2, we observed a transfer of oscillator strengths from low-frequency phonons to these excitations, which we assign to electromagnons.
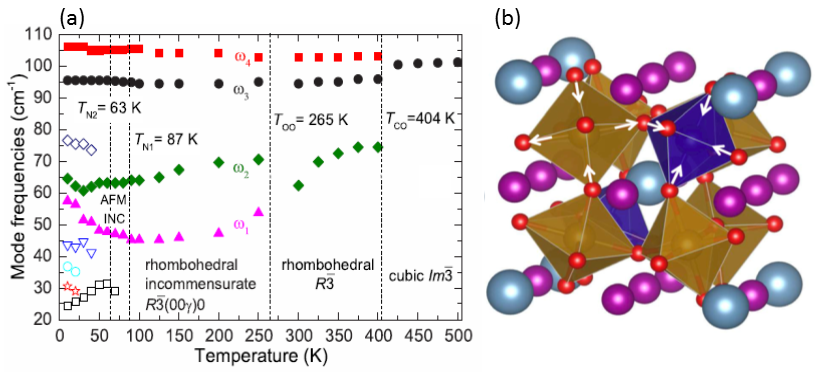
Figure: (a) Temperature dependence of the low-frequency excitations observed in THz and IR spectra of SrMn7O12. The open symbols correspond to spin excitations or phonons activated by breaking of the inversion center, whereas the remaining phonons are marked by solid symbols. (b) Rhombohedral quadruple perovskite crystal structure of SrMn7O12.
[1] S. Kamba, V. Goian, F. Kadlec, D. Nuzhnyy, C. Kadlec, J. Vít, F. Borodavka, I. S. Glazkova, A. A. Belik, Changes in spin and lattice dynamics induced by magnetic and structural phase transitions in multiferroic SrMn7O12, Phys. Rev. B 99, 184108 (2019).
(show less)

Raman scattering yields cubic crystal grain orientation
The anisotropy of Raman scattering was applied to determine the orientation of individual microcrystal grains, as small as a few µm, of GaV4S8 polycrystalline compound. This was possible by measuring polarised Raman spectra as a function of rotation of the sample along the laser direction. On comparing the resulting set of spectra with a computer simulation for particular symmetries, the orientation of the crystal grains could of the determined with good precision.
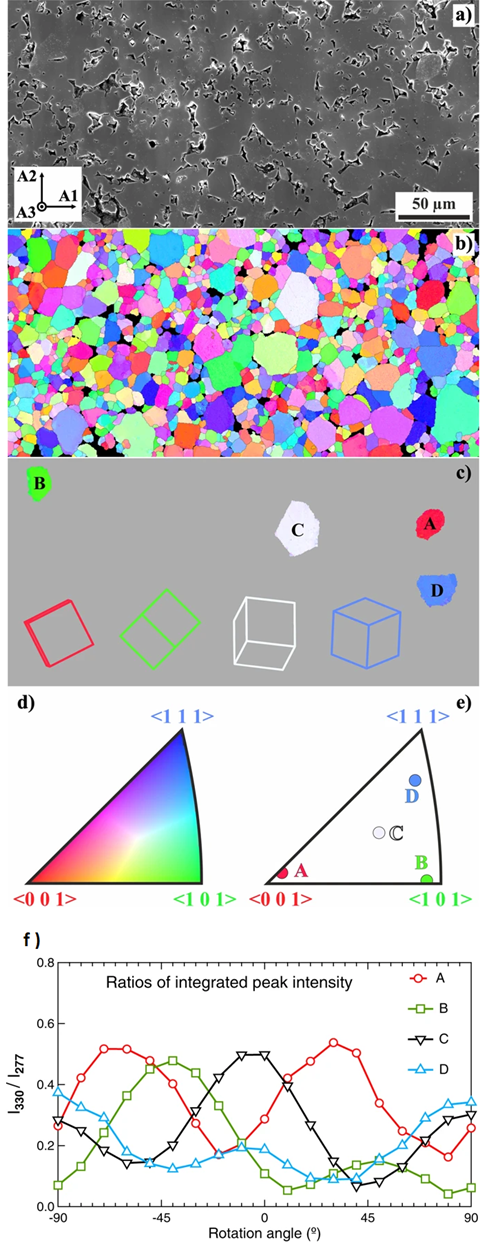
Figure:
Grain morphology of the investigated GaV4S8 ceramics.
(a) Scanning electron microscope image of an area of interest with sample coordinate system as an inset;
(b) Inverse pole figure map from EBSD analysis of the area in (a);
(c) positions of four grains chosen for detailed Raman measurements,
indicated projections of elementary cubic cells clarify their crystallographic orientation;
(d) unit triangle with the colour code of the inverse pole figure map;
(e) surface normals of the chosen grains;
(f) Parallel-polarised Raman scattering intensity ratios detected from the four grains,
which allows determination of their crystallographic orientation independent of the EBSD analysis.
Data shows intensity ratio at selected frequencies as a function of the angle ϕ
between the polariser and the reference direction on the sample surface.
K. Tesar, I. Gregora, P. Beresova, P. Vanek, P. Ondrejkovic, and J. Hlinka, Raman scattering yields cubic crystal grain orientation, Scientific Reports 9, 9385 (2019).
(show less)
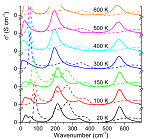
Soft mode driven local ferroelectric transition in lead-based relaxors
Analysis of IR and THz spectra using Bruggeman effective medium approach revealed that the mesoscopic structure of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 and Pb(Mg1/3Ta2/3)O3 consists of dynamic randomly oriented uniaxially anisotropic polar nanoregions with harder transverse optical polar modes in the direction along the local dipoles [1,2].
The lowest-frequency phonon of the E symmetry polarized perpendicular to the local dipole moments undergoes softening towards T* ≈ 400 K, which brings evidence about a local structural phase transition. This softening is also responsible for previously observed high temperature dependence of permittivity, which follows the Curie-Weiss law.
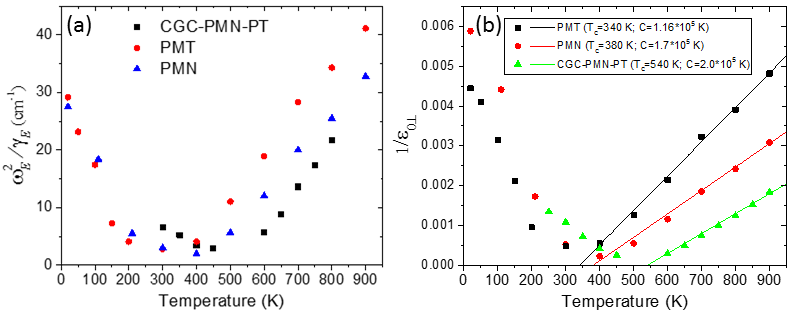
Figure: (a) Temperature dependence of the overdamped E component of the soft mode in PMN, PMT and PMN-PT characterized by frequency of the peak in dielectric loss. (b) Temperature dependence of the reciprocal static permittivity (perpendicular to local polarization in nanodomains) obtained from the fits of IR and THz spectra.
[1] D. Nuzhnyy, J. Petzelt, V. Bovtun, S. Kamba, J. Hlinka, Infrared, terahertz, and microwave spectroscopy of the soft and central modes in Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3, Phys. Rev. B 96, 174113 (2017).
[2] D. Nuzhnyy et al., Soft mode driven local ferroelectric transition in lead-based relaxors, Appl. Phys. Lett. 114, 182901 (2019).
(show less)
Degenerate (identity) chemical reactions in ferroelastic crystals
The work points to reconsideration of degenerate chemical reactions because of the chemical reactions which take place in a solid phase where the orientation of the substituting molecules is maintained. The work points to the examples of a ferroelastic switching which is accompanied by braking and reestablisment of chemical bonds. The article suggests that the definition of the degenerate chemical reactions might distinguish the reactions where the truly identical molecules are formed from those ones where the resulting molecules are enantiomers or enatiomorphs in case of domains.
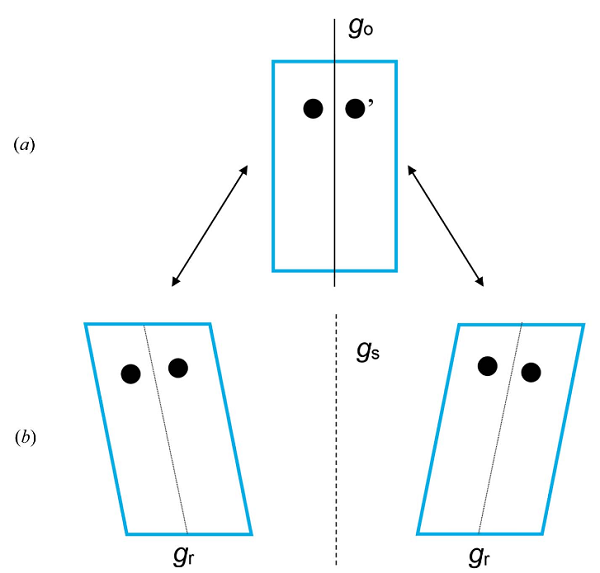
Figure: (a) The prototypic (paraelastic) phase with a pair of equivalent atoms related by the symmetry operation g with the related symmetry element go. (b) The ferroelastic domain pair is related by the suppressed (lost) symmetry element gs. There is a pseudosymmetry element gr within each domain state which is a remnant of the suppressed (lost) symmetry element go.
J. Fábry, Degenerate (identity) chemical reactions in ferroelastic crystals, Acta Cryst. B75, 287(2019).
(show less)
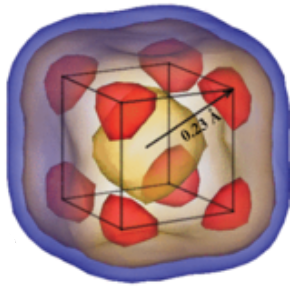
Spatio-temporal distribution of relative Ti-O6 displacements in cubic BaTiO3
BaTiO3 is often considered a model ferroelectric material in which the dielectric properties are defined by the displacements of Ti ions with respect to surrounding oxygen atoms. However, despite the decades of a dedicated research, certain controversies have remained as to the description of collective movements of the Ti ions. We approached this problem using nonoscale-oriented X-ray scattering methods and large-scale atomistic simulations [1]. Together these allowed us to show that the Ti dynamics can be exhaustively explained by phonons excited on a timescale of picoseconds.
The three-dimensional distribution of the x-ray diffuse scattering intensity of BaTiO3 has been recorded in a synchrotron experiment and simultaneously computed using molecular dynamics simulations of a shell model. Together, these have allowed the details of the disorder in paraelectric BaTiO3 to be clarified. The narrow sheets of diffuse scattering, related to the famous anisotropic longitudinal correlations of Ti ions, are shown to be caused by the overdamped anharmonic soft phonon branch. This finding demonstrates that the occurrence of narrow sheets of diffuse scattering agrees with a displacive picture of the cubic phase of this textbook ferroelectric material. The presented methodology allows one to go beyond the harmonic approximation in the analysis of phonons and phonon-related scattering.
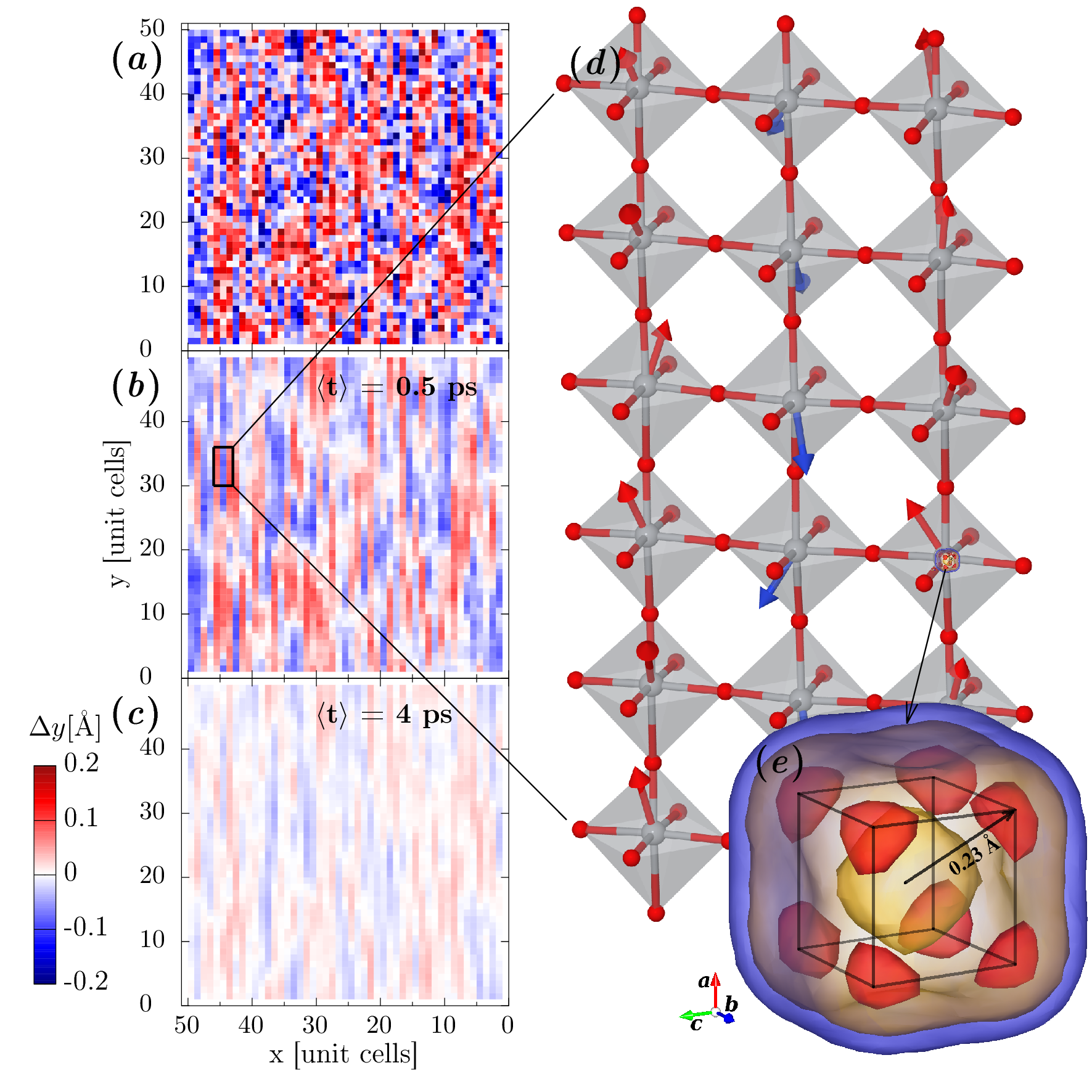
Fig. 1: One component of the relative Ti-O6 displacement is mapped within one layer of the material using different time averages (a-c) which clearly shows that chain correlations exist on a timescale of picoseconds. The displacements averaged over the simulation time and all unit cells of the crystal have a cuboidal distribution with shallow minima along diagonal directions.
[1] M. Paściak, T. R. Welberry, J. Kulda, S. Leoni, and J. Hlinka, Dynamic Displacement Disorder of Cubic BaTiO3, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 167601 (2018).
(show less)
Electromagnon in the Y-type hexaferrite BaSrCoZnFe11AlO22
We investigated static and dynamic magnetoelectric properties of single crystalline BaSrCoZnFe11AlO22 which is a room-temperature multiferroic with Y-type hexaferrite crystal structure. THz and Raman spectra reveal an electrically active spin wave (electromagnon) below 300 K at ≈1.2 THz. We show that the electromagnon is activated due to the magnetostriction mechanism involving spin vibrations along the hexagonal axis.
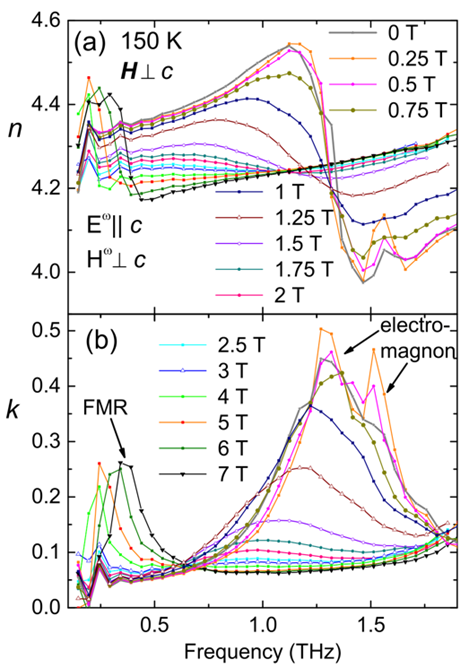
Figure: Electromagnon in THz spectra of BaSrCoZnFe11AlO22.
[1] J. Vít, F. Kadlec, C. Kadlec, F. Borodavka, Y.S. Chai, K. Zhai, Y. Sun and S. Kamba, Electromagnon in the Y-type hexaferrite BaSrCoZnFe11AlO22, Phys. Rev. B 97, 134406 (2018).
(show less)
Wide Range Dielectric and Infrared Spectroscopy of (Nb+In) co-doped rutile ceramics
The dielectric response of ceramics of co-doped rutile Ti1-x(Nb0.5In0.5)xO2 has been measured via a combination of impedance, high-frequency coaxial, THz transmission, and IR reflectivity spectroscopies spanning 15 decades of frequency between 0.1 Hz and 240 THz [1]. It is argued that the colossal dielectric permittivity reported by other authors can be explained by a combination of thin low-conducting grain boundaries and low-conducting depletion near-electrode layers which give rise to thermally activated dielectric relaxations in higher radiofrequency and low-frequency ranges, respectively.
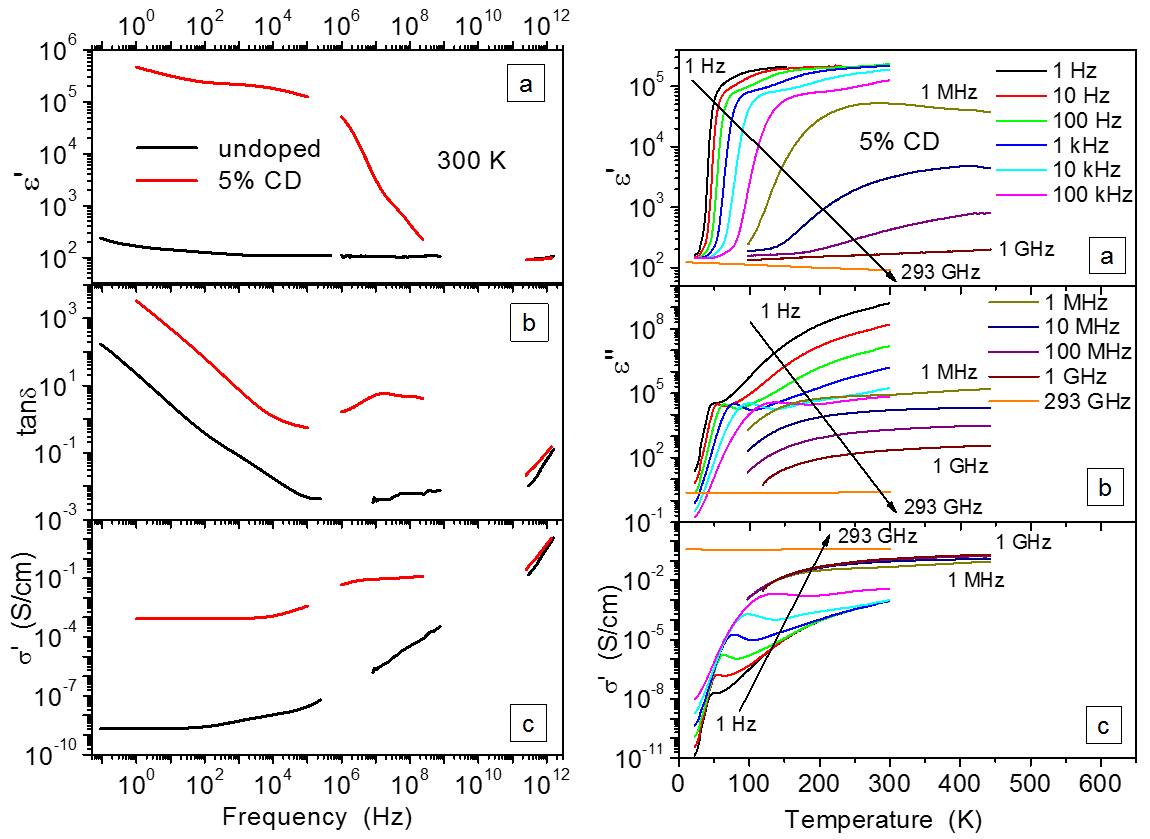
Figure: Left: Broadband spectra of the undoped and 5% co-doped rutile ceramics at 300 K. Right: Temperature dependences of the 5% (Nb+In) co-doped rutile ceramics at selected frequencies: (a) dielectric permittivity, (b) dielectric loss, (c) ac conductivity. Symbols denote the experimental data, lines correspond to the fits.
[1] V. Bovtun, J. Petzelt, M. Kempa, D. Nuzhnyy, M. Savinov, S. Kamba. S. M. M. Yee, D. A. Crandles, Wide range dielectric and infrared spectroscopy of (Nb+In) co-doped rutile ceramics, Phys. Rev. Mat. 2, 075002 (2018).
(show less)
Physics and applications of charged domain walls
One of the “inner” properties of ferroic walls is their ability to carry some bound charge, which is apt to be screened with free carries. Walls carrying bound charge are termed charged domain walls (CDWs). Remarkably, the screening takes place even in the case where the adjacent domains are insulating. Keeping in mind that the walls are often easily movable, CDWs can be viewed as ultrathin movable conductive sheets embedded into an insulating material.
The pursuit of nano-electronic applications motivated CDW studies in the 21st century.
CDWs have been documented in many ferroelectrics, including perovskite and
non-perovskite oxide materials, polymer compositions, and improper ferroelectrics.
A conductivity wall/domain contrast up to 13 orders of magnitude has been recently reported.
A number of methods enabling CDW engineering have been developed, and
first device prototypes exploiting CDWs appeared.
In the present work, we are aiming at a synoptic presentation
of the main concepts behind the understanding of CDWs,
combined with a brief and updated review of important findings in the field
[1].
Fig. 1: Schematic of a 180-degree non-ferroelastic charged domain wall. Arrows show directions of spontaneous polarization.
[1] P. S. Bednyakov, B. I. Sturman, T. Sluka, A. K. Tagantsev, and P. V. Yudin, Physics and applications of charged domain walls, npj Computational Materials 4, 65 (2018).
(show less)
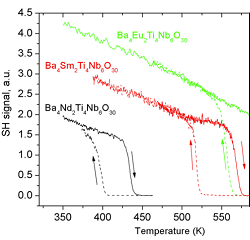
Electric-field-induced transition from incommensurately to commensurately modulated phase
Antiferroelectric-like polarization hysteresis loops in Ba4Sm2Ti4Nb6O30 and Ba4Eu2Ti4Nb6O30 were explained by electric-field induced structural phase transition from nonpolar incommensurately modulated structure to polar and commensurately modulated phase [1]. This discovery opens new perspective direction of investigation of lead-free materials for possible electric energy storage.
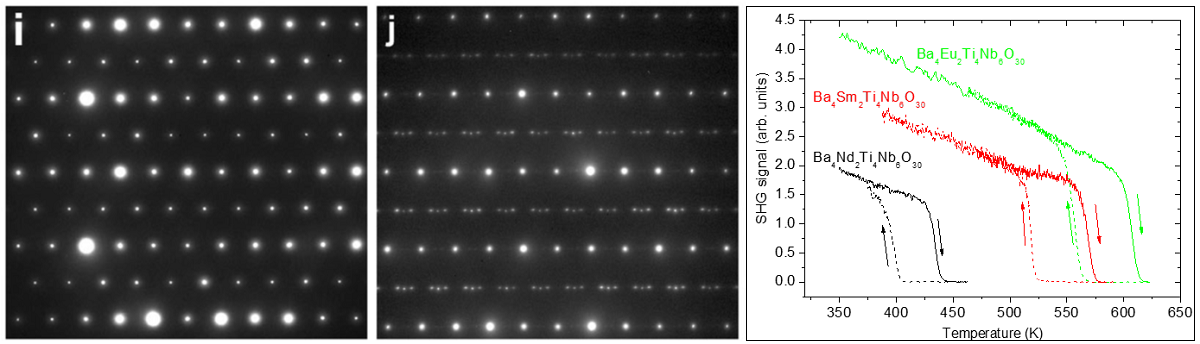
Fig. 1: Left – electron diffraction patterns in commensurately and incommensurately modulated phases in Ba4Sm2Ti4Nb6O30. Right – temperature dependence of second harmonic generation signal showing temperature hysteresis near ferroelectric phase transitions in investigated materials.
[1] Kun Li, Xiao Li Zhu, Xiao Qing Liu, Xiao Ma, Mao Sen Fu, Jan Kroupa, Stanislav Kamba, and Xiang Ming Chen, Electric-field induced phase transition and pinched P-E hysteresis loops in Pb-free ferroelectrics with tungsten bronze structure, NPG Asia Mat. 10, 71 (2018).
(show less)
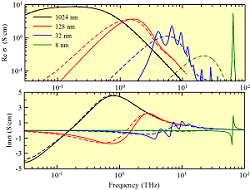
Quantum theory of terahertz conductivity of semiconductor nanostructures
In collaboration with T. Ostatnický of Charles University we participated to the development of the first theory of the quantum conductivity describing the transport in the terahertz spectral range, which does not contain internal contradictions. We have shown that the broken translation symmetry of the nanostructures induces a broadband drift-diffusion current which must be explicitly taken into account.
Usually, all the relevant charge carrier scattering processes
in the studied system are not known since their independent experimental determination is difficult.
The usual approach based on the Kubo formula introduces a phenomenological charge scattering rate
(or relaxation time) accounting for all the scattering processes.
This approximation is highly pertinent in the optical range.
However, the approach fails at low frequencies in nanocrystals in the regime
where the scattering rate is comparable to the probing frequency;
e.g., it always yields nonzero conductivity at zero frequency (dc regime)
even if the nanocrystals are mutually perfectly isolated.
We have shown
[1]
that the broken translation symmetry of the nanostructures induces
a broadband drift-diffusion current, which is not taken into account in the analysis
based on Kubo formula in the relaxation time approximation.
The proper introduction of this current removes all the contradictions,
fulfills the classical limit in the case of large nanocrystals and it is
at the origin of significant reshaping of the conductivity spectra up to terahertz or
multiterahertz spectral ranges. It is used for the interpretation of
temperature dependent photoconductivity spectra in various nanocrystal systems.
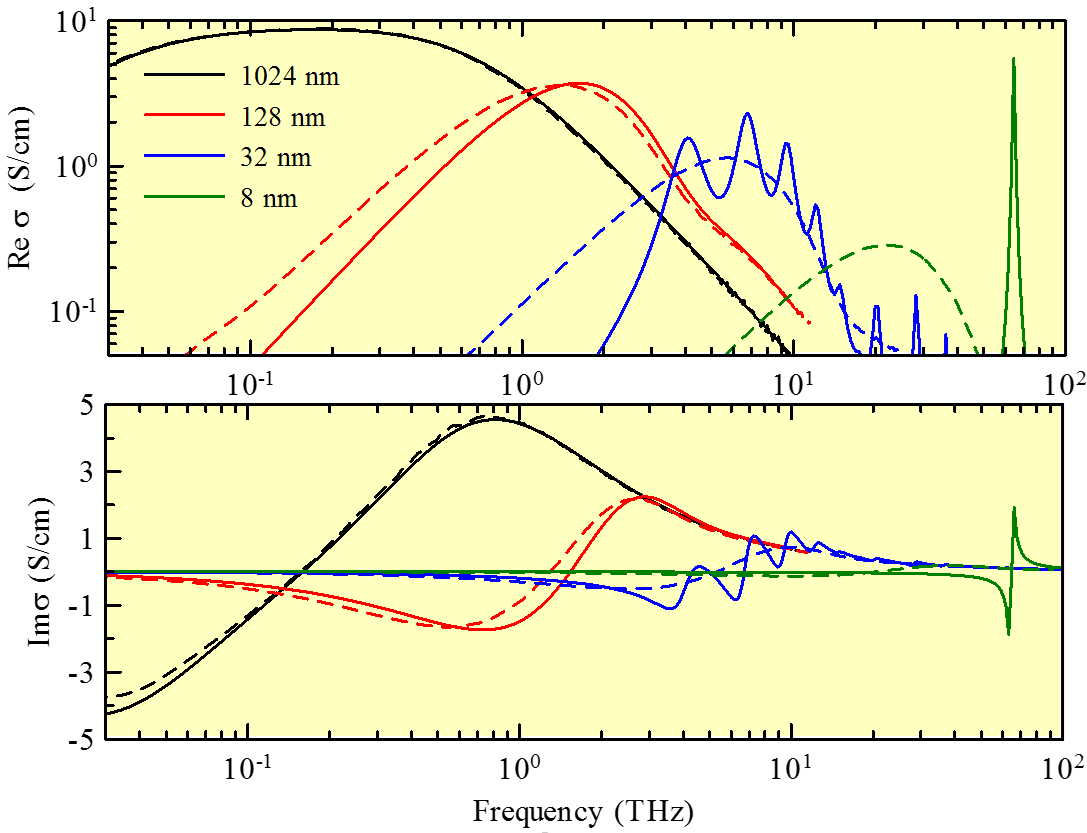
Fig. 1: Comparison of quantum (solid line) and classical (dashed line) conductivity in GaAs cube-shaped nanocrystals of selected sizes at 300 K and free carrier concentration of 1016 cm-3. Note the excellent agreement of quantum calculations with the classical ones for large nanocrystals (1024 nm).
[1] T. Ostatnický, V. Pushkarev, H. Němec, and P. Kužel, Quantum theory of terahertz conductivity of semiconductor nanostructures, Phys. Rev. B 97, 085426 (2018).
(show less)

Přibramite, a new Se-containing mineral from the Czech Republic, characterized by Raman spectroscopy
Minerals containing selenium are interesting and worthy to study due to its inherent photovoltaic effect. The characterization and understanding of these natural minerals is important to be able to make synthetic analogues.
In the paper by Sejkora et al [1] several members of the CuSbS2-CuSbSe2 join were studied by micro–Raman spectroscopy:
- příbramite CuSbSe2, which got its name from its bith place, Příbram (Czech Republic)
- chalcostibite CuSbS2 from Dúbrava (Slovak Republic)
- Se-rich chalcostibite
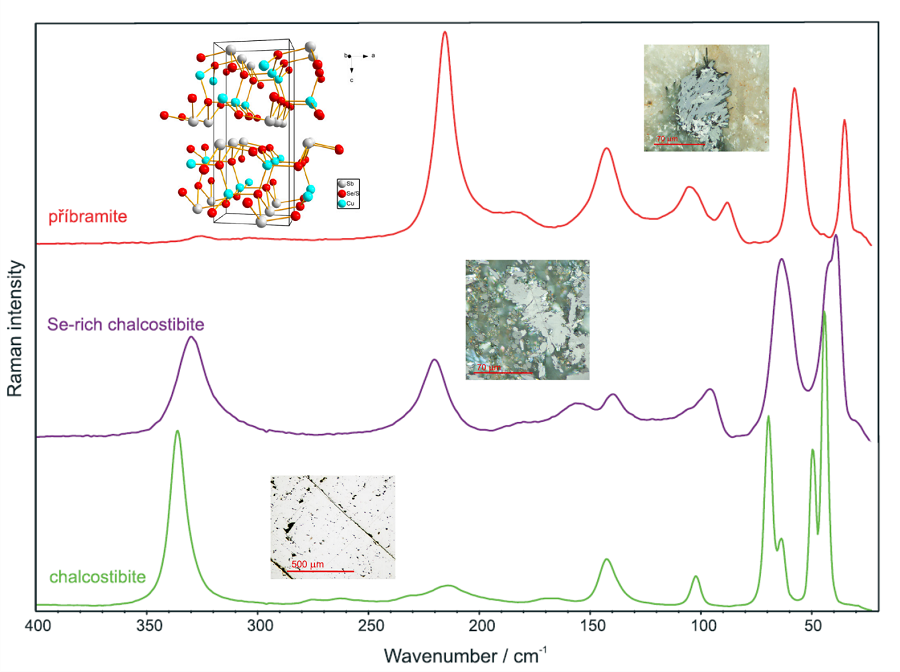
Figure: Raman spectra of the three mineral members along the CuSbS2-CuSbSe2 join, together with their micrographs and the depicted structure for příbramite.
[1] Jiří Sejkora, Elena Buixaderas, Pavel Škácha, Jakub Plášil, Micro-Raman spectroscopy of natural members along CuSbS2-CuSbSe2 join , J. Raman Spectroscopy 49, 1364 (2018).
(show less)
Unusual behaviour under the applied electric field for new cholesteric liquid crystals with extremely short pitch
Unusual behaviour of new cholesteric liquid crystals has been observed under applied electric field. Positive dielectric anisotropy causes reorientation of the long molecular axis along the applied electric field direction. Due to extremely short pitch length a stripe texture has been observed under applied electric field. A model based on disclinations has been proposed and anchoring energy evaluated.
New lactic acid derivatives have been prepared and studied. We have found that they form cholesteric phase with the helix pitch length in interval 120 – 200 nm within a broad temperature range. Due to the positive dielectric anisotropy and the short pitch, the applied electric field causes reversible optical changes in planar cell, due to reorientation the long molecular axis in the applied electric field and electro-optical effect was observed under polarizing microscope. Presence of short pitch and possibility to effectively affect the optical properties is promising from the point of view of specific applications. A model based on disclinationswas developed to explain the stripe texture under a sufficiently high electric field. The model also allows us to estimate the surface anchoring energy.
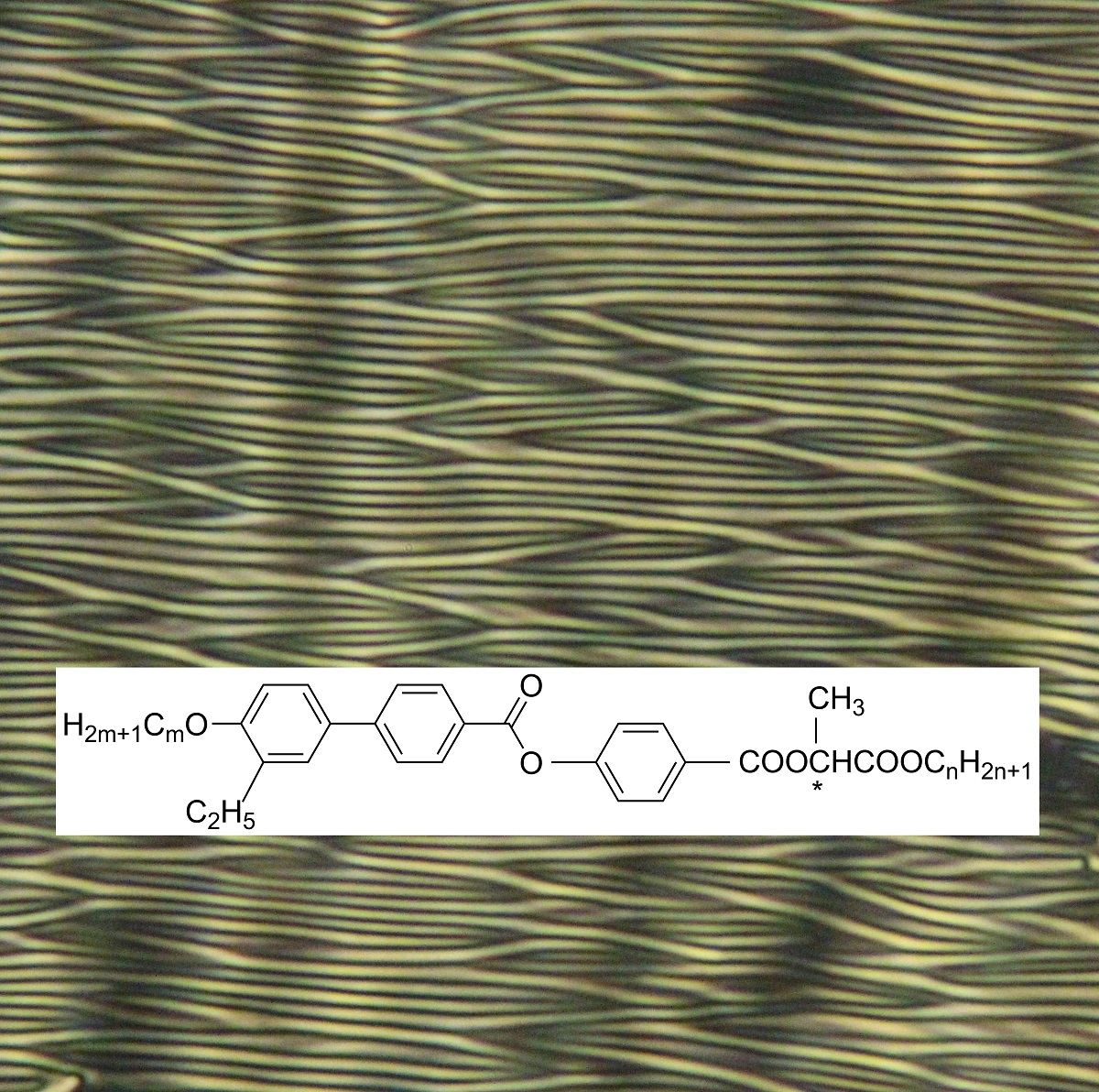
Fig. 1: Texture of the cholesteric liquid crystal in applied electric field. In the inset the chemical formula of the studied compounds is present.
[1] V. Novotná, V. Hamplová, M. Glogarová, L. Lejček, E. Gorecka, Effect of the applied electric field on new cholesterics with extremely short pitch, Liq. Cryst. 45, 634 (2018),
[2] L. Lejček, V. Novotná, M. Glogarová, A model of field induced stripe texture in the cholesterics with extremely short pitch, Liq. Cryst. 46 (2019), DOI 10.1080/02678292.1550689.
(show less)
The ferroelectric phase transition of the tetragonal tungsten-bronze SBN-35 unveiled
The structural ferroelectric-paraelectric transition has been definitely observed by electron diffraction tomography in the tetragonal tungsten-bronze (TTB) Sr0.35Ba0.61Nb2O6.04 (SBN-35) from the paraelectric group P4/mbm to the ferroelectric Pmbm. At 625 K, the refined structure shows that the average structure of SBN-35 is tetragonal with an almost negligible orthorhombic distortion [Fig.1].
The combination of structural and broad-band dielectric studies in SBN-35 suggests that ferroelectricity in TTBs in caused by a more complex mechanism than in perovskites. Several excitations were identified related to the multiple mechanisms responsible for the ferroelectric phase transition [Fig.2]:
- Phonons, related to cation displacements along the polar axis,
- An anharmonic excitation located in the THz range (the CM νTHz), caused by the dynamic disorder of Sr and Ba atoms located at the A2 sites in the pentagonal channels, as supported by the high anisotropic displacements found in the electron diffraction experiment.
- A relaxation in the GHz range, ν01, which slows down to several MHz on cooling and related probably to Nb atoms dynamics.
- A relaxation which appears in the spectra below TC near 1 GHz and hardens on cooling, consistent with the oscillations of the ferroelectric domain walls.
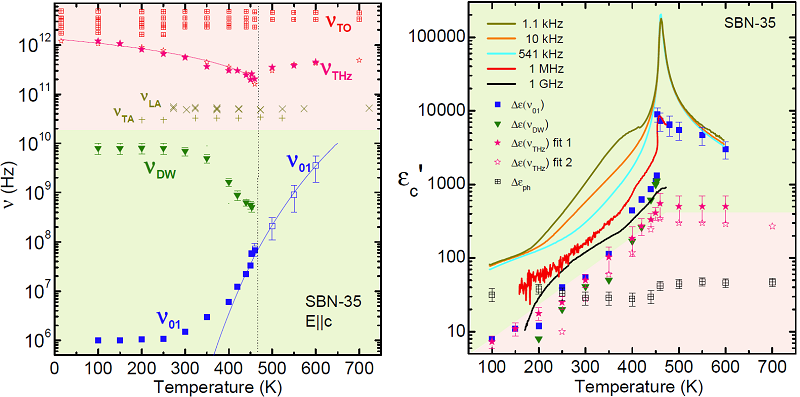
Fig. 2: Temperature dependences of the frequencies of the different excitations found in SBN-35 and their dielectric contributions.
[1] E. Buixaderas, M. Kempa, V. Bovtun, C. Kadlec, M. Savinov, F. Borodavka, P. Vaněk, G. Steciuk, L. Palatinus, and J. Dec, Multiple polarization mechanisms across the ferroelectric phase transition of the tetragonal tungsten-bronze Sr0.35Ba0.61Nb2O6.04 , Phys. Rev. Materials 2, 124402 (2018).
(show less)
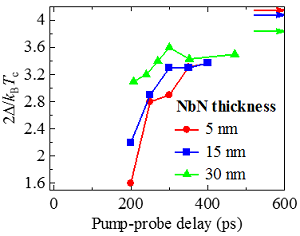
Departure from BCS response in photo-excited superconducting NbN films observed by terahertz spectroscopy
Ultrashort laser pulses can be used to induce transient exotic states of matter and cause phenomena of a vital interest such as room temperature superconductivity. We have focused on the photo-induced dynamics in niobium nitride (NbN) thin films [1] under strong excitation.
NbN is a prototypical BCS superconductor in the ground state. In the strong excitation regime the pump pulse immediately breaks all the Cooper pairs into separate quasiparticles. Subsequently, as the heat is dissipated out of the films towards the substrate, Cooper pairs start to recover. Using time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy, we characterized a series of NbN films with various thicknesses under such strong photoexcitation. Analysis of the photoconductivity spectra reveals that the recovery of Cooper pairs initially proceeds through the emergence of mutually isolated superconducting islands, which subsequently grow with increasing time towards a nearly percolated superconducting network. The superconductivity restoring is faster than the recovery of the superconducting gap to its equilibrium value. Most interestingly, experiments suggest that the profile of the density of states of strongly photoexcited films differs during the recovery process from the ones obtained for the thermal equilibrium at any temperature. This phenomenon is controlled by confinement effects within the films.
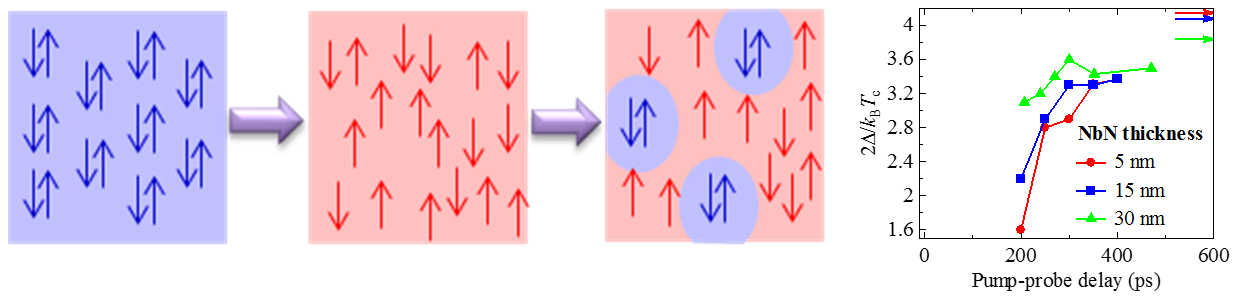
Fig. 1: Left panel: Photo-induced dynamics of quasiparticles (red) and Cooper pairs (blue). Right panel: Evolution of the superconducting gap 2Δ with time after photoexcitation. The arrows in indicate the gap widths in equilibrium.
[1] M. Šindler, C. Kadlec, P. Kužel, K. Ilin, M. Siegel, and H. Němec, Departure from BCS response in photoexcited superconducting NbN films observed by terahertz spectroscopy, Phys. Rev. B 97, 054507 (2018).
(show less)
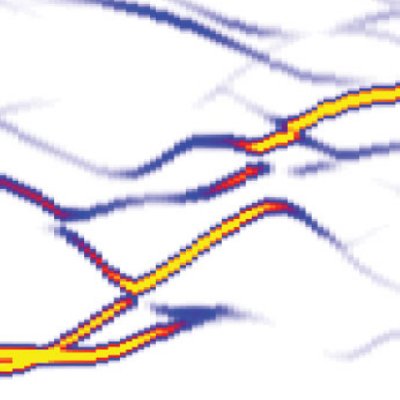
Domain wall contribution to lattice dynamics and permittivity of BiFeO3
Ferroelectric materials are known for their exceptionally high dielectric permittivity. It turns out, that important part of it originates from a material's complicated microstructure and in particular from interfaces between ferroelectric domains.
In this study we investigate different types of interfaces in a multiferroic BiFeO3. By means of atomistic modelling we show that some configurations of interfaces can greatly enhance the permittivity by hosting terahertz-range collective polar fluctuations. The key result is that the permittivity is modified in the THz range. This fundamental finding and its understanding can be used in a design of new materials [ J. Hlinka, M. Pasciak, S. Körbel, and P. Márton, Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 057604 (2017) ].
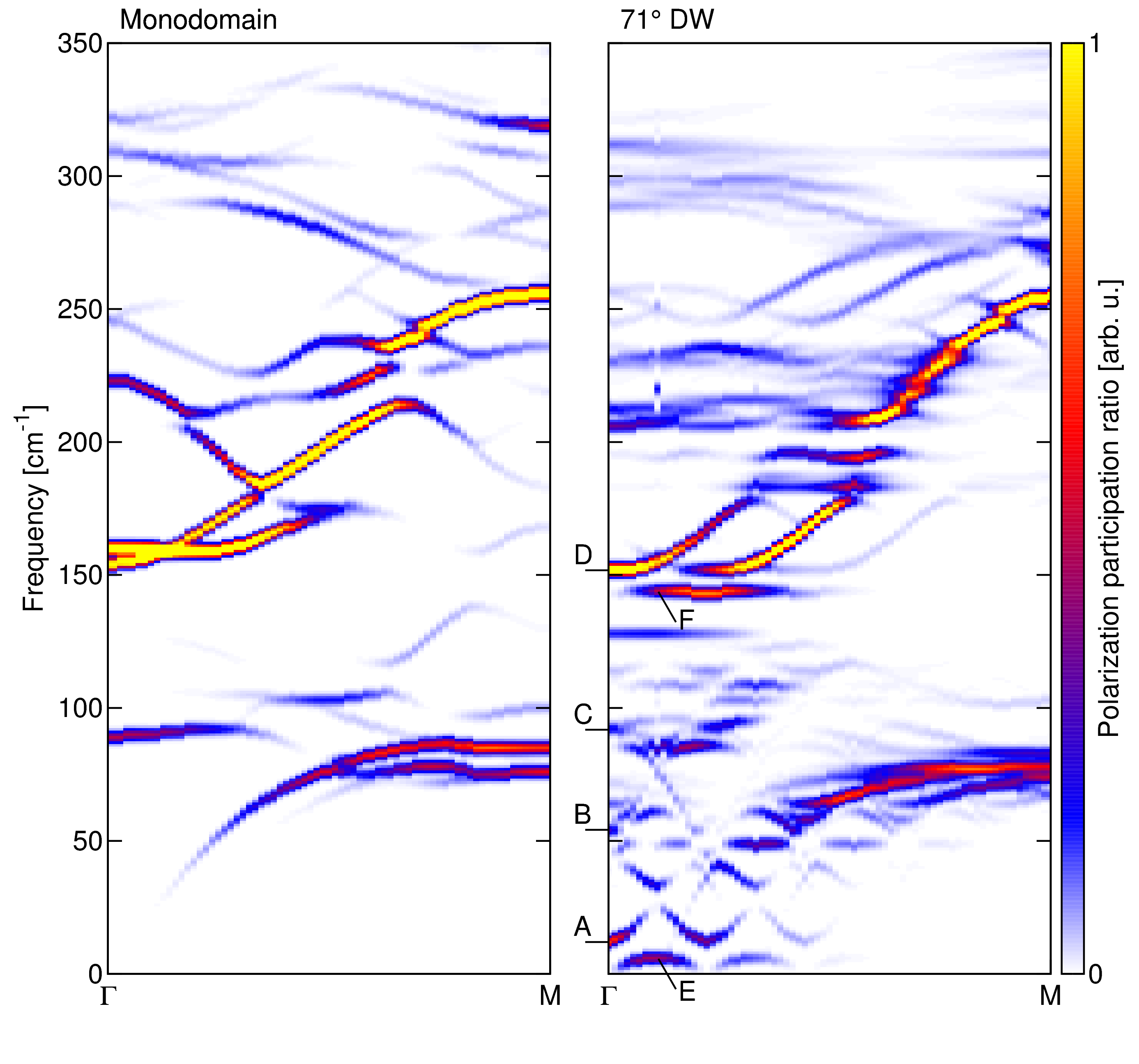
Figure: Change of the phonon spectrum due to presence of dense domain-interface structure (right panel) in comparison with the single-domain case (left panel). Change of the (polar-active) phonon spectrum due to presence of dense domain-interface structure of BiFeO3 (right panel) in comparison with the single-domain case (left panel). Additional low-frequency Γ-point mode (labelled A) is responsible for 25x enhancement of permittivity in the domain engineered material.
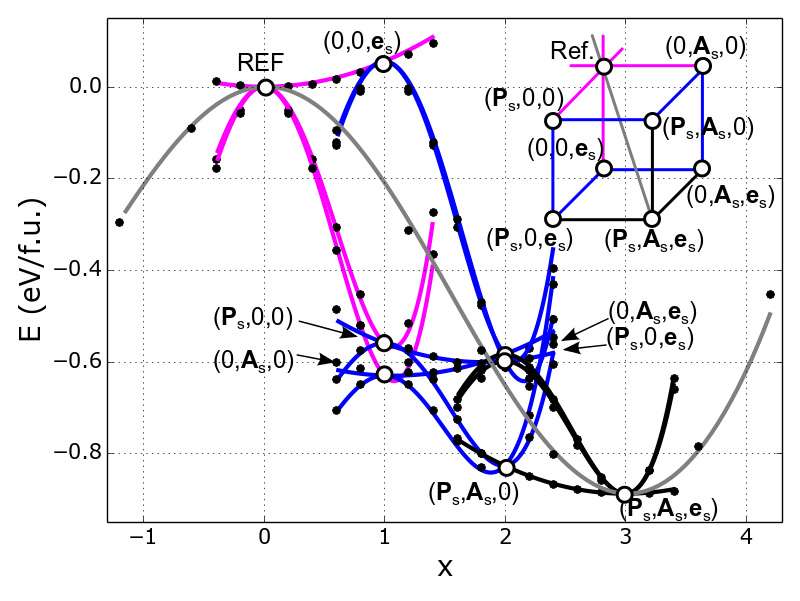
First-principles-based Landau-Devonshire potential for BiFeO3
We describe a first-principles-based computational strategy for determination of the Landau-Devonshire potential.
It exploits the configuration space attached to the eigenvectors of the modes frozen in the ground state. This allows to probe the energy surface in the vicinity of the ground state, which is most relevant for the properties of the ordered phase. We apply this procedure to BiFeO3 in order to determine potential energy associated with strain, polarization, and oxygen octahedra tilt. [ P. Marton, A. Klíč, M. Paściak, and J. Hlinka, Phys. Rev. B 96, 174110 (2017) ].
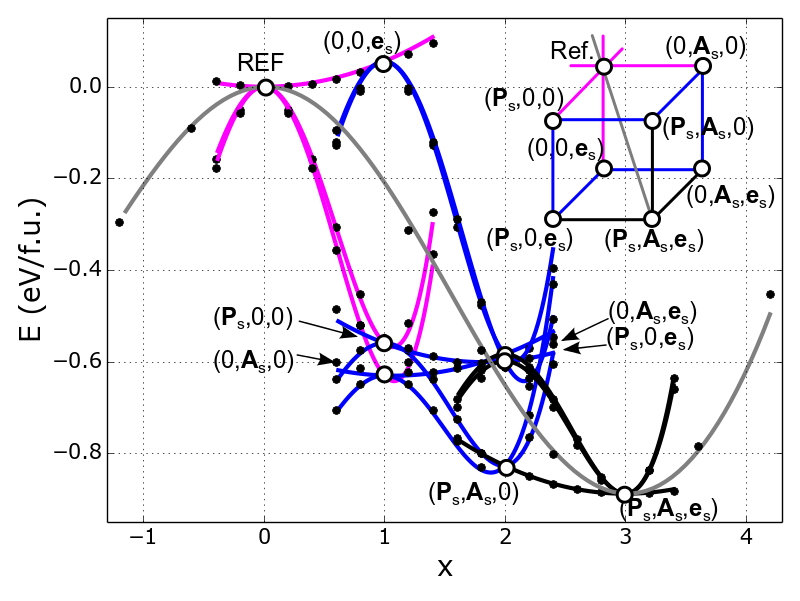
Figure: Energy profiles along selected paths in order parameter space of BiFeO3, connecting the cubic reference state (REF) and the ground state (Ps , As , es). Point symbols are outcomes of the first-principles calculations, lines are evaluated from the present Landau-Devonshire potential.
Fast polarization mechanisms in uniaxial tungsten-bronze SBN-81
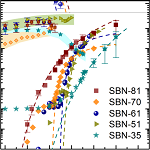
The high-frequency dielectric response of the uniaxial strontium barium niobate (SrxBa1−xNb2O6) crystals with 81% of Sr (x = 0.81) was studied from 1 kHz to 30 THz along the polar axis in a wide temperature interval [E. Buixaderas et al, Sci. Rep. 7, 18034 (2017)]. Relaxor properties were observed in the complex dielectric response and four main excitations were ascertained below the phonon frequencies. These fast polarization mechanisms take place at THz, GHz and MHz ranges and show different temperature evolution.
A central mode excitation in the THz range, due to anharmonic dynamics of cations, shows critical behaviour
towards T~400 K. At lower frequencies, around 10 GHz, another excitation (νDW) appears below Tm~330K,
which is related to the development of ferroelectric microdomains.
In addition, several relaxations below the phonon frequencies, play an essential role in the dielectric
response of the crystal. The main contribution to the permittivity comes from a strong relaxation (ν01) present
in the GHz range at high temperatures which slows down on cooling following the Arrhenius law.
A second relaxation with lower frequency (ν02) slows down, as well, contributing to
the permittivity mainly near Tm.
Both these relaxations can be assigned to polar fluctuations, probably flipping and breathing of polar nanodomains.
Altogether, the four mechanisms explain, above the kHz range, the ferroelectric transition in SBN-81 as well as
its relaxor character, which differs from the behaviour displayed by SBN-61 and lead-based relaxors.
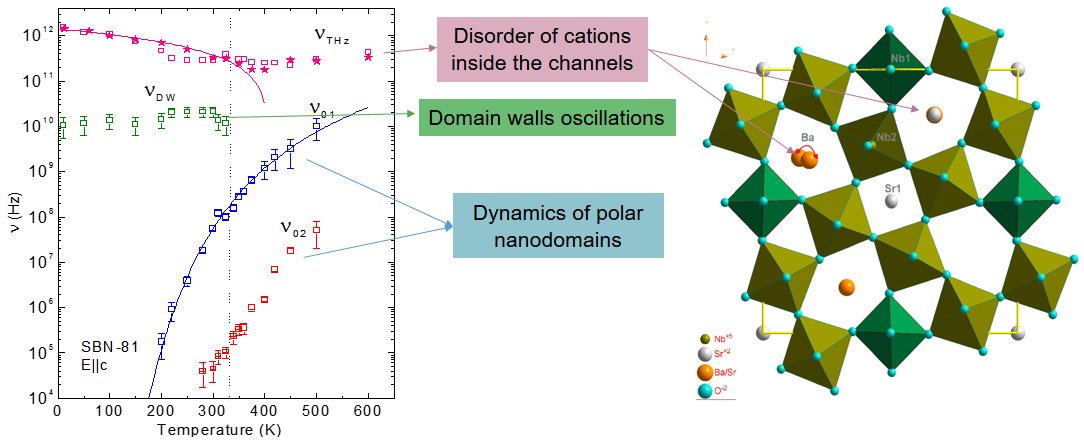
Figure: Temperature dependences of the frequencies of main excitations in the tetragonal tungsten-bronze structure SBN-81, related to the microstructure of the crystal.
New type of dimers composed of bent-core molecules connected through their central cores
Structurally new type of dimers composed of bent-core molecules connected through their central cores has been prepared and studied. The switching behaviour in the applied electric field is reported.
We have synthesized and characterized mesomorphic behaviour of a new type of bent-core dimers in which bent-core molecules are connected core-to-core via the alkoxy chain. Interestingly, despite short linkage connecting the mesogenic cores, which should stiffen the molecular structure, the liquid crystalline properties characteristic for bent-core mesogens have been observed. Dimers are more stable in comparison with analogous monomers and the type of mesophases strictly depends on the length of the terminal chains. The shortest studied homologues formed the intercalated smectic A phase, For the dimers with intermediate terminal chains, the columnar phase appears, built of small layer fragments arranged into body centred 2-dimensional crystallographic lattice. The longest homologues exhibit the SmCP phase with antiferroelectric type of switching in the applied electric field [ M. Horčic, J. Svoboda, V. Novotná, D. Pociecha, and E. Gorecka, Chem. Commun. 53, 2721 (2017)].
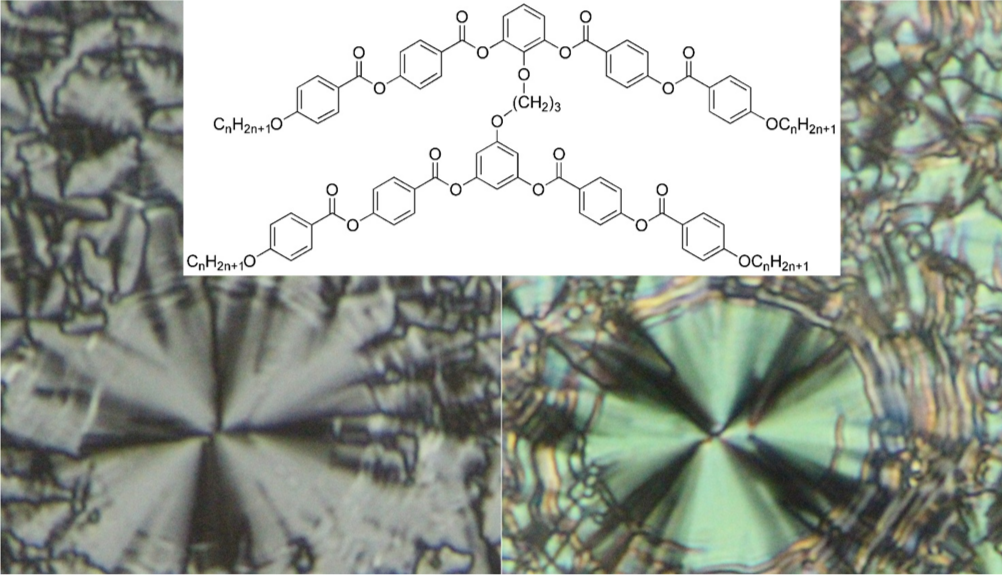
Figure: Chemical formula (top central) and electro-optical behaviour in the planar texture without applied electric field (left) and under electric field (right).
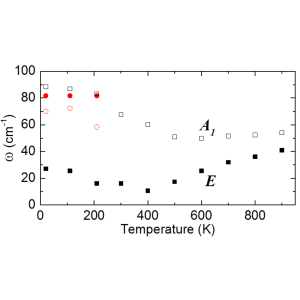
Infrared, terahertz and microwave spectroscopy of the soft and central modes in PMN
Analysis of IR and THz spectra using Bruggeman effective medium approach revealed that the mesoscopic structure of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 (PMN) consists of randomly oriented uniaxially anisotropic polar nanodomains with harder transverse optical polar modes in the direction along the local dipoles.
The lowest-frequency phonon of the E symmetry polarized perpendicular to the local dipole moments undergoes softening towards T* ≈ 400 K, which gives evidence about a local structural phase transition. This softening is also responsible for previously observed high temperature dependence of permittivity, which follows the Curie-Weiss law with the same critical temperature even without any anomaly in the low-frequency permittivity [D. Nuzhnyy et al, Phys. Rev. B 96, 174113 (2017)].
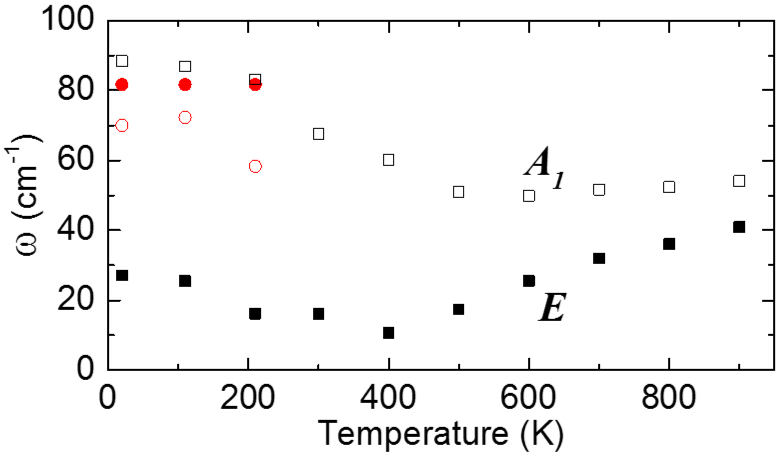
Figure: Temperature dependence of soft-mode components A1 and E in PMN from our terahertz and IR spectra.
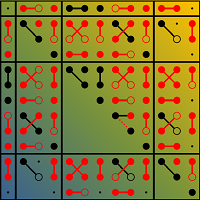
Existence conditions for ferroaxial materials
All 212 species of structural phase transitions with a macroscopic symmetry breaking were inspected with respect to the simultaneous occurrence of the ferroelastic, ferroelectric, and ferroaxial properties.
For each species, a matrix of representative equilibrium property tensors in both high-symmetry and low-symmetry phases, showing emergence of spontaneous components, were explicitly worked out [http://palata.fzu.cz/species/13x13axial]. Results can serve as a useful tool in search of fundamentally new material properties [J. Hlinka et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 177602 (2016)].
Figure: Dichromatic matrix of material property tensors for a symmetry-breaking structural phase transition from tetragonal to monoclinic phases, showing relations between tensor components of both phases and emergence of spontaneous components (red points).
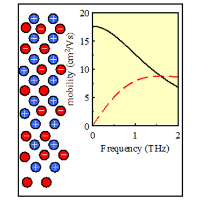
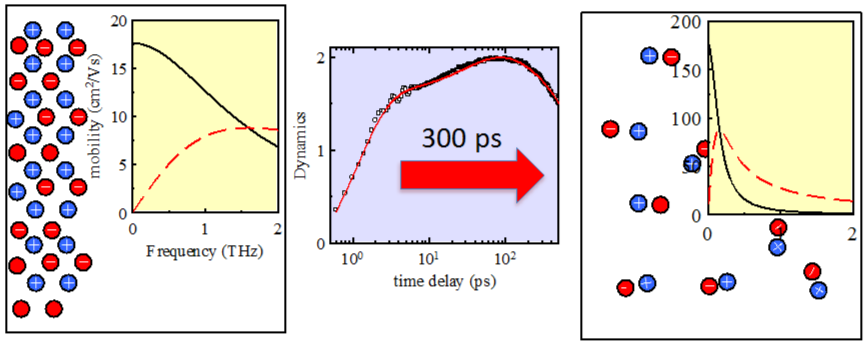
Picosecond charge transport in rutile at high carrier densities studied by transient terahertz spectroscopy
In rutile the charge carriers form polarons with high effective mass owing to the strong electron-phonon coupling. In this paper we studied ultrafast terahertz photoconductivity in rutile under strong optical excitation.
In this regime the polaron mobility depends on the polaron density;
as a consequence, highly complex transport phenomena occur on a picosecond scale
involving fine interplay between diffusion and recombination.
We developed a general model to disentangle these phenomena and
we determined dynamical properties of electron and hole polarons.
At room temperature internal degrees of freedom of polarons
are also observed through a dramatic increase of the transient permittivity
in photoexcited state
[
V. Zajac, H. Němec, and P. Kužel, Phys. Rev. B 94, 115206 (2016)].
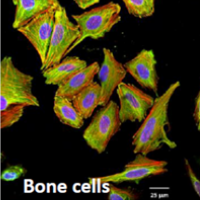
Coating of Ti39%Nb substrates by ferroelectric BaTiO3 promotes the bone cell growth
We proved that ferroelectric immersed in a liquid influences electric charge distribution at the surface. Therefore ferroelectric coating on bone implant surface promotes bone cell growth and proliferation, healing should be improved [1].
We synthesized ferroelectric BaTiO3 films on Ti and Ti39%Nb substrates by hydrothermal method [2, 3]. The bone cell growth is significantly higher on Ti39%Nb substrates coated by BaTiO3 than that on non-coated Ti39%Nb, glass and reference polystyrene [3].
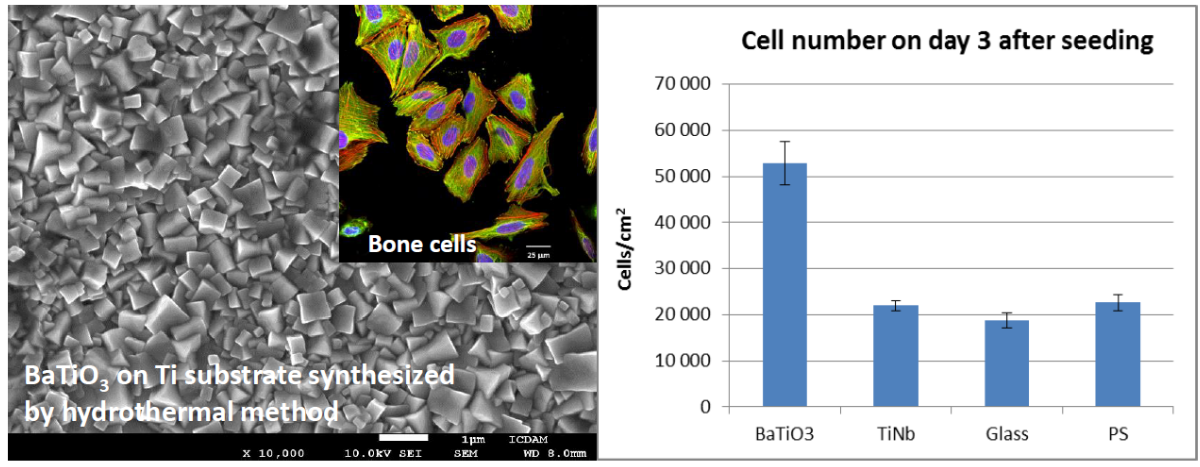
References
[1] P. Vaněk, Z. Kolská, T. Luxbacher, J.A.L. García, M. Lehocký, M. Vandrovcová, L. Bačáková, and J. Petzelt,
Electrical activity of ferroelectric biomaterials and its effects on the adhesion, growth and
enzymatic activity of human osteoblast-like cells, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49, 175403 (2016),
[2] P. Vaněk et al., Biocompatible ferroelectric coatings for bone implants,
oral presentation at ISAF/ECAPD/PFM conference, Darmstadt, (2016),
[3] P. Vaněk, M. Vandrovcová et al., to be published.
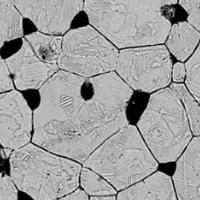
Extrinsic influence on the dielectric response of morphotropic PZT ceramics
The dielectric behaviour of the most famous piezoelectric material, Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 ceramics, below room temperature is explained by the topology of the sample, and not by intrinsic structural changes.
The dielectric anomaly found below room temperature has purely extrinsic origin and it is related to two excitations in the GHz range: piezoelectric resonances in grains (PR) with nearly temperature independent frequency and domain wall oscillations (DW) that slows down towards ~ 270 K [ Buixaderas et al, Phys. Rev. B 94, 054315 (2016) ].
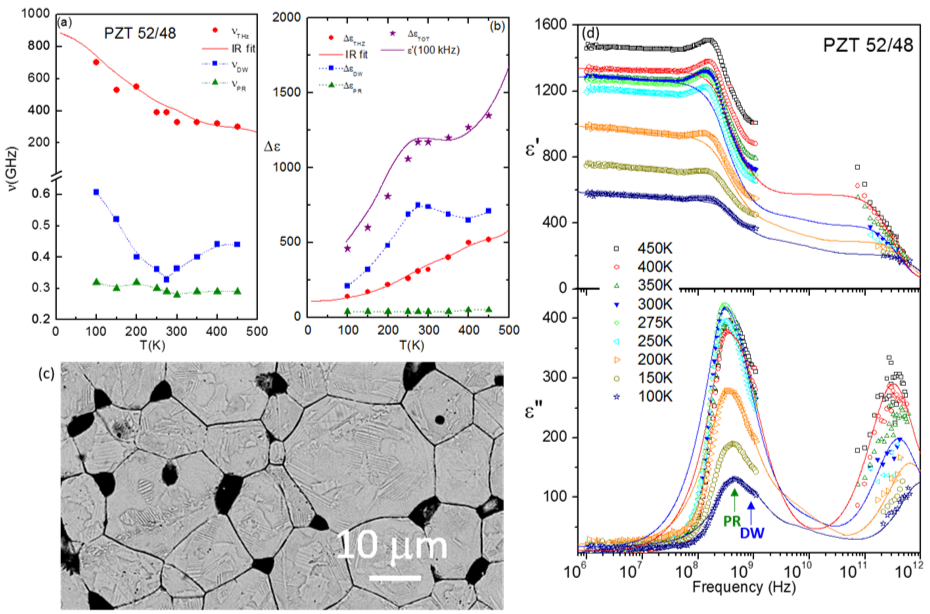
Figure: (a) Temperature dependence of the frequencies of the MW and THz excitations of PZT 52/48, (b) their contributions to the permittivity together with the permittivity measured at 100 kHz, (c) micrograph of the PZT ceramics, showing grain boundaries and domains, and (d) complex dielectric spectra of PZT 52/48 in the high-frequency and THz ranges.
All-organic liquid crystalline radicals with a spin unit in the outer position of a bent-core system
All-organic paramagnetic liquid crystals offer the advantage of a long-range order of liquid crystalline phases and the magnetic properties of the individual molecules. In such systems, the magnetic properties can be modified by phase transition or the application of external fields. In our work paramagnetic all-organic bent-core liquid crystals having the radical-bearing unit (TEMPO) in the terminal position of an elongating side arm are studied.
The mesomorphic properties of the materials are ensured by the optimized molecular structure. The paramagnetic nature of the mesogenic materials is investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance, the magnetic properties of the bulk materials are studied by SQUID magnetometry. It is shown that the materials preserve their magnetic properties within the whole temperature range of liquid crystalline behaviour. Moreover, a strong correlation between spin orientation and molecular alignment within different mesophases has been observed [ K. Bajzıkova er al, J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 11540 (2016). ].
Figure: Texture in the smectic C phase for the paramagnetic liquid crystalline compound.
Can a tensile tensile strained TiO2 thin film be ferroelectric?
A series of papers about discovery of new ferroelectrics using PFM microscopy has recently been published. On the example of strained TiO2 thin films, which exhibit ferroelectric-like hysteresis loops, we have shown that PFM response can come from electrochemical effects like migration of defects.
Additional experiments like temperature dependent second harmonic generation, IR spectroscopy of phonons and X-ray diffraction are always necessary for unambiguous confirmation of ferroelectric phase transitions [ S. Skiadopoulou et al, Adv. Funct. Matt. 26, 642 (2016) ].
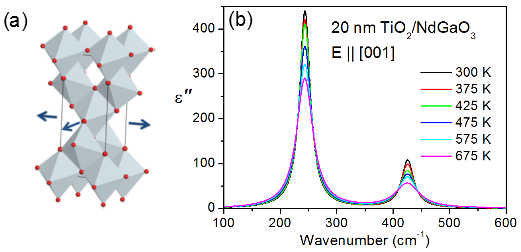
Figure: (a) Schema of anatase crystal structure of TiO2 under tensile strain. (b) Dielectric loss spectra calculated from temperature-dependent reflectance spectra of 20 nm thin film of TiO2 reveal no temperature shifts of phonon frequencies, because crystal structure is stable. PFM studies detected loss of “ferroelectric” polarization at 460 K.
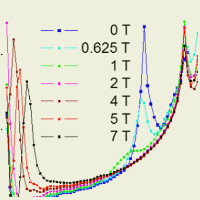
Electromagnon in Z-type hexaferrite (Ba0.2Sr0.8)3Co2Fe24O41
THz spectra of Z-type hexaferrite (Ba0.2Sr0.8)3Co2Fe24O41 reveal an electrically active spin wave (electromagnon) at temperatures below 250 K. This excitation is activated due to dynamic magnetoelectric coupling (exchange striction).
Its intensity is highly sensitive to an external magnetic field: its strength drastically drops for magnetic field values above 0.5 Tesla and it completely disappears above 2 Tesla, when the spin structure changes from transverse conical to collinear. This work was published in [ F. Kadlec et al, Phys. Rev. B 94, 024419 (2016) ].
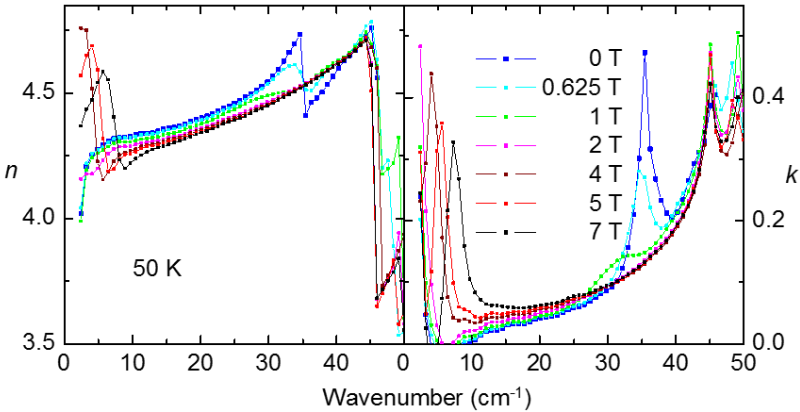
Figure: Magnetic field dependence of index of refraction n and extinction coefficient k in the THz region measured at 50 K. The electromagnon resonance seen at 35 cm-1 completely disappears for magnetic field above 2 Tesla. A ferromagnetic resonance appears at 4 Tesla and its frequency increases linearly with magnetic field (see the features below 10 cm-1).
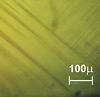
Macroscopic heterophase pattern in Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 crystals
Polarization dependence of the Raman scattering intensities demonstrate that lamellar structures observed in (1 - x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 (PMN-xPT) single crystals are composed of tetragonal-like and rhombohedral-like layers extending over macroscopic (mm) lengths.
Lamellar heterostructures, observed in PMN-0.32PT single crystals are formed in samples cooled under bias electric field applied along [001]pc and then zero-field heated to the vicinity of the so-called depoling temperature TRT. Similar structures were also encountered at ambient conditions. Spatially resolved polarized Raman scattering techniques confirmed that the stripe pattern is due to the coexistence of the phases attached to the opposite sides of the morphotropic phase boundary in the temperature-composition phase diagram [ I. Rafalovskyi et al., Phys. Rev. B 93, 064110 (2016) ].
Figure: a) Optical micrograph in a reflection mode, and (b) schematic illustration. Red crosses indicate orientation of polarizers on incident and scattered beam in configurations with a minimum Raman intensity at 570 cm−1. Right panel shows angular dependence of the I570/I510 intensity ratio for the parallel-polarized Raman scattering intensities, evaluated from the measurements taken at ambient conditions. Panels allow us to compare (c) data taken in the dark stripe, (d) data taken in a single-domain ([111]pc-poled) sample, (e) data taken in a multidomain, frustratively poled ([100]pc-poled) sample, and (f) data taken in the light stripe. The scattering geometry with respect to the pseudocubic crystallographic axes is common to all four cases displayed.
Broadband dielectric spectroscopy of lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics
Ba(Zr,Ti)O3 (BZT) and Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3 (NBT) have recently become recently the most studied lead-free relaxor materials for their attractive piezoelectric and interesting physical properties.
Our dielectric spectra of BZT of various compositions revealed that in addition to the lowest-frequency phonon mode near 1 THz, which is not much temperature dependent (no soft mode), there appear two relaxations in the spectra, the high-frequency one in the 1011 Hz range (assigned to quasi-Debye losses) and the dominant low-frequency one, which obeys the common Arrhenius law for all the relaxor compositions below ~ 200 K (see Fig. 1) [1,2] and accounts for the permittivity vs. temperature maxima characteristic for the relaxor behaviour. Since from first-principles calculations as well as structural characterization it follows that the local Ti-O and Zr-O distances in BZT are independent of composition, the characteristic polar nanoregions (PNRs) should be localised within the chemical nanoclusters of BaTiO3, where the Ti4+ ions are off-centred. Their simple Arrhenius thermal activation allowed us the assignment of the relaxations to local hopping of the Ti4+ ions among the off-centred positions within the Ti-O6 octahedra. This picture was also confirmed by analysing the relaxation and phonon dynamics using first-principles calculations for the BaZr1/2Ti1/2O3 composition in collaboration with the University of Arkansas, also separately for the Ti and Zr clusters [3]. This picture differs strikingly from the Vogel-Fulcher dynamics in lead-based relaxors, where there is no clear correlation between the PNRs and chemical clusters [4].
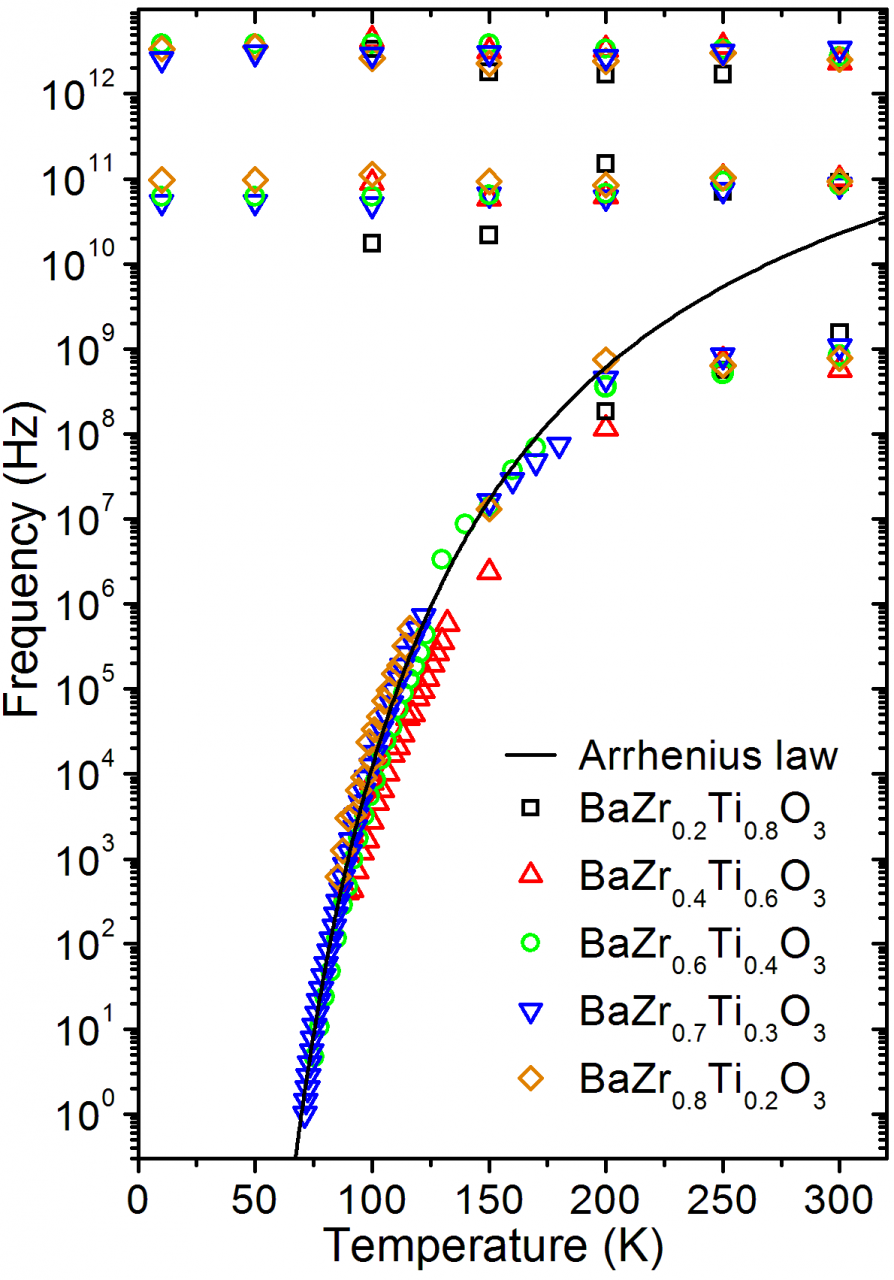
Figure 1: Temperature dependence of the characteristic frequencies of the main excitations in BZT at the THz and lower-frequency range. The low-frequency relaxation follows the same Arrhenius law for all the compositions and is assigned to local Ti ions hopping within the Ti-O6 octahedra in BaTiO3 clusters.
In collaboration with Institute Jozef Stefan in Ljubljana, Slovenia, the composition BaZr0.5Ti0.5O3 was particularly studied [5] and from the dielectric behaviour in external electric field it was concluded that the material lies on the crossover between a relaxor and dipolar glass.
In NBT the nature of the well-known dielectric anomaly near Tm ≈ 600 K was analysed for the first time [6], since its dielectric dispersion is not apparent below the standard MHz range. We have shown that the soft mode contributes only weakly to the permittivity, but it couples to two relaxations, from which the lower-frequency one is thermally activated and dominates the dielectric anomaly. At low temperatures only the soft mode contributes to the spectra. At higher temperatures it transfers part of its oscillator strength to both relaxations. Since Tm is specified by domination of the ferroelectric rhombohedral phase in the rhombohedral-tetragonal coexistence region, the permittivity maximum at Tm is caused by a smaller coupling of relaxation with the soft mode in the rhombohedral phase compared to that in the cubic and tetragonal phase. Some of the measured spectra and the analysed frequencies and dielectric strengths are shown in Fig. 2. The whole rather peculiar dynamics up to the soft mode in the THz range was assigned to highly anharmonic motion of the Bi3+ ions, which are known to be highly underbonded.
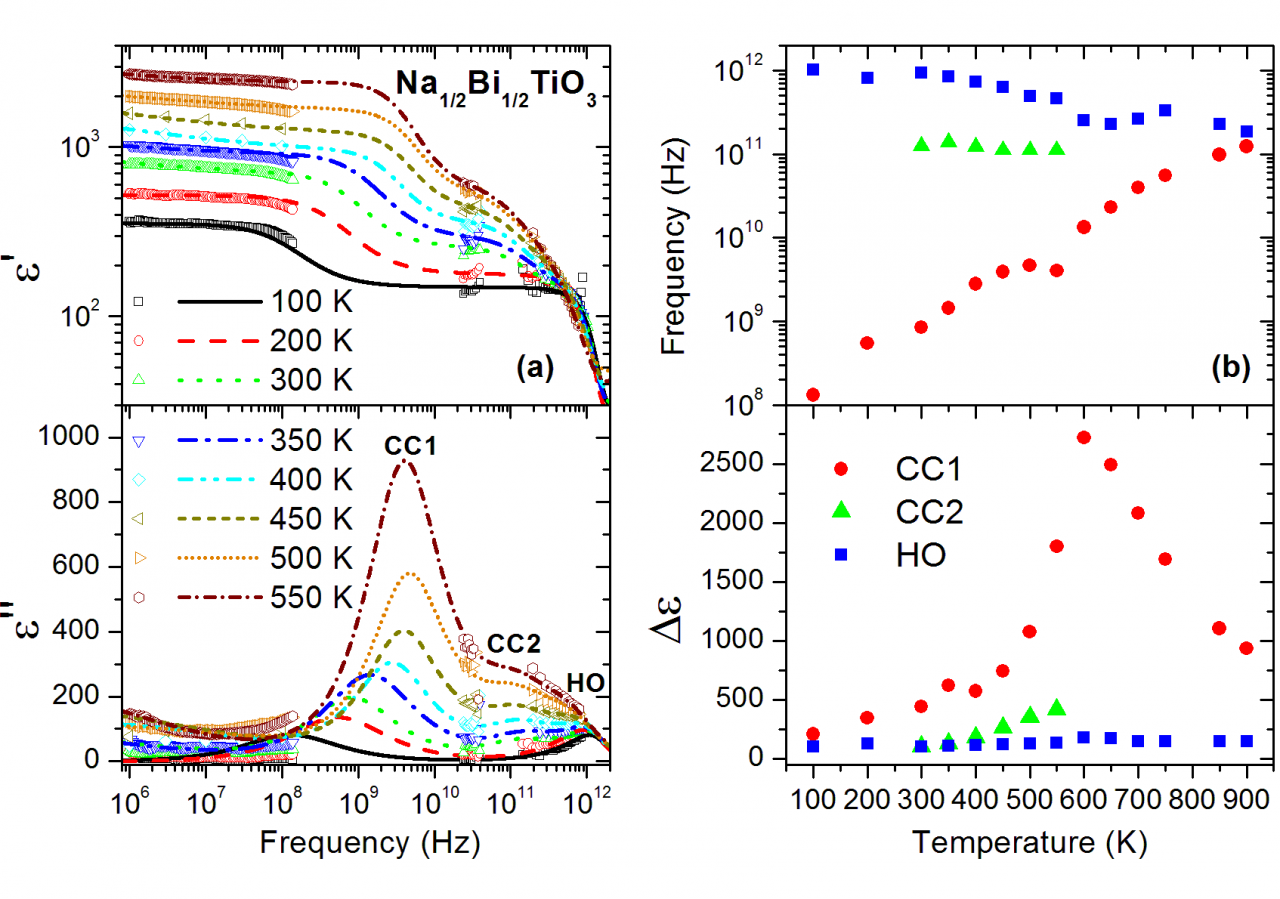
Figure 2: (a) Selected measured and fitted spectra in NBT. (b) Evaluated characteristic frequencies and dielectric strengths of the three modes below ~ 100 cm-1. Notice that the dominant relaxation is thermally activated and continues slowing down above as well as below the permittivity maximum near 600 K.
References
[1] D. Nuzhnyy et al., Phys. Rev. B 86, 014106 (2012).
[2] J. Petzelt et al., Ferroelectrics 469, 14 (2014).
[3] D. Wang et al., Nature Communications 5, 5100 (2014).
[4] J. Petzelt et al., Phase Transitions 88, 320 (2015).
[5] C. Filipic et al., Phys. Rev B 93, 224105 (2016).
[6] J. Petzelt et al., Phase Transitions 87, 953 (2014).
Compositional behaviour of phonons in Pb(Zr1-xTix)O3 ceramics
Raman spectra of PZT ceramics were studied systematically in a broad temperature interval (10–600 K) and a broad Ti/Zr concentration range around the morphotropic phase boundary (x = 0.25–0.70) [ E. Buixaderas et al., Phys. Rev. B 91, 014104 (2015) ].
We developed a purposely designed mathematical analysis of the Raman spectra based on their frequency derivatives: the method finds the curvature maxima in concave-down regions of the spectra (CMCD analysis), in order to count peaks and shoulders of the experimental spectra, comparing them to the results of the standard fitting with damped harmonic oscillators. The combination of the two approaches is very helpful to find “hidden” structure in the spectra of disordered materials.
In the case of PZT, the crossover from the tetragonal to the rhombohedral phase is clearly visible in the Raman spectra; however, there are no indications of a systematic splitting of the E-symmetry modes into A’–A’’ doublets related to the monoclinic symmetry in the morphotropic samples. Detailed adjustment of the response function to the spectrum requires to assume additional Raman active modes, but this holds for a much broader concentration range than that of the anticipated monoclinic phase.
The analysis of the phonons found also that the lowest frequency transverse optic mode of E-symmetry (soft mode of the ferroelectric phase transition) is split into two components, a THz frequency anharmonic (central mode-like) component and a resonant component (at frequencies ω ~ 80 cm-1). A new Raman band appearing in this frequency range at low temperatures is rather associated with the anti-phase tilt vibrations of the oxygen octahedra. These results are in perfect agreement with our previous IR studies on these ceramics [ E. Buixaderas et al., Phys. Rev. B 84, 184302 (2011) ].
Figure 1: CMCD analysis of the Raman spectrum of the PZT 52/48 ceramics at 400 K together with the simulated smoothed spectrum and its derivatives up to the third order. Arrows denote frequencies of the maxima and the cross-symbols denote CMCD points, defined as negative minima of the second derivative of the spectrum..
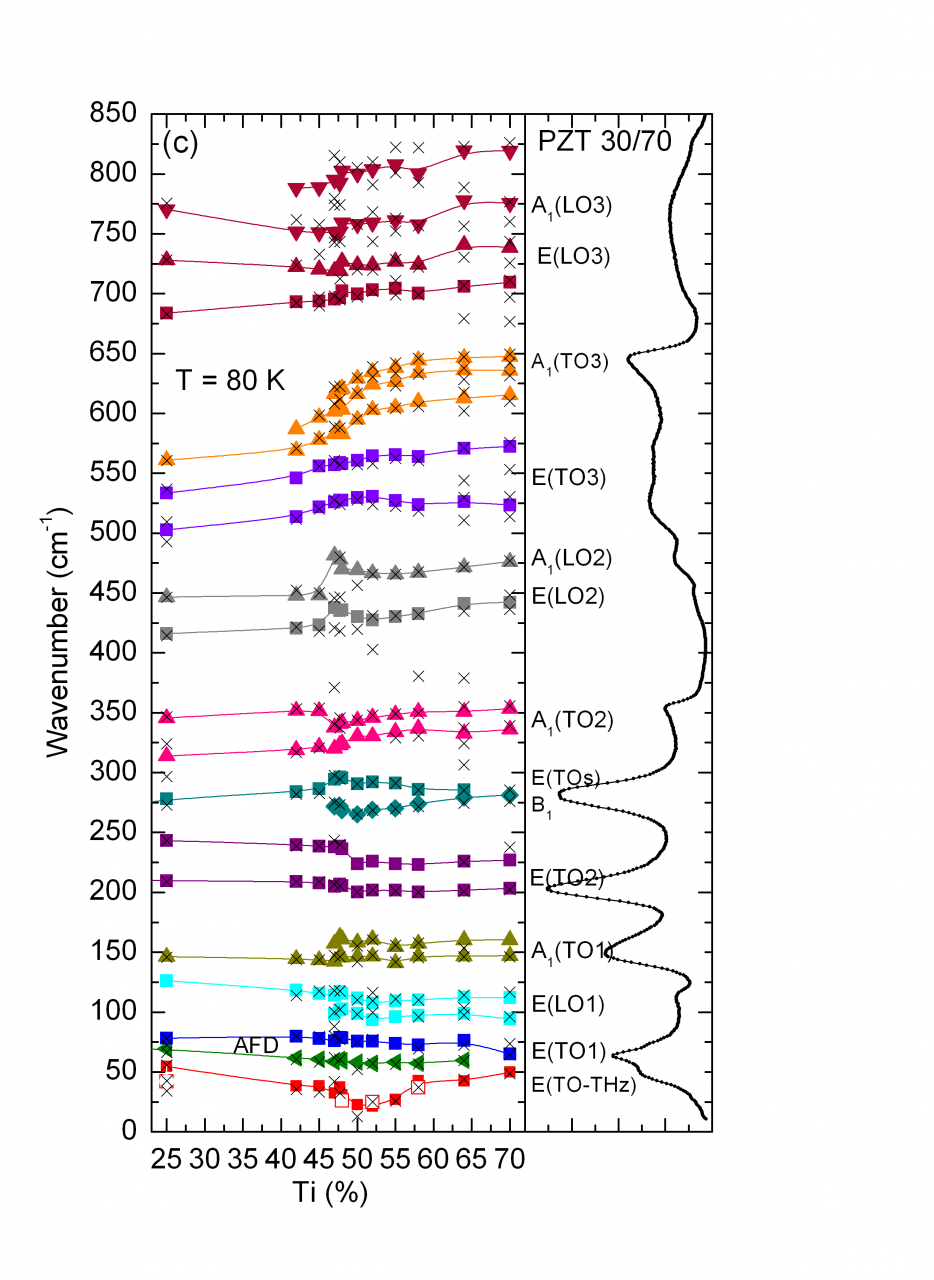
Figure 2: Compositional dependence of the phonon frequencies in PZT ceramics at 80 K. Black crosses correspond to the negative minima of the second derivative (peaks and shoulders). Spectra of the tetragonal sample 30/70 with labels are shown for illustration.
Ultrafast photoconductivity in semiconductor nanostructures
Time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy provides a useful insight into charge carrier motion in nanostructured semiconductors: it provides a contact-free access to local response of charge carriers inside nanostructures averaged over macroscopic volume of a sample. This is a very pertinent quantity for many applications of disordered materials which still have a larger potential than perfectly aligned nanostructures.
Straightforward fitting of the raw terahertz conductivity spectra by the Drude-Smith model, which was abundantly used in the literature, did not lead to a significant advance in an in-depth understanding of these phenomena. This is mainly because of the depolarization fields which build up in any inhomogeneous system. On the one hand, these fields reflect the sample morphology and their understanding in each particular system may provide new information about the nanostructure connectivity. On the other hand, the effect of unknown depolarization fields can hide or distort fingerprints of the nanoscopic transport.
Recently, we devoted a systematic effort to describe the depolarization fields in photoconductive nanostructures and to disentangle their effect from that of the local carrier response function [1].
- We proposed a general relation between the effective photoconductivity (measured in the THz experiment) and the microscopic response function. It is based on the general Bergman representation of effective medium theory for a two-component system with a single dominant depolarization factor. We have shown that our model describes both percolated and non-percolated samples and structures with complex percolation pathways [2].
- We solved the wave equation in an inhomogeneous sample and demonstrated that the transient sheet photoconductivity is directly measured in THz experiments for any spatial profile of the photoconductivity and any thin film sample morphology [1,3].
- The microscopic response function can be determined by Monte-Carlo calculations of the motion of a single carrier inside nanoparticles [4].
Analysis of experimental data within this framework allows us to uncover the nature of charge carrier transport at nanoscale and to assess the sample morphology in quite arbitrary nanostructured systems.
Based on this approach we proposed microscopic models of the response of partly or completely localized charge carriers in a number of systems including various TiO2 nano- and microparticle networks [2,5], in Sb-doped SnO2 nanoparticles [6,7], and in various nanocrystalline silicon systems [3,8], For example, in [9] we investigated a regular array of vertically aligned InP nanowires (Fig. 1). In this structure, photonic waveguiding effects inside nanowires and interferences of the excitation optical beam should have been properly taken into account to describe the sample photoexcitation. We were able to determine high transversal electron mobility in nanowires which, in comparison with the longitudinal mobility, indicates the presence of stacking faults in the growth direction (Figure 1).
Figure: (a) Sketch of the preparation of the vertically aligned InP nanowires and scheme of the investigated structure. (b) Distribution of the excitation density in the nanowires for two different excitation wavelength λexc. (c) The transversal mobility (μxx, μyy) is considerably higher than the longitudinal one (μzz) which is limited by the stacking faults along the growth direction.
References
[1] P. Kuzel and H. Nemec, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47, 374005 (2014).
[2] H. Nemec et al., IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 3, 302 (2013).
[3] V. Zajac et al., New J. Phys. 16, 093013 (2014).
[4] H. Nemec et al., Phys. Rev. B 79, 115309 (2009).
[5] S. A. Jensen et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 1191 (2014).
[6] K. Peters et al., Chem. Mater. 27, 1090 (2015).
[7] K. V. Skoromets et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 19485 (2015).
[8] H. H. Němec et al., Phys. Rev. B 91, 195443 (2015).
[9] C. S. Ponseca et al., Phys. Rev. B 90, 085405 (2014).
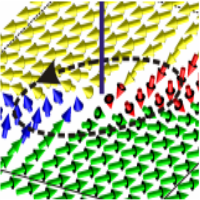
Ising lines: Natural topological defects within ferroelectric Bloch walls
Phase-field simulations demonstrate that the polarization order-parameter field in the Ginzburg-Landau-Devonshire model of rhombohedral ferroelectric BaTiO3 allows for an interesting linear defect, stable under simple periodic boundary conditions. This linear defect, here called the Ising line, can be described as an about 2-nm-thick intrinsic paraelectric nanorod acting as a highly mobile borderline between finite portions of Bloch-like domain walls of opposite helicity.
These Ising lines play the role of domain boundaries associated with the Ising-to-Bloch domain-wall phase transition. Therefore, the electric field parallel to the Ising line can be used to induce the Ising line motion, which mediates the switching of both polarization and chirality of the Bloch wall without changing the bulk domain polarization. Detailed description of this study can be found in the paper [ V. Stepkova, P. Marton, and J. Hlinka, Phys. Rev. B 92, 094106 (2015)]
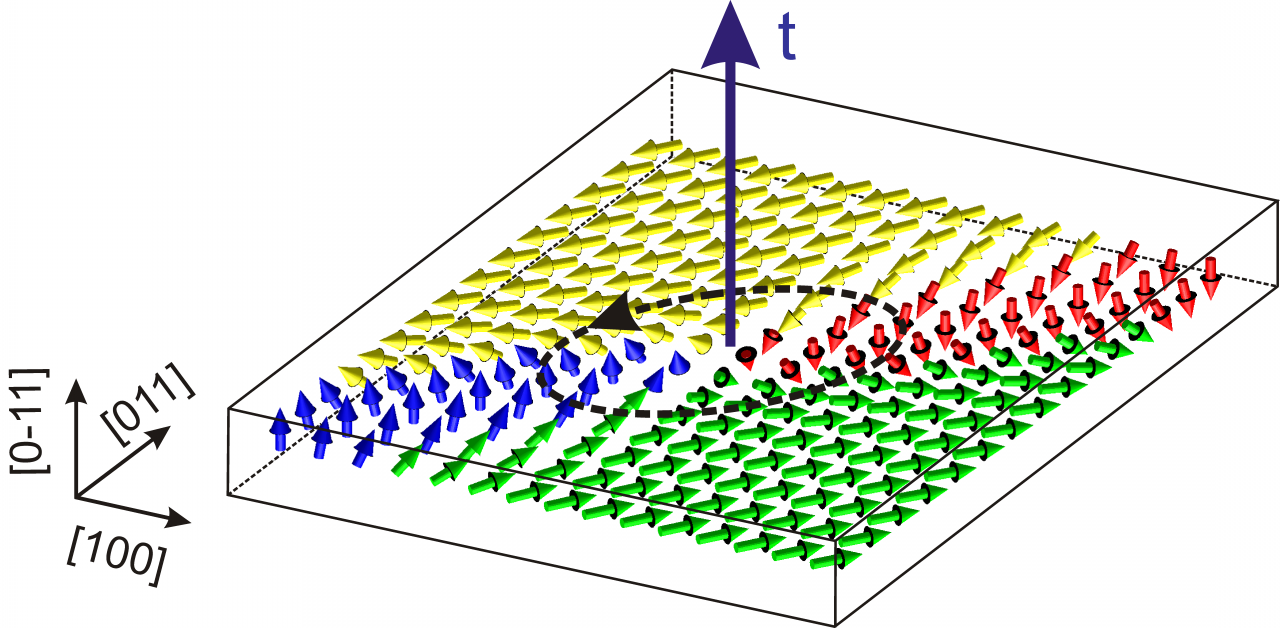
Figure: Ising line defect in rhombohedral BaTiO3. When circumventing the core of this defect following a closed path (dashed line) around its axis t, the polarization on this path rotates around the [-211] axis, which is perpendicular to t.
Unique effect of the electric field on a new liquid crystalline lactic acid derivative
We found a unique effect of the applied electric field for new chiral liquid crystalline compound, namely lactic acid derivative. We observed reversible transformation of the planar TGBA texture to the homeotropic one, homogeneously dark in crossed polarizers. The transformation is an analogy of the Frederiks transition known in nematics and only rarely can be found for smectics.
The unusual behavior of the TGBA phase under the electric field can be explained by the specific packing of molecules within the smectic layers, resulting in relatively high layer compressibility, which lowers the energy of structural defects and thus facilitates the structure transformation. The perfectly dark state of studied compounds, induced by the electric field, either stable or reversible, is appealing for specific applications. Positive dielectric anisotropy in both chiral compound and racemic mixture is detected up to the field frequency of about 10 kHz, above this frequency the anisotropy is negative.Such change of the dielectric anisotropysign, known in nematics as the dual frequency effect, might be important for photonics such as adaptive or diffractive optics [ V. Novotna et al., Soft Matter 11, 4649 (2015)].
Figure: The liquid crystalline texture for the racemate of the studied compound in smectic phase after the field application: the planar texture below the electrode is transformed to homogeneous and remains homogeneously dark in crossed polarizers. The original anchoring of molecules in the planar texture is marked by a white arrow and the polarizers are parallel to the edge of the photo.
Polar fluctuations of nanoscale size as a source of giant dielectric response of relaxor ferroelectrics
Characteristic frequencies of nanoscale polar fluctuations have been resolved by means of neutron diffuse scattering measurements on a Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 single crystal in the MHz-GHz frequency region.
Comparison with dielectric measurements proved that these polar fluctuations are a source of giant dielectric response, whose temperature-frequency dependence is specific for a significant group of substances exhibiting a glass-type ferroelectric phase transition, so-called relaxor ferroelectrics [ P. Ondrejkovic et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 167601 (2014)].
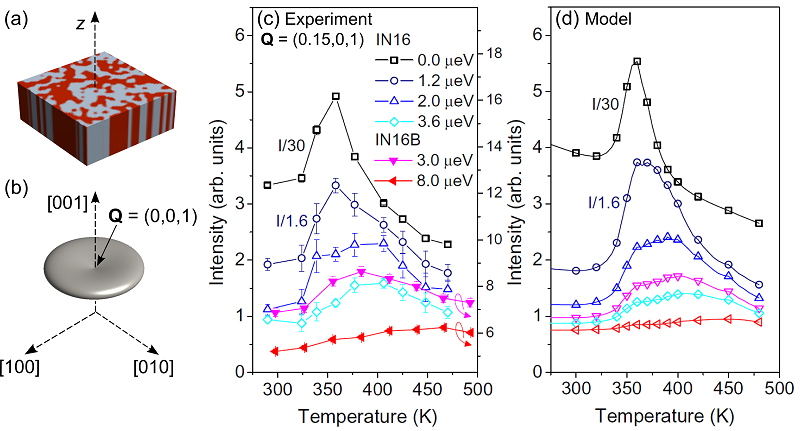
Figure: (a) Typical domain structure with polar nanodomains and (b) its characteristic disk-like diffuse scattering. Comparison of temperature dependence of diffuse scattering intensity obtained (c) experimentally on neutron spectrometers at Institut Laue-Langevin (Grenoble) and (d) numerically from a model based on dielectric data at various energy transfers.
Ultra-broadband spectroscopy of dielectric-conductor nanocomposites
The ultra-broadband dielectric spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying dielectric–conductor nanocomposites, particularly near the electrical percolation threshold. Theoretically, we have studied the spectra of effective dielectric response of such composites using several models within the effective medium approximation. It was shown that the divergence of the static permittivity at the percolation threshold is caused by a strong dielectric relaxation, which softens on approaching the threshold with changing the composition, passing through the whole frequency range from infrared down to zero [1-3].
Experimentally, we have studied e.g. nanocomposites of polymers with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) [4]. A well electrically conducting CNT, due to its specific shape, enables processing composites with extremely low percolation threshold. Within our collaboration with Queen’s University in Belfast, who prepared well-dispersed composites of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer with CNTs, we characterized them by broadband conductivity and dielectric spectroscopy, covering up to 17 orders of magnitude in frequency (10−4–1013 Hz) from room temperature down to 5 K. An extremely low percolation threshold of 0.07 vol% CNT was revealed as appearance of the low-frequency AC conductivity plateau corresponding to the DC conductivity, whose value increased with CNT concentration according to the power law with a high critical exponent of 4.3. Its semiconductor temperature dependence obeying the tunnelling law confirmed the model that each CNT in the percolating clusters is covered by a thin (~ 1 nm) layer of PET [4].
Our results on other nanocomposites of similar type were reviewed in [2,3]. Successful modelling of porosity in high-permittivity ceramics in infrared as well as low-frequency range using the Lichtenecker model was achieved for a classical relaxor PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3 (PMN) [3,5]. In collaboration with Brock University in Ontario, Canada, the giant permittivity in co-doped rutile TiO2 ceramics was explained as due to interfacial Schottky barrier layers between the electrodes and samples [6].
[1] J. Petzelt et al., Ferroelectrics 526, 171 (2012).
[2] J. Petzelt et al., Phys. Status Solidi A 210, 2259 (2013).
[3] J. Petzelt and D. Nuzhnyy, Phase Trans. 89, 651 (2016).
[4] D. Nuzhnyy et al., Nanotechnology 24, 055707 (2013).
[5] D. Nuzhnyy et al., Phys. Rev. B 89, 214307 (2014).
[6] D. A. Crandles et al., J. Appl. Phys. 119, 154105 (2016).
Figure: Room-temperature AC conductivity spectra dependent on the CNT concentration show that from the concentration 0.114 vol.% up, CNT plateaus of low-frequency conductivity appear, which correspond to DC conductivities and increase and broaden with the CNT concentration. The inset shows the critical power dependence of the conductivity at 1 Hz above the percolation threshold. At high frequencies the conductivity increases up to the THz range, which corresponds to the increase in localized conductivity due to the contributions from non-percolated CNT clusters.

Catching intermediate phases in antiferroelectric single crystals
Ferroelectric and antiferroelectric single crystals show phase transitions that can be evidence by different experimental methods. In this work we investigated single crystals of antiferroelectric PbZrO3 substituted with 1% of Ti (PZT 99/1) by means of optical microscopy, micro-Raman scattering, second harmonic generation and dielectric spectroscopy, on heating to and cooling from its cubic phase.
Our measurements confirmed that these crystals undergo two phase transitions within the approximate temperature range 488–503 K. Second harmonic generation showed a marked signal between the two anomalies, implying that the intermediate phase is non-centrosymmetric. In situ Raman spectroscopy and the presence of second harmonic signal, excluded the antiferroelectric state of this phase. The intermediate phase of PZT 99/1 crystal is similar to the rhombohedral ferroelectric one with the R3m space group [ E. Buixaderas et al., Phase Transitions 87, 1105 (2014) ].

Figure 1: Micrograph of the PZT 99/1 crystal showing the growth of the intermediate ferroelectric phase within the cubic one, near 503 K, taken on cooling.
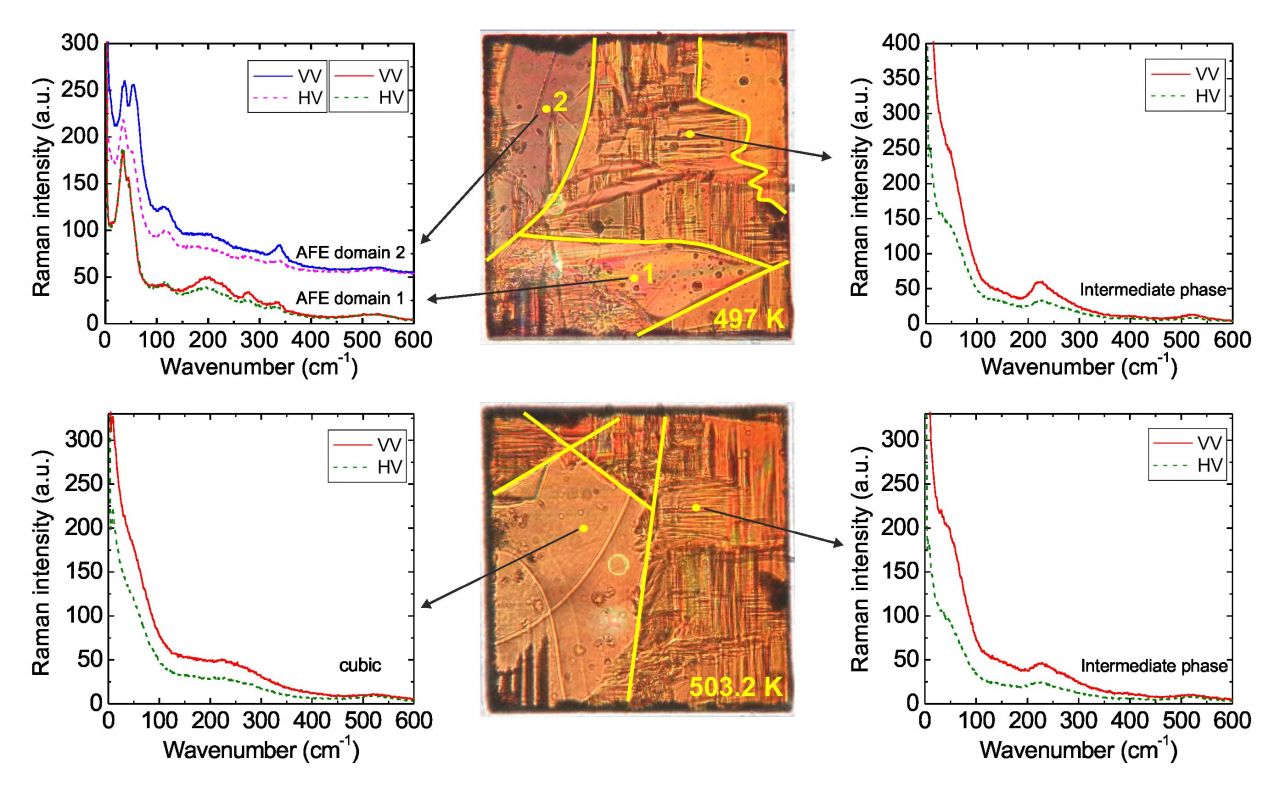
Figure 2: Raman spectra and HD optical micrographs taken at 497 and 503.2 K. Raman spectra recorded in different regions of the PZT 99/1 crystal are pointed by arrows. Left panels show Raman spectra of AFE and cubic phases, respectively; right panels show Raman spectra of the intermediate phase at these two temperatures.

Preparation of CaMn7O12 single phase ceramics
Variety of multiferroic materials is prepared in our department. One of them was CaMn7O12 which exhibits strong magnetoelectric coupling. Small crystals (~ 0.1 mm) were prepared from high temperature solution of CaCl2 and MnO2, but they contained 9% of undesirable admixtures. An alternative method – modified sol-gel synthesis using water solutions of Ca and Mn nitrates and malic acid – produced pure CaMn7O12 powder with less than 1% admixtures. However, this method was not reproducible.
Using ethylene glycol instead of malic acid (modified Pechini method) gives reproducible results, no admixtures were detected by powder XRD. The ceramic pellets were prepared by uniaxial pressing and sintering and were used for spectroscopic measurements [ F. Kadlec et al., Phys. Rev. B 90, 054307 (2014)].
Figure: Uniaxial pressing of powders for ceramics preparation – pressing die (a) and hydraulic press (b). The pressed powder is filled into the die and is compressed between two pistons (13 mm in dia) using a hydraulic press. The pistons and die cylinder are made from hard metal. Maximum permissible pressure is 739 MPa.
Molecular tilt induced by gold nanoparticles or clusters of nanoparticles in the liquid crystalline smectic A phase of “de Vries” type of compound
For the first time a tilt of molecules around the gold nanoparticles or their clusters has been observed in the liquid crystalline smectic A phase. We have shown the tilt is a consequence of interaction of the molecules with the surface of nanoparticle leading to a local smectic A-smectic C transition. Nanoparticles attracted to edge dislocations enable to visualize them under an optical polarizing microscope.
The observed effect proves the concept of existence of a disordered tilt in the smectic A phase of “de Vries” type [ L. Lejcek et al., Phys. Rev. E 89, 012505 (2014)].
Figure: Texture in the smectic A phase observed in the polarized light for liquid crystalline compound 9HL with admixture of gold nanoparticles. Nanoparticles decorate the edge dislocations lines.
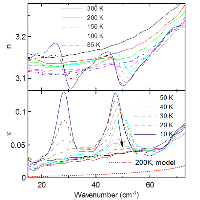
Paraelectromagnon in Multiferroic CaMn7O12
We investigated spin and lattice dynamics of CaMn7O12 ceramics using infrared (IR), THz and inelastic neutron scattering (INS) spectroscopies in the temperature range 2 to 590 K, and, at low temperatures, in applied magnetic fields up to 12 T
In the two antiferromagnetic phases below TN1 = 90 K and TN2 = 48 K, several IR-active excitations emerge below 90 cm-1.
Their frequencies correspond to the maxima in the magnon density of states obtained by INS. At the magnetic phase transitions,
these modes display strong anomalies and, for some of them, a transfer of dielectric strength from the higher-frequency phonons
is observed. We propose that these modes are electromagnons, i.e. spin waves excited by electric field.
Remarkably, at least one of these modes lying near 50 cm-1 remains IR active in the paramagnetic phase;
for this reason, we call it a paraelectromagnon. This mode becomes overdamped above 150 K,
but it remains in the spectra at least up to 300 K. In accordance with this observation,
quasielastic neutron scattering revealed short-range magnetic correlations persisting within temperatures up to 500 K above TN1.
Our paper is the first report about paraelectromagnon in literature
[
F. Kadlec et al., Phys. Rev. B 90, 054307 ()2014)
].
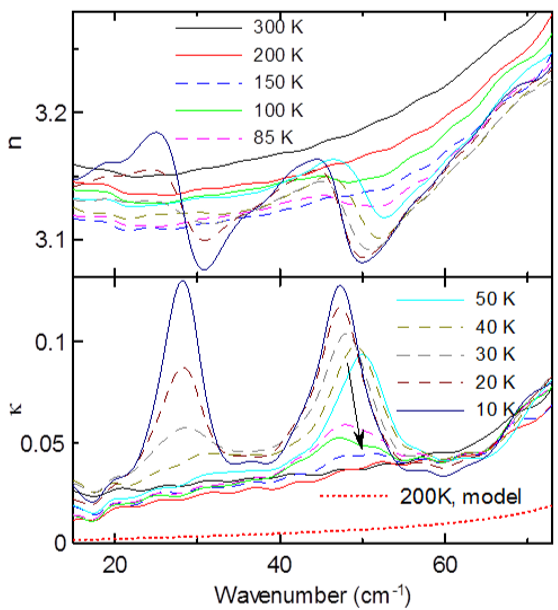
Figure: Real and imaginary parts of the complex refractive index obtained by THz spectroscopy. The red dotted line in k(ω) spectra shows the low-frequency wing from the phonons at frequencies above 90 cm-1, obtained from fits. A heavily damped electromagnons (marked by arrow) is needed for the fit of experimental spectra above TN1.
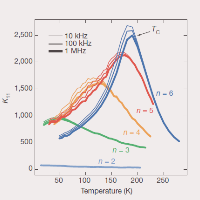
New approach to preparation of highly tunable microwave dielectrics
Srn+1TinO3n+1 is paraelectric material with layered perovskite structure. We have shown that thin films of Srn+1TinO3n+1 become ferroelectric under tensile strain and their critical temperatures increase to room temperature with rising n. Owing to this, their permittivity and electric tunability increase.
Since these films exhibit one-order-of-magnitude better microwave properties than previously-used materials, they have high potential for application in microwave electronics. The paper was published in Nature [ Che-Hui Lee et al., Nature 502, 532 (2013) ].
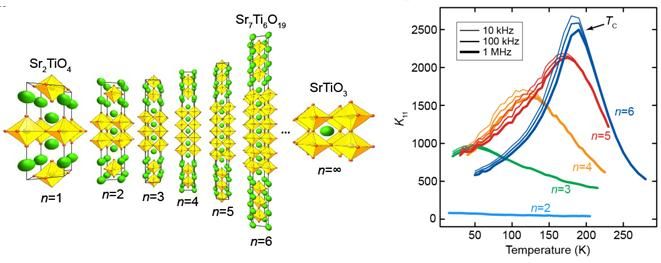
Figure: Layered crystal structure of Srn+1TinO3n+1 with n=1-6, ∞ and temperature dependence of dielectric permittivity in thin films of Srn+1TinO3n+1. Temperatures of permittivity maxima correspond to paraelectric-ferroelectric phase transition temperature.
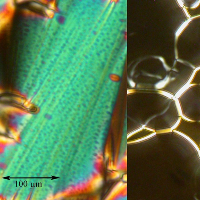
Nanocomposite of superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles and ferroelectric liquid crystal
We present a novel type of hybrid nanocomposite prepared by mixing maghemite nanoparticles (MNPs) and a chiral liquid crystalline compound. The multiferroic system exhibits the ferroelectricity as well as superparamagnetic (SPM) properties. The impact of nanoparticles and effect of applied magnetic field on ferroelectric liquid crystalline properties were established. The magnetic behavior is typical for a system of SPM nanoparticles with inter-particle dipolar interactions and surface spin disorder.
The unique SPM properties are preserved in the studied nanocomposite system and the magnetic response was analyzed. We established that the magnetic properties are modified due to the reduction of the dipolar interactions strength between the MNPs. Moreover, we were able to influence the ferroelectric properties by applying the magnetic field. [ V. Novotna et al., RSC Advances 3, 10919 (2013) ].
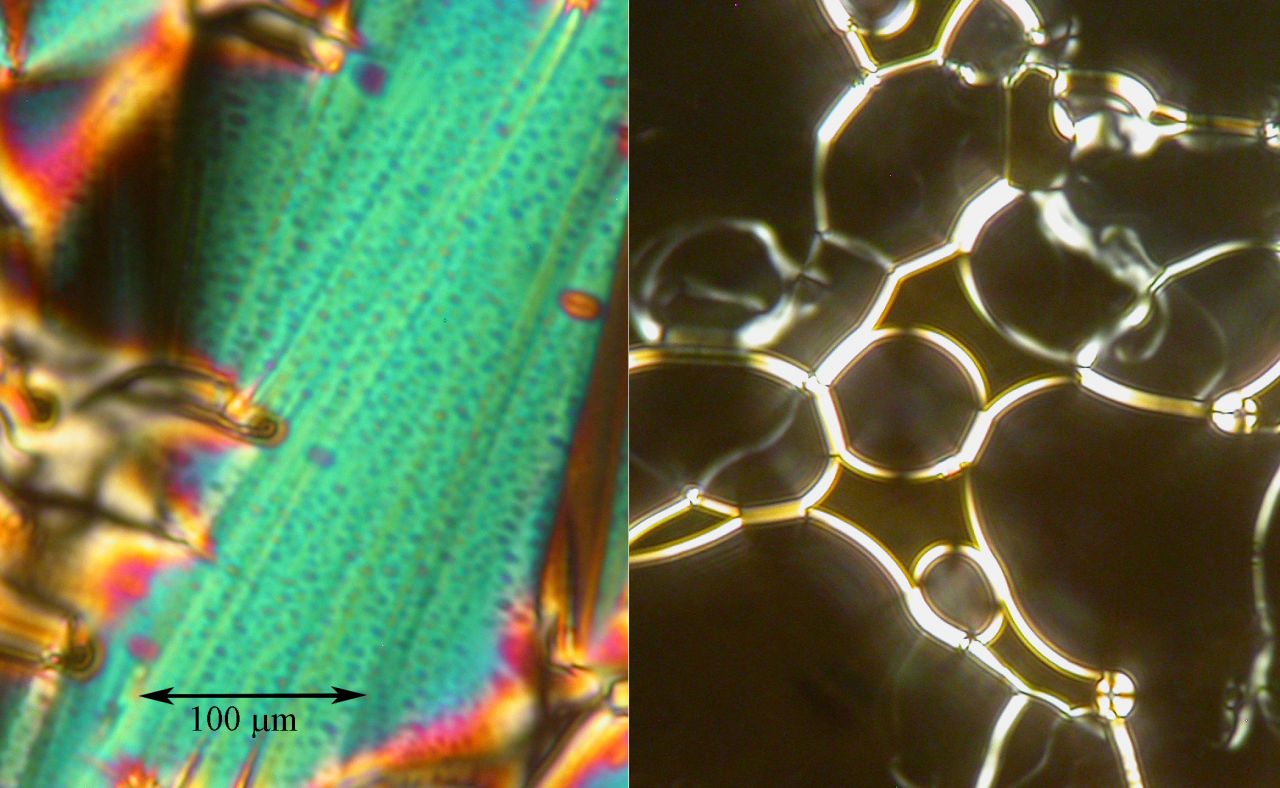
Figure 1: Texture of the smectic liquid-crystalline phase for two different nanocomposites with magnetic nanoparticles.
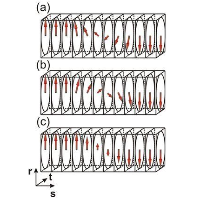
Phase transition in ferroelectric domain walls of BaTiO3
The seminal paper by Zhirnov (1958 Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 35 1175–80) explained why the structure of domain walls in ferroelectrics and ferromagnets is so different. We have recently realized that the antiparallel ferroelectric walls in rhombohedral ferroelectric BaTiO3 can be switched between the Ising-like state (typical for ferroelectrics) and a Bloch-like state (unusual for ferroelectric walls but typical for magnetic ones) [see Figure 1] by a compressive epitaxial stress.
Phase-field simulations using a Ginzburg–Landau–Devonshire model allows to explore this strain-induced phase transition within the domain wall in detail [Figure 2]. Strain-tunable chiral properties of ferroelectric Bloch walls promise a range of novel phenomena in epitaxial ferroelectric thin films. Results are published in JPCM [ V. Stepkova et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 24, 212201 (2012)].
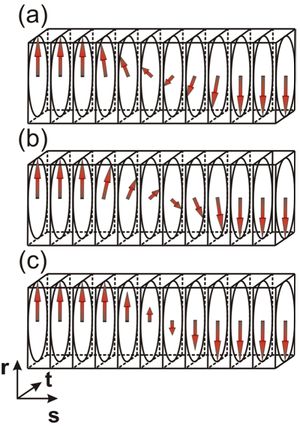
Figure 1: Variation of polarization P within Bloch- and Ising-type domain walls. The Bloch-type structure (a,b) conserves the magnitude of the local vectorial order parameter. This is typically encountered in ferromagnetism. In contrast, ferroelectric materials usually have large anisotropy and the magnitude of the polarization can be more easily adjusted. Therefore, antiparallel walls in ferroelectrics are known to correspond to the achiral Ising solution (c). We show here that in rhombohedral BaTiO3, both types of 180° domain walls can be stabilized.
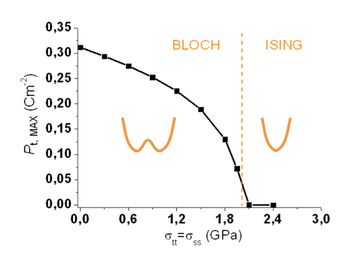
Figure 2: Chiral order parameter. The extremal value of the Pt polarization component in the core of the domain wall is plotted as a function of the epitaxial stress. This quantity can be taken as an order parameter of this chiral phase transition within the domain wall. For the wall under study, the phase transition is continuous and it can be associated with the Landau free-energy sketched in the figure.
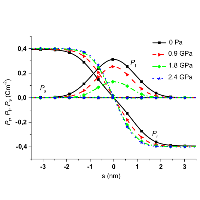
Dielectric response of a phase transition in domain wall
Computer simulations based on Ginzburg-Landau-Devonshire theory was used to study details of a phase-transition between Ising and Bloch type of a domain wall.
Such transition was predicted to appear for 180 degree domain wall in the rhombohedral ferroelectric phase of BaTiO3 close to 2GPa compressive stress [ V. Stepkova et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 24, 212201 (2012)]. We confirm the hypothesis that the phase transition is of the first-order and predict corresponding divergent increase of the dielectric permittivity in the vicinity of the transition. In case of dense domain-wall pattern it can represent a substantial part of the dielectric response of the material [ P. Marton et al., Phase Transitions 86, 103 (2012)].
Figure 1: Dielectric permittivity in dependence on mechanical pressure in the vicinity of the transition from Ising (larger pressure) to Bloch-type of the domain wall.
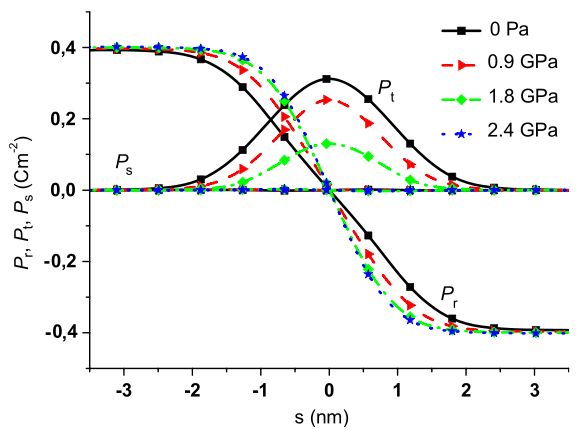
Figure 2: Bloch-to-Ising phase transition within a rhombohedral 180° domain wall.
Electron localization in CdS nanocrystals
Ultrafast electron dynamics and short-range electron transport in CdS nanocrystals prepared by chemical-bath deposition were investigated in terahertz regime [Z. Mics et al., Phys. Rev. B 83, 155326 (2011)]. Initially high mobility of photogenerated electrons exhibits a decrease within 1 picosecond due to the relaxation of their excess energy. Role of nanocrystal surfaces and nanocrystalline aggregates in electron transport was elucidated.
Despite the fast development of optoelectronic applications of nanocrystalline materials, very little is known about interplay between charge transport and carrier confinement. The absence of a long-range crystal order fundamentally complicates the transport properties. In this work we used time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy to probe nanoscopic transport in nanocrystalline films of cadmium sulfide (CdS) prepared by chemical bath deposition. The sub-picosecond time resolution of the experiment allowed us to resolve the initial stages of the electron transport. The major conclusions are:
Two length scales (nanocrystals and their clusters) control electron localization at the nanoscale. While interfaces between nanocrystals are highly permeable for electron transport, the interfaces between the clusters efficiently block the motion due to the existence of air voids.
The efficiency of short-range transport is controlled by energy barriers due to electrostatic interaction between electrons and captured holes. The excess energy of electrons then plays the essential role in the conductive coupling between adjacent nanocrystals. (i) Relaxation of electrons with high excess energy leads to a decrease of their mobility on a subpicosecond time scale. (ii) Filling of conduction-band states by increasing the optical excitation fluence allows us to maintain a high level of conductive coupling even at later times.
Figure: Left panel: Scheme of the electron transport in CdS nanocrystalline films (parameters of the electron scattering at the nanocrystal boundaries concern electrons with low kinetic energy). Middle panel: occupancy of the conduction-band states after photoexcitation (0 ps) and after the subsequent energy relaxation process (>1 ps) for various experimental conditions [(a) low intensity, (b) high intensity, (c) photoexcitation at the bottom of the conduction band]. Right panel: kinetic model of electron energy and mobility relaxation including trapping and recombination of carriers.
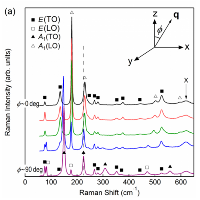
New experimental method allowed to record dispersion curves of polar lattice modes in magnetoelectric BiFeO3
Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) is a prototypical multiferroic system exhibiting extraordinary properties; it is ferroelectric up to TC ~ 1100 K as well as antiferromagnetic up to TN ~ 640 K. Characterisation of polar phonon modes is essential for understanding its dielectric and electromechanical behaviour.
Assigning the BiFeO3 polar modes probed detected in Raman spectroscopy is not straightforward due to the presence of so-called oblique phonon modes that do not match any pure TO or LO mode frequencies; instead, their frequencies continuously vary with the orientation of the phonon propagation vector. Using a monocrystal, mode assignment can be obtained by analysing a set of Raman spectra taken for different values of the angle between the phonon propagation vector and the optical axis (angular dispersion). To achieve the goal in absence of a de-twinned single crystal sample, we have developed an original technique in collaboration of the Institute of Physics AS CR and The University of Sheffild which enabled for the first time assigning these strongly anisotropic crystal properties using a polycrystalline material. We have taken advantage of the efficiency and spatial resolution of up-to-date micro-Raman spectrometers to collect a large enough set of spectra acquired on different randomly oriented grains of coarse-grain bulk ceramics. The pure TO and LO frequencies needed for angular dispersion determination were obtained from limit values of the phonon frequencies within the whole set of data. For each grain, the angle between the phonon propagation vector and optical axis was than determined from measured frequency of a chosen oblique mode. The obtained angular dispersion of the phonon mode parameters served as a basis of a full mode assignment [ J. Hlinka et al., Phys. Rev. B 83, 020101 (2011)].
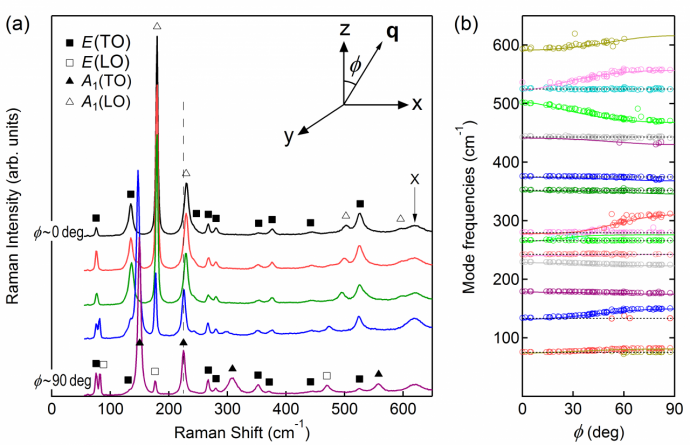
Figure: Phonon spectra of multiferroic BiFeO3. (a) Raman spectra from selected ceramic grains. Point symbols indicate positions of the pure modes. (b) Angular phonon dispersion curves. Full lines represent the oblique modes, dashed lines the purely transverse E(TO) branches, open circles are frequencies determined from individual Raman spectra as a function of the angle between the phonon propagation vector and the optical axis.
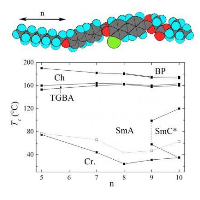
Reentrancy phenomenon of a smectic A phase in chiral liquid crystalline compounds
Unique sequence of phases was discovered in a chiral smectic, namely reentrance of orthogonal paraelectric A phase below the ferroelectric C phase. This behavior was explained by non-monotonous temperature dependence of the principal coefficient in the free energy expansion and microscopically by changes of molecular conformations and intermolecular distances due to occurrence a lateral bulky group in the molecule. This phenomenon is accompanied with anomalies in dielectric, optical and switching properties.
Stabilization of the reentrant phase was determined by mixing of the studied compound with the next homologues, which exhibit normal sequence without reentrancy. In the mixtures a direct transition between A and reentrant A phases was found, which can be understand as an analogy of crossover between liquid-like and gas-like behavior in supercritical fluids (widom-line phenomenon). The reentrant A phase can be easily influenced by electric field and exhibit strong electrooptic effect, which is promising for electrooptic application [ V. Novotná et al., Phys. Rev. E 83, 020701 (2011), N. Podoliak et al., Phys. Rev. E 84, 061704 (2011)].
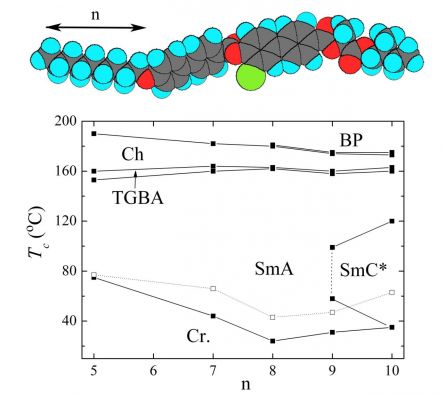
Figure: Liquid crystalline molecule of compound exhibiting reentrancy of the smectic A phase. The length of non-chiral chain is connected with the number of carbon atoms n. Phase diagram shows the homologue series of lactic acid derivatives with respect to n.
Magnetoelectric multiferroics
Magnetoelectric multiferroics are materials, which exhibit simultaneously magnetic and ferroelectric order. There is theoretically possible to influence magnetic or ferroelectric domains with electric or magnetic fields, respectively, therefore these materials are intensively studied for their promising potential applications in non-volatile memories. Unfortunately, there are only few multiferroics in nature and most of them work only at low temperatures. We suggested to use large mechanical strain in ultrathin films for preparation of new „artificial“ multiferroics.
We proved that originally antiferromagnetic and paraelectric EuTiO3 changes in films to strong ferromagnet and ferroelectrics due to strong spin-lattice coupling. Such system should exhibit strong magnetoelectric coupling which can be used in future memories. Paper was published in Nature [ J. H. Lee et al., Nature 466, 954 (2010)].
We also suggested using strong internal electric field in multiferroic Eu0.5Ba0.5TiO3 for the search of permanent electric dipole moment (EDM) of the electron. According to standard model of particles its value should be of order of 10–40 e.cm. Recently it has been shown that spontaneous violation of charge parity symmetry is much larger then it follows from the standard model, therefore this model needs an extension. New particle theories propose EDM of electrons 8 or 12 orders of magnitude larger then the standard model. The physicists try to measure EDM of electron already 40 years, unfortunately fruitlessly. They reached sensitivity of only 10–27 e.cm. We have shown that in multiferroic Eu0.5Ba0.5TiO3 the sensitivity should be one order of magnitude higher. We synthesized this material and prepared ceramic samples suitable for this measurement. In case of successful determination of EDM value it will be possible to prove and specify new theories going beyond the standard model. The paper was published in Nature Materials [ K. Z. Rushchanskii et al., Nature Mat. 9, 649 (2010)].
Figure: Scheme of the principle of measurement of an electric dipole moment of the electron. Electric and magnetic moments of the electrons switch with switching of the electric field which leads to a change of the measured magnetization.

Study of linear and nonlinear optical properties of GUHP
Within a common project with I. Němec and M. Fridrichová from Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Charles University, focused on development of new advanced nonlinear-optical materials, we studied in detail the optical properties of guanylurea(1+) hydrogen phosphite (GUHP) crystal.
GUHP presents a novel highly birefringent (i.e. phase matchable) monoclinic non-centrosymmetric material with considerably large optical nonlinearities, wide transparency range and surprisingly high optical damage threshold, at least comparable with the best commonly used NLO crystals as LBO. Favorable properties of GUHP in addition allowed an investigation of several rather rare nonlinear optical effects, as e.g. the second harmonic conical refraction or second harmonic conoscopy (both top pictures) and also the spontaneous noncollinear SHG (bottom left), Fabry-Perot enhanced SHG (middle right) and the two beam noncolinear SHG under various conditions (bottom right).
[1] M. Fridrichová et al., Phase Transit. 83, 761 (2010)[2] J. Kroupa, J. Opt. 12, 045706 (2010)
[3] J. Kroupa and M. Fridrichová, J. Opt. 13, 035204 (2011)
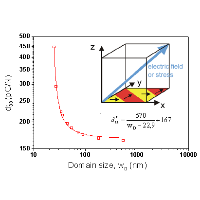
Piezoelectric response of nanotwinned ferroelectric perovskites
Computer simulations based on Ginzburg-Landau-Devonshire theory has benn used to investigate piezoelectric properties of tetragonal BaTiO3 crystals. We have shown that piezoelectric response of twinned BaTiO3 increases with increasing density of 90-degree domain walls.
A considerable enhancement of piezoelectric coefficients is predicted below 50 nm. We have also shown that main contribution to the longitudinal piezoelectric coefficient comes from volume of domain, rather than from the domain wall region. Nevertheless, the experimentally reported impact of domain wall density is even stronger than in our simulations. Our most recent theoretical investigations [P. Marton et al, Physical Review B 81, 144125 (2010)] suggest that ferroelectric perovskites such as BaTiO3 most likely support also more exotic domain walls, resembling Bloch walls known from ferromagnetism. This kind of domain walls might account for additional enhancement of the electromechanical material response.
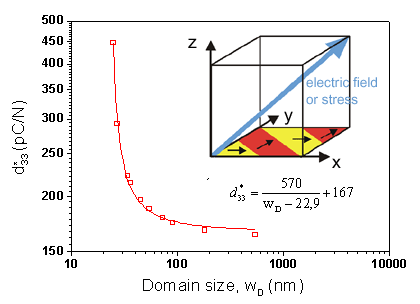
Figure 1: Dependence of the effective longitudinal piezoelectric coefficient on domain size calculated from the response of the ideal 2D laminar domain structure to weak uniaxial stresses applied along the [111] crystallographic direction. The inset shows the geometry of the initial 2D laminate domain structure assumed in the simulations.
Figure 2: Set of mechanically compatible and electrically neutral domain walls in the three ferroelectric phases o f BaTiO3. Letter denominating the phase (T, O and R stay for tetragonal, orthorhombic and rhombohedral phase, resp.) is followed by an angle between the polarization in adjacent domains and in some cases also by the domain-wall normal.